Intro
Manage Gdm sugar levels with 5 effective ways, including diet, exercise, and monitoring blood glucose to prevent complications, promoting healthy pregnancy outcomes and reducing risk of gestational diabetes mellitus.
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is crucial for overall well-being, especially for individuals diagnosed with gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM). GDM is a condition characterized by high blood sugar levels that are first recognized during pregnancy. Managing GDM sugar levels is essential to prevent complications for both the mother and the baby. In this article, we will delve into the importance of managing GDM sugar levels and explore effective strategies to achieve this goal.
The importance of managing GDM sugar levels cannot be overstated. High blood sugar levels can lead to various complications, including macrosomia (excessive birth weight), preterm labor, and increased risk of cesarean delivery. Furthermore, uncontrolled GDM can also increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes and other health problems later in life. Therefore, it is essential for individuals with GDM to work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a personalized plan for managing their blood sugar levels.
Effective management of GDM sugar levels requires a comprehensive approach that incorporates lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, and, if necessary, medication. By making informed choices and adopting healthy habits, individuals with GDM can reduce their risk of complications and ensure a healthy pregnancy outcome. In the following sections, we will discuss five ways to manage GDM sugar levels, including dietary changes, physical activity, stress management, monitoring blood sugar levels, and medication.
Understanding GDM Sugar Levels
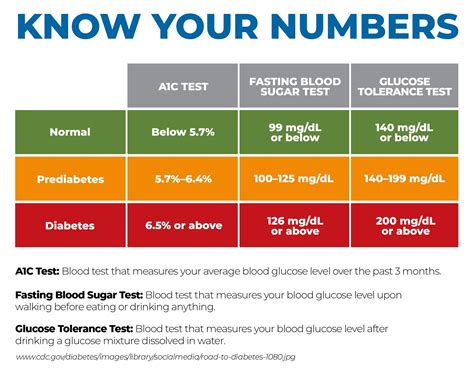
Factors Affecting GDM Sugar Levels
Several factors can affect GDM sugar levels, including diet, physical activity, stress, and sleep. Consuming high-carbohydrate foods, for example, can cause blood sugar levels to rise, while regular physical activity can help lower them. Stress and lack of sleep can also disrupt blood sugar control, making it essential to manage these factors as part of an overall GDM management plan.Dietary Changes for Managing GDM Sugar Levels

Meal Planning Tips
Meal planning is essential for managing GDM sugar levels. Here are some tips to get started: * Plan meals in advance to ensure a balanced diet * Keep a food diary to track food intake and blood sugar levels * Consult with a registered dietitian or a certified diabetes educator for personalized guidancePhysical Activity for Managing GDM Sugar Levels

Types of Physical Activity
There are various types of physical activity that can help manage GDM sugar levels, including: * Brisk walking * Swimming * Cycling * Prenatal yoga or Pilates * Resistance trainingStress Management for Managing GDM Sugar Levels

Coping with Stress
Coping with stress is crucial for managing GDM sugar levels. Here are some additional tips: * Prioritize self-care activities, such as getting enough sleep and engaging in relaxation techniques * Seek support from family, friends, or a mental health professional * Stay connected with others through social activities or support groupsMonitoring Blood Sugar Levels
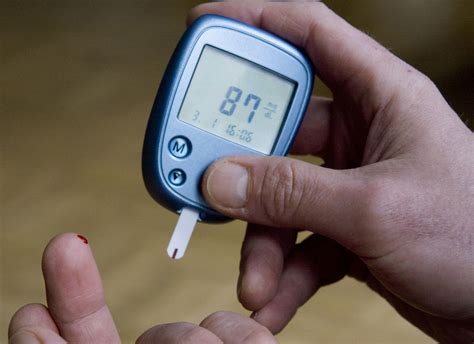
How to Monitor Blood Sugar Levels
Monitoring blood sugar levels involves using a glucose meter to measure the amount of glucose in the blood. Here are some steps to follow: * Wash your hands before testing * Use a clean and sterile lancet to prick your finger * Apply a small drop of blood to the test strip * Wait for the glucose meter to provide a readingMedication for Managing GDM Sugar Levels

Types of Medication
There are several types of medication that may be prescribed to manage GDM sugar levels, including: * Metformin: a oral medication that improves insulin sensitivity * Insulin: a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels * Glyburide: an oral medication that stimulates insulin releaseWhat are the symptoms of GDM?
+The symptoms of GDM may include increased thirst and urination, fatigue, blurred vision, and recurring infections. However, many individuals with GDM may not experience any noticeable symptoms, making regular prenatal care and screening essential for diagnosis.
How is GDM diagnosed?
+GDM is typically diagnosed between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy using a glucose screening test. If the results are abnormal, a follow-up glucose tolerance test may be performed to confirm the diagnosis.
Can GDM be prevented?
+While GDM cannot be completely prevented, certain factors can reduce the risk of developing the condition. These include maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, and eating a balanced diet before and during pregnancy.
In conclusion, managing GDM sugar levels requires a comprehensive approach that incorporates dietary changes, physical activity, stress management, monitoring blood sugar levels, and medication, if necessary. By working closely with their healthcare providers and making informed choices, individuals with GDM can reduce their risk of complications and ensure a healthy pregnancy outcome. We encourage readers to share their experiences and tips for managing GDM sugar levels in the comments below and to explore additional resources for further information and support.
