Intro
Discover the 5 key glands on neck, including thyroid, parathyroid, and lymph nodes, and learn about their functions, locations, and related health issues like glandular problems and neck pain.
The human body is a complex and fascinating system, with numerous glands and organs working together to maintain overall health and well-being. One area of the body that is often overlooked, but plays a crucial role in our daily lives, is the neck. The neck is home to several important glands, including the thyroid, parathyroid, salivary, lymph, and adrenal glands. In this article, we will delve into the world of these 5 glands on the neck, exploring their functions, importance, and potential health issues associated with them.
The neck is a vital part of our body, connecting the head to the torso and facilitating a range of essential functions, from swallowing and breathing to moving and communicating. The glands located in the neck play a critical role in regulating various bodily processes, including metabolism, growth, and development. Understanding the functions and importance of these glands can help us appreciate the intricate mechanisms of the human body and take better care of our overall health.
The 5 glands on the neck are responsible for producing and regulating various hormones, enzymes, and other substances that are essential for maintaining proper bodily functions. From the thyroid gland, which produces hormones that regulate metabolism, to the lymph glands, which help filter out toxins and fight infection, each gland plays a unique and vital role in our overall health. In the following sections, we will explore each of these glands in more detail, discussing their functions, importance, and potential health issues associated with them.
Thyroid Gland
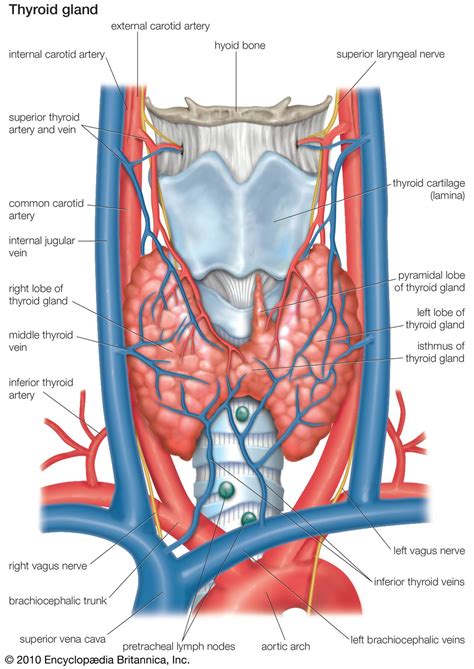
The thyroid gland is essential for maintaining proper bodily functions, and any problems with the gland can have significant consequences. For example, an underactive thyroid gland (hypothyroidism) can lead to fatigue, weight gain, and dry skin, while an overactive thyroid gland (hyperthyroidism) can cause weight loss, anxiety, and irregular heartbeat. Thyroid problems can be caused by a range of factors, including iodine deficiency, autoimmune disorders, and certain medications.
Functions of the Thyroid Gland
The thyroid gland performs several essential functions, including: * Regulating metabolism: The thyroid gland produces hormones that help control the rate at which the body uses energy. * Controlling growth and development: The thyroid gland helps regulate the growth and development of cells, tissues, and organs. * Producing hormones: The thyroid gland produces two main hormones, T4 and T3, which play a crucial role in maintaining proper bodily functions.Parathyroid Gland
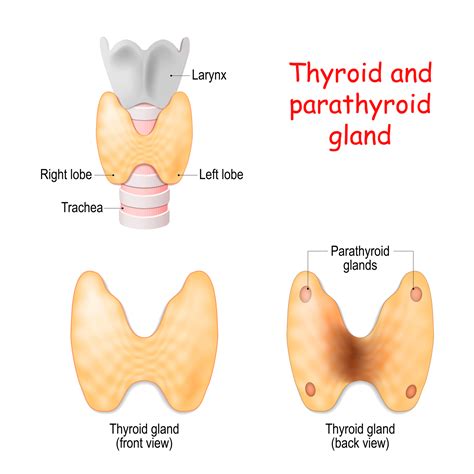
The parathyroid gland helps regulate calcium levels by stimulating the release of calcium from bones, increasing calcium absorption from food, and reducing calcium excretion in the urine. Any problems with the parathyroid gland can lead to calcium imbalances, which can cause a range of symptoms, including muscle weakness, numbness, and tingling.
Functions of the Parathyroid Gland
The parathyroid gland performs several essential functions, including: * Regulating calcium levels: The parathyroid gland produces PTH, which helps regulate calcium levels in the blood. * Maintaining bone health: The parathyroid gland helps regulate calcium levels, which is essential for building and maintaining strong bones. * Stimulating calcium release: The parathyroid gland stimulates the release of calcium from bones, increasing calcium levels in the blood.Salivary Gland
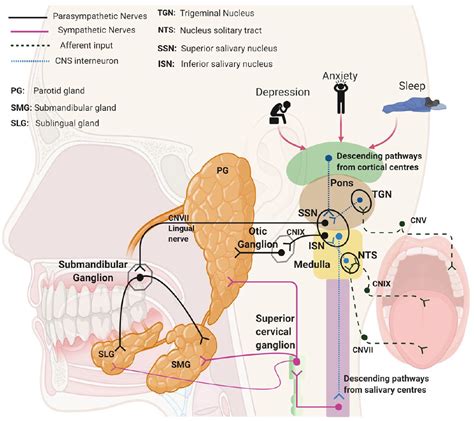
The salivary gland produces several types of saliva, including serous, mucous, and mixed saliva. Serous saliva is clear and watery, while mucous saliva is thick and sticky. Mixed saliva is a combination of serous and mucous saliva. Any problems with the salivary gland can lead to dry mouth, difficulty swallowing, and increased risk of oral infections.
