Intro
Learn about Giant Cell Arteritis, a chronic inflammatory disease, and its symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options, including temporal arteritis and polymyalgia rheumatica.
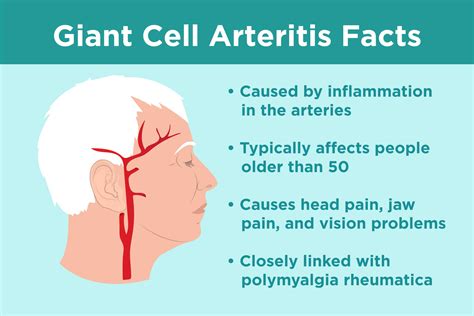
Giant cell arteritis, also known as temporal arteritis, is a medical condition that affects the blood vessels, specifically the arteries, in the body. It is a type of vasculitis, which means inflammation of the blood vessels. This condition is characterized by the presence of giant cells, which are a type of immune cell, in the inflamed arteries. Giant cell arteritis is a serious condition that can cause a range of symptoms, from mild to severe, and can lead to complications if left untreated. In this article, we will delve into the world of giant cell arteritis, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and management.
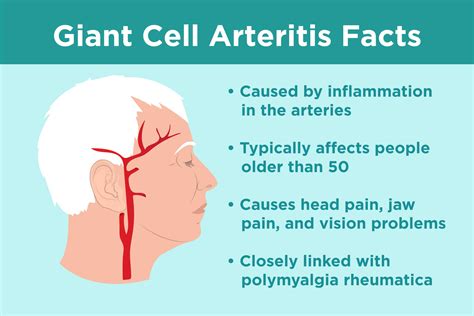
The importance of understanding giant cell arteritis cannot be overstated. This condition affects thousands of people worldwide, with the majority being over the age of 50. If left untreated, giant cell arteritis can lead to serious complications, including blindness, stroke, and aortic aneurysm. Therefore, it is crucial to recognize the symptoms and seek medical attention promptly. By doing so, individuals can receive timely treatment and prevent long-term damage.
Giant cell arteritis is a complex condition, and its exact causes are still not fully understood. However, research suggests that it is an autoimmune disease, where the immune system mistakenly attacks the blood vessels. This can be triggered by a combination of genetic and environmental factors, such as infections, stress, and hormonal changes. The condition is more common in women than men and is often associated with other autoimmune diseases, such as polymyalgia rheumatica.
Giant Cell Arteritis Symptoms
Giant Cell Arteritis Diagnosis
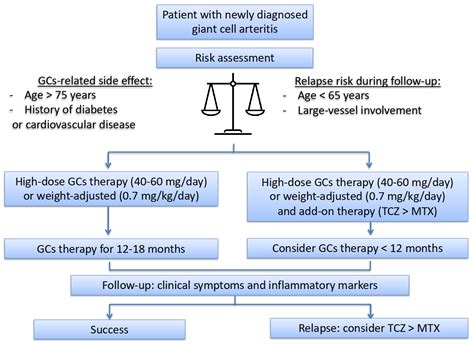
Giant Cell Arteritis Treatment
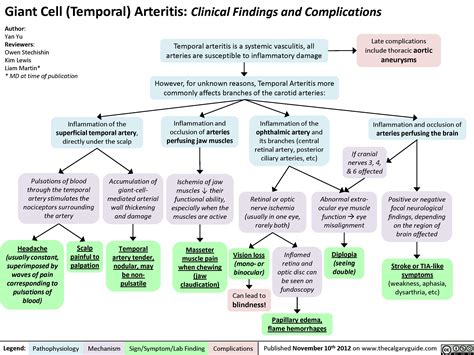
Giant Cell Arteritis Management
Managing giant cell arteritis requires a long-term commitment to treatment and lifestyle changes. Individuals with this condition should work closely with their healthcare provider to monitor their condition and adjust their treatment plan as needed. Additionally, making healthy lifestyle choices, such as maintaining a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and managing stress, can help reduce the risk of complications and improve overall health.Giant Cell Arteritis Complications
Giant Cell Arteritis Prognosis

Giant Cell Arteritis Research
Research on giant cell arteritis is ongoing, with scientists exploring new treatments and therapies to manage the condition. Studies are investigating the use of biologic medications, such as tocilizumab, to reduce inflammation and prevent damage to the blood vessels. Additionally, researchers are working to develop more effective diagnostic tests and imaging studies to improve diagnosis and treatment.Giant Cell Arteritis Support
Giant Cell Arteritis Prevention

Giant Cell Arteritis and Other Conditions
Giant cell arteritis is often associated with other autoimmune diseases, such as polymyalgia rheumatica. Individuals with giant cell arteritis are also at increased risk of developing other conditions, such as osteoporosis and cataracts. Regular monitoring and follow-up appointments with a healthcare provider are crucial to managing these conditions and preventing complications.What are the symptoms of giant cell arteritis?
+The symptoms of giant cell arteritis can include headaches, scalp tenderness, jaw pain, and vision problems. Some individuals may experience fever, fatigue, and weight loss, while others may have no symptoms at all.
How is giant cell arteritis diagnosed?
+Diagnosing giant cell arteritis can be challenging, but a combination of physical examination, medical history, laboratory tests, and imaging studies can help confirm the diagnosis. A temporal artery biopsy is often performed to examine the blood vessels for giant cells and inflammation.
What is the treatment for giant cell arteritis?
+Treatment for giant cell arteritis typically involves corticosteroids, which are powerful anti-inflammatory medications. These medications can help reduce inflammation and prevent damage to the blood vessels. In some cases, other medications, such as methotrexate or azathioprine, may be used in combination with corticosteroids.
In conclusion, giant cell arteritis is a complex and potentially serious condition that requires prompt medical attention and treatment. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and management of this condition, individuals can take control of their health and reduce the risk of complications. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of giant cell arteritis, do not hesitate to seek medical attention. Share this article with others to raise awareness about this condition, and let's work together to promote health and well-being.
