Intro
Discover the role of Gamma Glutamyl Transferase (GGT) in liver health, enzyme function, and bile ducts, and learn how elevated GGT levels relate to liver disease, pancreatitis, and alcohol use.
The liver is a vital organ that plays a central role in maintaining our overall health and wellbeing. One of the key enzymes produced by the liver is Gamma Glutamyl Transferase, commonly referred to as GGT. This enzyme is a crucial indicator of liver health, and its levels can provide valuable insights into the functioning of this vital organ. In this article, we will delve into the world of GGT, exploring its role, functions, and significance in maintaining our overall health.
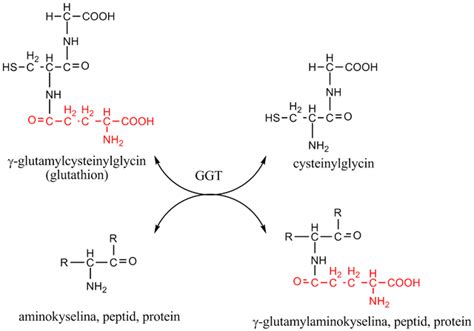
GGT is an enzyme that is found in many organs, including the liver, kidneys, and pancreas. However, it is primarily produced in the liver, where it plays a critical role in the metabolism of amino acids and the synthesis of glutathione. Glutathione is an antioxidant that helps to protect cells from damage caused by free radicals, which are unstable molecules that can cause oxidative stress and damage to cellular components. The liver uses GGT to break down glutathione, allowing it to be recycled and reused by the body.
The level of GGT in the blood is a sensitive indicator of liver health. Elevated levels of GGT can indicate liver damage or disease, such as hepatitis, cirrhosis, or liver cancer. It can also be used to monitor the effectiveness of treatment for liver diseases. In addition to its role in liver health, GGT has also been linked to other health conditions, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and obesity.
What is Gamma Glutamyl Transferase (GGT)?
Functions of GGT
GGT has several important functions in the body, including: * Metabolism of amino acids: GGT helps to break down amino acids, such as glutathione, allowing them to be recycled and reused by the body. * Synthesis of glutathione: GGT is involved in the synthesis of glutathione, which is an important antioxidant that helps to protect cells from damage caused by free radicals. * Protection against oxidative stress: GGT helps to protect cells against oxidative stress, which can cause damage to cellular components and contribute to the development of chronic diseases.Role of GGT in Liver Health

Causes of Elevated GGT Levels
There are several causes of elevated GGT levels, including: * Liver disease: GGT levels can be elevated in people with liver disease, such as hepatitis, cirrhosis, or liver cancer. * Alcohol consumption: Heavy alcohol consumption can cause liver damage, leading to elevated GGT levels. * Obesity: Obesity can lead to fatty liver disease, which can cause elevated GGT levels. * Diabetes: People with diabetes are at increased risk of developing liver disease, which can cause elevated GGT levels.GGT and Cardiovascular Disease
Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Disease
There are several risk factors for cardiovascular disease, including: * High blood pressure: High blood pressure can damage blood vessels, increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease. * High cholesterol: High levels of cholesterol can contribute to the development of cardiovascular disease. * Smoking: Smoking can damage blood vessels and increase the risk of cardiovascular disease. * Obesity: Obesity can lead to insulin resistance, which can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease.GGT and Diabetes

Risk Factors for Diabetes
There are several risk factors for diabetes, including: * Obesity: Obesity can lead to insulin resistance, which can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. * Family history: Having a family history of diabetes can increase the risk of developing the condition. * Physical inactivity: Physical inactivity can contribute to the development of insulin resistance, which can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. * Age: Age can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, with most cases occurring in people over the age of 45.GGT and Obesity

Risk Factors for Obesity
There are several risk factors for obesity, including: * Poor diet: A diet high in processed foods and added sugars can contribute to weight gain and obesity. * Physical inactivity: Physical inactivity can contribute to weight gain and obesity. * Genetics: Having a family history of obesity can increase the risk of developing the condition. * Age: Age can increase the risk of developing obesity, with most cases occurring in people over the age of 40.Conclusion and Future Directions

What is the normal range for GGT levels?
+The normal range for GGT levels varies depending on the laboratory and the individual, but it is typically between 0-55 IU/L.
What are the symptoms of elevated GGT levels?
+The symptoms of elevated GGT levels can vary depending on the underlying cause, but they may include fatigue, weakness, and jaundice.
How can I lower my GGT levels?
+GGT levels can be lowered by reducing alcohol consumption, losing weight, and eating a healthy diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