Functions of the Salivary Gland
The salivary gland performs several essential functions, including: * Producing saliva: The salivary gland produces saliva, which helps break down food, neutralize acids, and protect the teeth and mouth from infection. * Maintaining oral health: The salivary gland helps maintain proper oral health by washing away bacteria, food particles, and other debris. * Aiding digestion: The salivary gland helps aid digestion by breaking down carbohydrates and other nutrients.Lymph Gland
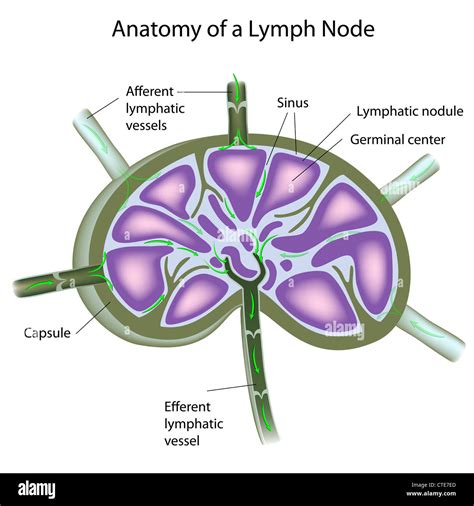
The lymph gland helps regulate the immune system by producing lymphocytes, which attack and destroy infected cells and foreign substances. Any problems with the lymph gland can lead to weakened immune function, making it harder for the body to fight off infection and disease.
Functions of the Lymph Gland
The lymph gland performs several essential functions, including: * Producing lymphocytes: The lymph gland produces lymphocytes, which help fight infection and disease. * Regulating immune function: The lymph gland helps regulate the immune system by producing lymphocytes and filtering out toxins and foreign substances. * Filtering out toxins: The lymph gland helps filter out toxins, bacteria, and other foreign substances from the blood.Adrenal Gland
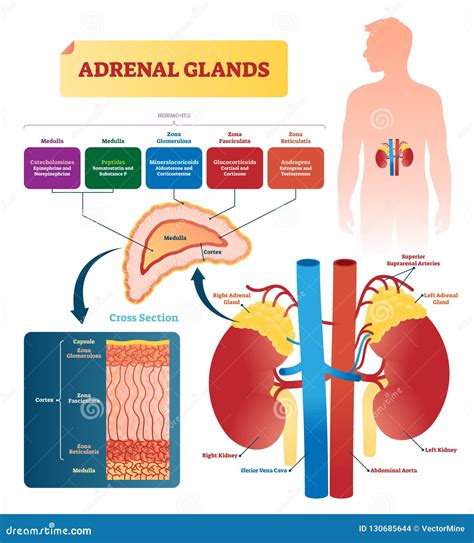
The adrenal gland helps regulate blood pressure by producing aldosterone, which helps control the amount of sodium and water in the blood. It also helps regulate the body's response to stress by producing cortisol, which helps suppress the immune system and reduce inflammation.
Functions of the Adrenal Gland
The adrenal gland performs several essential functions, including: * Regulating blood pressure: The adrenal gland produces aldosterone, which helps control the amount of sodium and water in the blood. * Regulating stress response: The adrenal gland produces cortisol, which helps suppress the immune system and reduce inflammation. * Producing hormones: The adrenal gland produces several hormones, including adrenaline, aldosterone, and cortisol, which help regulate a range of bodily functions.What are the 5 glands on the neck?
+The 5 glands on the neck are the thyroid gland, parathyroid gland, salivary gland, lymph gland, and adrenal gland.
What is the function of the thyroid gland?
+The thyroid gland produces hormones that regulate metabolism, growth, and development.
What is the function of the parathyroid gland?
+The parathyroid gland produces a hormone that helps regulate calcium levels in the blood.
What is the function of the salivary gland?
+The salivary gland produces saliva, which helps break down food, neutralize acids, and protect the teeth and mouth from infection.
What is the function of the lymph gland?
+The lymph gland produces lymphocytes, which help fight infection and disease.
In conclusion, the 5 glands on the neck play a crucial role in maintaining proper bodily functions, from regulating metabolism and growth to fighting infection and disease. Understanding the functions and importance of these glands can help us appreciate the intricate mechanisms of the human body and take better care of our overall health. If you have any questions or concerns about the 5 glands on the neck, we encourage you to comment below or share this article with others. By working together, we can promote greater awareness and understanding of the importance of these glands and take steps to maintain optimal health and well-being.
