Intro
Learn about the tubal ligation process, a permanent birth control method. Discover the tying your tubes procedure, risks, and recovery, also known as female sterilization or tube tying, for informed family planning decisions.
Tubal ligation, commonly known as "tying your tubes," is a popular method of permanent birth control for women. The process involves surgically blocking the fallopian tubes to prevent pregnancy. With over 700,000 procedures performed annually in the United States alone, it's essential to understand the ins and outs of this reproductive health option. In this article, we'll delve into the world of tubal ligation, exploring its benefits, risks, and what to expect during the procedure.
The decision to undergo tubal ligation is a personal one, often made after careful consideration of various factors, including family size, health, and lifestyle. Women who choose this method of birth control are typically those who have completed their families or are certain they do not want to become pregnant in the future. As with any medical procedure, it's crucial to weigh the advantages and disadvantages, discussing any concerns with a healthcare provider to ensure informed decision-making.
For many women, the benefits of tubal ligation far outweigh the potential drawbacks. This procedure offers a high degree of effectiveness, with a failure rate of less than 1%. Additionally, it provides a sense of security and freedom from the worry of unintended pregnancy. Tubal ligation can also be performed at various times, including postpartum, after a cesarean section, or as an interval procedure. The flexibility of this method makes it an attractive option for women seeking a permanent solution to birth control.
Understanding the Procedure
The tubal ligation process typically begins with a consultation with a healthcare provider, who will discuss the procedure, its risks and benefits, and answer any questions. On the day of the procedure, the patient will be administered anesthesia, either general or local, depending on the method chosen. There are several approaches to tubal ligation, including laparoscopic, minilaparotomy, and postpartum tubal ligation. The most common method, laparoscopic tubal ligation, involves making small incisions in the abdomen, through which a laparoscope and surgical instruments are inserted. The fallopian tubes are then located, and a small portion is removed or blocked using clips, rings, or other occlusion devices.
Types of Tubal Ligation
There are several types of tubal ligation, each with its unique characteristics and advantages. These include: * Laparoscopic tubal ligation: A minimally invasive procedure using a laparoscope to visualize the fallopian tubes. * Minilaparotomy: A small incision is made in the abdomen to access the fallopian tubes. * Postpartum tubal ligation: Performed after childbirth, usually within 24-48 hours. * Interval tubal ligation: Performed at any time, not related to childbirth.Benefits of Tubal Ligation
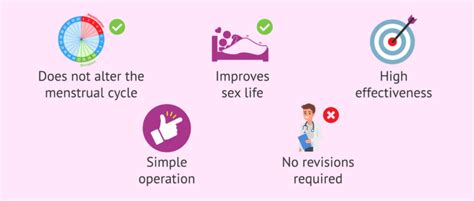
The benefits of tubal ligation are numerous, making it a popular choice for many women. Some of the advantages include:
- High effectiveness: Tubal ligation has a failure rate of less than 1%, making it a reliable method of birth control.
- Permanent solution: This procedure provides a permanent solution to birth control, eliminating the need for ongoing contraceptive methods.
- Reduced risk of ovarian cancer: Studies have shown that tubal ligation may reduce the risk of ovarian cancer.
- No impact on hormones: Unlike some hormonal birth control methods, tubal ligation does not affect hormone levels.
Risks and Complications
While tubal ligation is generally a safe procedure, there are potential risks and complications to be aware of. These include: * Infection: As with any surgical procedure, there is a risk of infection. * Adverse reaction to anesthesia: Some women may experience an adverse reaction to the anesthesia used during the procedure. * Injury to surrounding organs: There is a small risk of injury to surrounding organs, such as the bowel or bladder. * Ectopic pregnancy: Although rare, there is a small risk of ectopic pregnancy after tubal ligation.Recovery and Aftercare

The recovery process for tubal ligation typically involves several days of rest and avoiding strenuous activities. It's essential to follow the healthcare provider's instructions for post-operative care, which may include:
- Taking pain medication as directed
- Applying ice packs to reduce swelling
- Avoiding heavy lifting or bending
- Attending follow-up appointments to ensure proper healing
Emotional and Psychological Aspects
The decision to undergo tubal ligation can have emotional and psychological implications. It's essential to consider these aspects and discuss any concerns with a healthcare provider. Some women may experience feelings of: * Relief: Knowing that they have a permanent solution to birth control can bring a sense of relief. * Sadness: The realization that they will not be able to become pregnant again can be difficult for some women. * Anxiety: Concerns about the procedure or potential complications can cause anxiety.Alternatives to Tubal Ligation
While tubal ligation is a popular method of permanent birth control, there are alternatives to consider. These include:
- Vasectomy: A surgical procedure that cuts or blocks the vas deferens, preventing sperm from reaching the semen.
- Essure: A non-surgical procedure that uses small metal coils to block the fallopian tubes.
- Implanon: A small rod implanted under the skin, releasing hormones to prevent pregnancy.
Reversal of Tubal Ligation
Although tubal ligation is considered a permanent method of birth control, it is possible to reverse the procedure. However, the success of reversal depends on various factors, including: * Age: Women under 30 have a higher success rate for reversal. * Type of procedure: The type of tubal ligation performed can impact the success of reversal. * Length of time since procedure: The longer it has been since the procedure, the lower the success rate.Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, tubal ligation is a reliable and effective method of permanent birth control. While it's essential to consider the potential risks and complications, the benefits of this procedure make it a popular choice for many women. If you're considering tubal ligation, it's crucial to discuss your options with a healthcare provider, weighing the advantages and disadvantages, and making an informed decision.
What is the success rate of tubal ligation?
+The success rate of tubal ligation is over 99%, with a failure rate of less than 1%.
Can tubal ligation be reversed?
+Yes, tubal ligation can be reversed, but the success of reversal depends on various factors, including age, type of procedure, and length of time since the procedure.
What are the potential risks and complications of tubal ligation?
+Potential risks and complications include infection, adverse reaction to anesthesia, injury to surrounding organs, and ectopic pregnancy.
How long does it take to recover from tubal ligation?
+Recovery from tubal ligation typically takes several days, with most women returning to normal activities within 1-2 weeks.
Is tubal ligation covered by insurance?
+Insurance coverage for tubal ligation varies, so it's essential to check with your provider to determine if the procedure is covered.
We hope this comprehensive guide to tubal ligation has provided you with a deeper understanding of this permanent birth control method. If you have any further questions or concerns, please don't hesitate to reach out to a healthcare provider. Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below, and help others make informed decisions about their reproductive health.
