Intro
Discover 5 crucial gallstone facts, including symptoms, causes, and treatment options, to understand gallbladder health, prevention, and dietary influences on gallstone formation and relief.
Gallstones are a common health issue that affects millions of people worldwide. They are small, hard deposits that form in the gallbladder, a small organ located under the liver that stores bile. Gallstones can cause severe abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting, and if left untreated, can lead to serious complications. Despite their prevalence, many people are unaware of the risks and consequences of gallstones. In this article, we will delve into the world of gallstones, exploring their causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
The formation of gallstones is a complex process that involves the interaction of various factors, including diet, lifestyle, and genetics. People who are overweight or obese, have a family history of gallstones, or have certain medical conditions, such as diabetes or high cholesterol, are at increased risk of developing gallstones. Additionally, a diet high in fat and cholesterol can increase the risk of gallstone formation. Understanding the causes and risk factors of gallstones is crucial in preventing and managing this condition.
Gallstones can be asymptomatic, meaning that they do not cause any symptoms, or they can cause severe abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. The symptoms of gallstones can be similar to those of other conditions, making diagnosis challenging. If you are experiencing symptoms of gallstones, it is essential to seek medical attention to determine the cause of your symptoms and receive proper treatment. With the right treatment, it is possible to manage and even prevent gallstones from forming.
Gallstone Formation
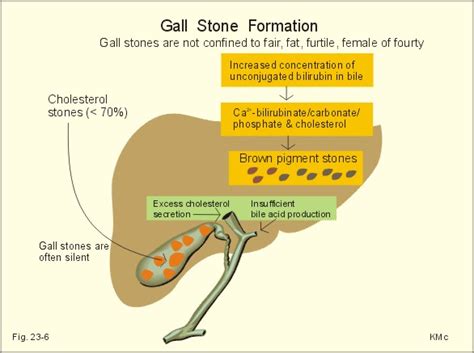
Causes of Gallstone Formation
The causes of gallstone formation are multifactorial and include: * Diet: A diet high in fat and cholesterol can increase the risk of gallstone formation. * Lifestyle: People who are overweight or obese, have a family history of gallstones, or have certain medical conditions, such as diabetes or high cholesterol, are at increased risk of developing gallstones. * Genetics: People with a family history of gallstones are at increased risk of developing gallstones. * Age: The risk of gallstone formation increases with age. * Gender: Women are more likely to develop gallstones than men.Gallstone Symptoms
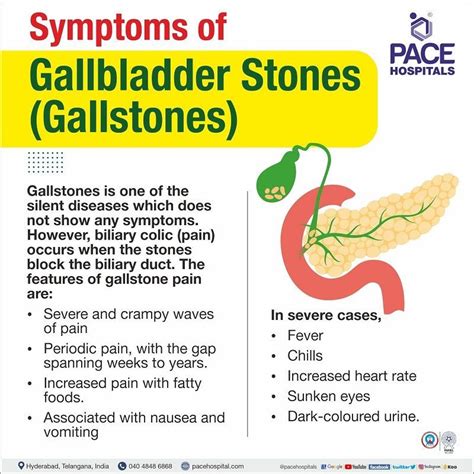
Diagnosing Gallstones
Diagnosing gallstones can be challenging, as the symptoms can be similar to those of other conditions. To diagnose gallstones, your doctor may use the following tests: * Ultrasound: An ultrasound is a non-invasive test that uses sound waves to create images of the gallbladder and bile ducts. * CT scan: A CT scan is a non-invasive test that uses X-rays and computer technology to create images of the gallbladder and bile ducts. * Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP): ERCP is a minimally invasive test that uses a flexible tube with a camera and light on the end to visualize the bile ducts and gallbladder.Gallstone Treatment

Preventing Gallstones
Preventing gallstones is possible by making lifestyle changes and managing underlying medical conditions. To prevent gallstones, you can: * Maintain a healthy weight: Being overweight or obese can increase the risk of gallstone formation. * Eat a healthy diet: A diet low in fat and cholesterol can help prevent gallstone formation. * Exercise regularly: Regular exercise can help maintain a healthy weight and improve overall health. * Manage underlying medical conditions: Managing underlying medical conditions, such as diabetes and high cholesterol, can help prevent gallstone formation.Gallstone Complications
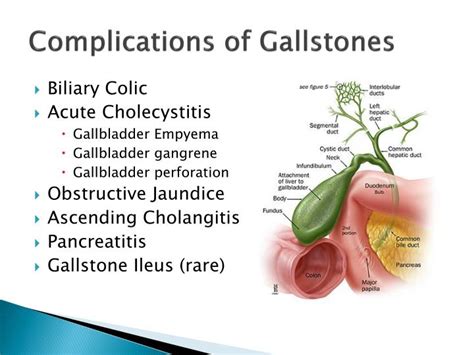
Managing Gallstone Complications
Managing gallstone complications requires prompt medical attention. To manage gallstone complications, your doctor may use the following treatments: * Antibiotics: Antibiotics can help treat infections caused by gallstones. * Pain medications: Pain medications can help manage pain caused by gallstones. * Surgery: Surgery may be necessary to remove the gallbladder or to unblock the bile ducts.Gallstone Diet

Foods to Avoid
Foods to avoid on a gallstone diet include: * High-fat foods: Foods high in fat can increase the risk of gallstone formation. * Fried foods: Fried foods can increase the risk of gallstone formation. * Processed meats: Processed meats can increase the risk of gallstone formation.Gallstone Prevention
Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, gallstones are a common health issue that can cause severe abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Understanding the causes and risk factors of gallstones is crucial in preventing and managing this condition. By making lifestyle changes and managing underlying medical conditions, you can prevent gallstones and improve overall health. If you are experiencing symptoms of gallstones, it is essential to seek medical attention to determine the cause of your symptoms and receive proper treatment.We hope this article has provided you with valuable information about gallstones. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to comment below. Share this article with your friends and family to help raise awareness about gallstones and their prevention.
What are the symptoms of gallstones?
+The symptoms of gallstones can include severe abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, fever, and jaundice.
How are gallstones diagnosed?
+Gallstones can be diagnosed using ultrasound, CT scan, and endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP).
What are the treatment options for gallstones?
+The treatment options for gallstones include watchful waiting, medications, and surgery.
Can gallstones be prevented?
+Yes, gallstones can be prevented by making lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and eating a healthy diet.
What are the complications of gallstones?
+The complications of gallstones can include infection, blockage of the bile ducts, and pancreatitis.
