Intro
The enzyme G.Glutamyl Transpeptidase, also known as GGT, plays a crucial role in the body's antioxidant defense system and the metabolism of glutathione, the most abundant antioxidant in the body. Elevated levels of GGT in the blood can indicate liver disease, bile duct disease, or other health issues, making it an important marker for health professionals to monitor. In this article, we will delve into the world of GGT, exploring its functions, the benefits of monitoring its levels, and the potential risks associated with abnormal levels.
As we navigate the complexities of GGT, it becomes clear that this enzyme is not just a simple marker of liver health, but a key player in the body's overall antioxidant defense system. The liver, being the primary site of GGT activity, is responsible for filtering toxins and waste products from the blood, and GGT helps to regulate the levels of glutathione, which is essential for protecting the liver and other tissues from oxidative damage. With the increasing prevalence of liver disease and other health issues related to oxidative stress, understanding the role of GGT is more important than ever.
The importance of GGT in maintaining overall health cannot be overstated. Research has shown that elevated levels of GGT are associated with an increased risk of chronic diseases, such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. Furthermore, GGT has been linked to other health issues, including pancreatitis, kidney disease, and neurodegenerative disorders. As we explore the functions and benefits of GGT, it becomes clear that monitoring its levels can provide valuable insights into the body's antioxidant defense system and overall health.
What is G.Glutamyl Transpeptidase (GGT)?
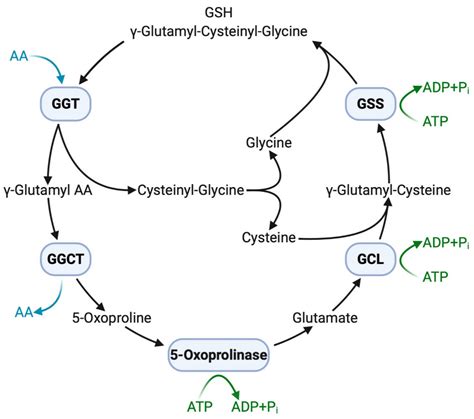
Functions of GGT
The primary function of GGT is to catalyze the transfer of the gamma-glutamyl group from glutathione to other amino acids, such as cysteine and glycine. This reaction helps to regulate the levels of glutathione in the body and maintain the balance of the gamma-glutamyl cycle. GGT also plays a role in the metabolism of other amino acids, such as glutamine and methionine.Benefits of Monitoring GGT Levels
- Early detection of liver disease: Elevated GGT levels can indicate liver damage or disease, allowing for early intervention and treatment.
- Monitoring of antioxidant status: GGT levels can provide insights into the body's antioxidant defense system, helping to identify individuals who may be at risk of oxidative stress-related diseases.
- Identification of other health issues: Elevated GGT levels have been linked to other health issues, including pancreatitis, kidney disease, and neurodegenerative disorders.
Risks Associated with Abnormal GGT Levels
Abnormal GGT levels can indicate a range of health issues, from mild liver damage to more serious diseases such as liver cancer. Some of the risks associated with abnormal GGT levels include:- Liver disease: Elevated GGT levels can indicate liver damage or disease, including conditions such as hepatitis, cirrhosis, and liver cancer.
- Bile duct disease: GGT levels can also indicate bile duct disease, including conditions such as cholestasis and bile duct cancer.
- Pancreatitis: Elevated GGT levels have been linked to pancreatitis, a condition characterized by inflammation of the pancreas.
- Kidney disease: GGT levels can also indicate kidney disease, including conditions such as nephrotic syndrome and kidney failure.
Factors that Influence GGT Levels

- Age: GGT levels tend to increase with age, making it essential to monitor levels in older adults.
- Sex: GGT levels are generally higher in men than in women.
- Body mass index (BMI): Elevated GGT levels have been linked to obesity and high BMI.
- Lifestyle factors: Smoking, heavy drinking, and a diet high in saturated fats and sugars can all contribute to elevated GGT levels.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as statins and anticonvulsants, can also influence GGT levels.
How to Maintain Healthy GGT Levels
Maintaining healthy GGT levels requires a combination of lifestyle changes and medical interventions. Some of the ways to maintain healthy GGT levels include:- Eating a balanced diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help to support liver health and maintain healthy GGT levels.
- Exercising regularly: Regular exercise can help to improve liver function and reduce GGT levels.
- Avoiding toxins: Avoiding exposure to toxins, such as heavy metals and pesticides, can help to reduce GGT levels.
- Managing stress: Chronic stress can contribute to elevated GGT levels, making it essential to manage stress through techniques such as meditation and yoga.
Conclusion and Future Directions

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with GGT in the comments section below. Have you or a loved one been affected by liver disease or other health issues related to GGT? What steps have you taken to maintain healthy GGT levels? Your input and feedback are invaluable in helping us to better understand the complexities of GGT and its role in maintaining overall health.
What is the normal range for GGT levels?
+The normal range for GGT levels varies depending on the laboratory and the individual's age and sex. Generally, GGT levels are considered normal if they are below 60 U/L.
What are the symptoms of elevated GGT levels?
+The symptoms of elevated GGT levels can vary depending on the underlying cause. Common symptoms include fatigue, jaundice, and abdominal pain.
How can I lower my GGT levels?
+Lifestyle changes, such as eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding toxins, can help to lower GGT levels. In some cases, medical interventions, such as medication or surgery, may be necessary to treat underlying conditions.
