Intro
Discover 5 uses of Glimepiride, a sulfonylurea medication, for managing type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance, and hyperglycemia, with benefits including improved glycemic control and reduced cardiovascular risk.
The management of type 2 diabetes mellitus is a complex and multifaceted process that involves lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, and pharmacological interventions. Among the various classes of antidiabetic drugs, sulfonylureas have been a cornerstone in the treatment of type 2 diabetes for decades. One such sulfonylurea that has gained significant attention and usage is Glimepiride. Glimepiride is a second-generation sulfonylurea that is known for its efficacy in lowering blood glucose levels, its relatively favorable side effect profile, and its ability to be used in combination with other antidiabetic agents.
Glimepiride works by stimulating the release of insulin from the pancreatic beta cells, thereby increasing insulin secretion. This mechanism of action is particularly beneficial for patients with type 2 diabetes who have impaired insulin secretion. The increased insulin levels help to reduce glucose production in the liver and enhance glucose uptake in the peripheral tissues, ultimately leading to a decrease in blood glucose levels.
The importance of managing type 2 diabetes cannot be overstated. Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to a plethora of complications, including cardiovascular disease, nephropathy, retinopathy, and neuropathy. Therefore, the use of effective antidiabetic medications like Glimepiride is crucial in preventing these complications and improving the quality of life for patients with diabetes. With its proven efficacy and safety profile, Glimepiride has become a preferred choice among healthcare providers for the management of type 2 diabetes.
Introduction to Glimepiride

Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics
The pharmacokinetics of Glimepiride involve rapid absorption after oral administration, with peak plasma concentrations achieved within 2-3 hours. The drug is highly bound to plasma proteins and has a relatively long half-life, which allows for once-daily dosing. The pharmacodynamics of Glimepiride are primarily related to its ability to stimulate insulin release from the pancreatic beta cells. This insulinotropic effect is dose-dependent and is achieved through the closure of potassium channels in the beta cell membrane, leading to cell depolarization and the opening of calcium channels, which ultimately results in insulin secretion.Benefits of Glimepiride

Common Uses of Glimepiride
Glimepiride is commonly used as a monotherapy or in combination with other antidiabetic agents, including metformin, thiazolidinediones, and insulin, to achieve better glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes. The drug is particularly useful in patients who have failed to achieve adequate glycemic control with lifestyle modifications alone or with other antidiabetic medications.Side Effects and Precautions
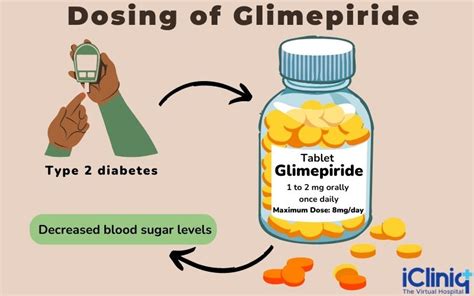
Dosage and Administration
The dosage of Glimepiride should be individualized based on the patient's response to the drug. The recommended starting dose is typically 1-2 mg once daily, which can be adjusted based on fasting blood glucose levels. The maximum recommended dose is 8 mg once daily.Interactions with Other Medications

Patient Education and Monitoring
Patient education is crucial when initiating Glimepiride therapy. Patients should be informed about the importance of regular blood glucose monitoring, the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia, and the potential interactions with other medications. Regular monitoring of renal function, liver function, and hemoglobin A1c levels is also recommended to assess the efficacy and safety of Glimepiride therapy.Conclusion and Future Directions
Final Thoughts
The management of type 2 diabetes is a lifelong commitment that requires patience, dedication, and the right therapeutic approach. Glimepiride, with its proven track record of efficacy and safety, is an excellent choice for many patients. By understanding the benefits, potential side effects, and proper use of Glimepiride, healthcare providers can help patients achieve optimal glycemic control and improve their overall quality of life.What is Glimepiride used for?
+Glimepiride is used in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus to improve glycemic control.
How does Glimepiride work?
+Glimepiride works by stimulating the release of insulin from the pancreatic beta cells, reducing glucose production in the liver, and enhancing peripheral glucose utilization.
What are the common side effects of Glimepiride?
+We hope this comprehensive overview of Glimepiride has provided you with valuable insights into its uses, benefits, and potential side effects. If you have any further questions or would like to share your experiences with Glimepiride, please do not hesitate to comment below. Your feedback is invaluable in helping us create more informative and engaging content for our readers. Additionally, if you found this article helpful, consider sharing it with others who may benefit from this information. Together, we can work towards better managing type 2 diabetes and improving the lives of those affected by this condition.
