Intro
Learn about Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR), a key kidney function test measuring renal health, including eGFR calculation, kidney disease stages, and chronic kidney disease diagnosis, to understand kidney function and overall well-being.
The kidneys are vital organs that play a crucial role in maintaining our overall health. One of the key functions of the kidneys is to filter waste products and excess fluids from the blood. The Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR) is a measure of how well the kidneys are performing this function. In this article, we will delve into the world of GFR, exploring its importance, how it is calculated, and what the results mean for our health.
The GFR is a critical indicator of kidney function, and it is essential to understand its significance. The kidneys contain tiny units called nephrons, which filter the blood to remove waste products and excess fluids. The GFR measures the rate at which the kidneys filter the blood, and it is expressed in milliliters per minute (mL/min). A normal GFR indicates that the kidneys are functioning correctly, while a low GFR suggests that the kidneys are not filtering the blood effectively. This can be a sign of kidney disease or other underlying health issues.
Understanding the GFR is vital for maintaining good health. Kidney disease can lead to serious complications, such as heart disease, stroke, and even kidney failure. By monitoring the GFR, healthcare professionals can diagnose and treat kidney disease early, reducing the risk of these complications. Additionally, knowing the GFR can help individuals take steps to protect their kidney health, such as maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and managing underlying health conditions.
What is Glomerular Filtration Rate?
How is GFR Calculated?
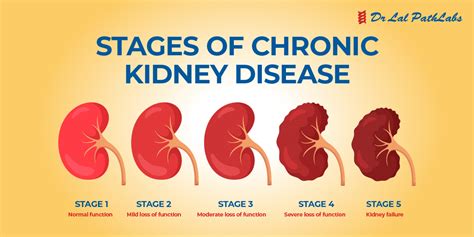
The GFR is calculated using a formula that takes into account the level of creatinine in the blood, as well as other factors such as age, sex, and body size. The most commonly used formula is the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease (MDRD) formula, which is as follows: * GFR (mL/min/1.73m^2) = 175 x (serum creatinine)^-1.154 x (age)^-0.203 x (0.742 if female) x (1.212 if African American) This formula provides an estimate of the GFR, which can then be used to diagnose and monitor kidney disease.Stages of Kidney Disease
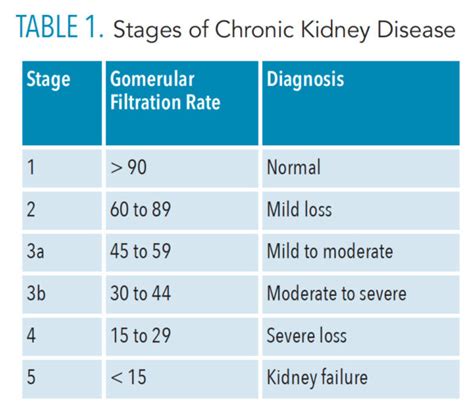
Treatment and Management of Kidney Disease
Treatment and management of kidney disease depend on the stage of the disease. In the early stages, treatment may involve lifestyle changes such as a healthy diet, regular exercise, and stress management. In more advanced stages, treatment may involve medications to control blood pressure and reduce proteinuria, as well as other interventions such as dialysis or kidney transplantation.Importance of Monitoring GFR
Risk Factors for Kidney Disease
There are several risk factors for kidney disease, including: * Diabetes * High blood pressure * Family history of kidney disease * Obesity * Age * Ethnicity (African Americans, Hispanics, and Native Americans are at higher risk) Understanding these risk factors can help individuals take steps to protect their kidney health and reduce their risk of developing kidney disease.Protecting Kidney Health
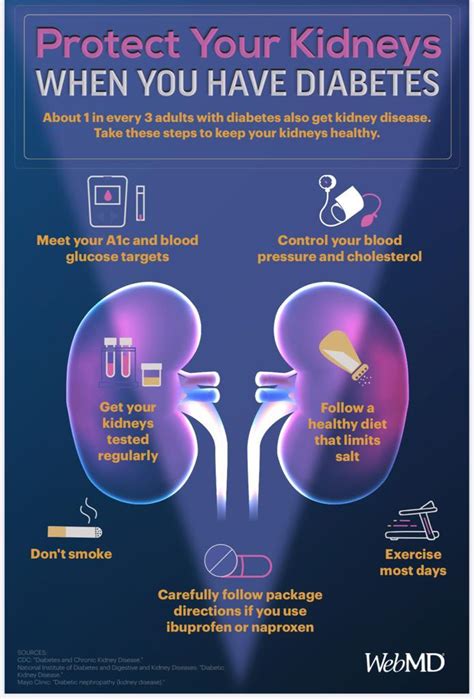
Common Causes of Kidney Disease
There are several common causes of kidney disease, including: * Diabetes * High blood pressure * Glomerulonephritis (inflammation of the kidneys) * Pyelonephritis (infection of the kidneys) * Kidney stones * Certain medications Understanding the causes of kidney disease can help individuals take steps to protect their kidney health and reduce their risk of developing kidney disease.Kidney Disease and Other Health Conditions
Complications of Kidney Disease
There are several complications of kidney disease, including: * Heart disease * Stroke * High blood pressure * Anemia * Bone disease * Nerve damage Understanding the complications of kidney disease can help individuals take steps to protect their health and reduce their risk of developing these complications.Current Research and Developments

Future Directions
The future of kidney disease treatment and management is promising, with several new developments on the horizon. These include: * Personalized medicine, which involves tailoring treatment to an individual's specific needs and genetic profile * Regenerative medicine, which involves using stem cells and other therapies to repair or replace damaged kidney tissue * Telemedicine, which involves using technology to provide remote care and monitoring for individuals with kidney disease Understanding the future directions of kidney disease treatment and management can help individuals stay informed and empowered to take control of their health.What is the normal range for GFR?
+A normal GFR is typically considered to be greater than 90 mL/min/1.73m^2.
What are the symptoms of kidney disease?
+The symptoms of kidney disease can vary, but may include fatigue, swelling, and changes in urine output.
How can I protect my kidney health?
+Protecting kidney health involves maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, managing underlying health conditions, and getting regular check-ups.
What are the complications of kidney disease?
+The complications of kidney disease can include heart disease, stroke, high blood pressure, anemia, bone disease, and nerve damage.
What is the current research in kidney disease?
+Current research in kidney disease includes new treatments such as stem cell therapy and gene therapy, advances in dialysis and kidney transplantation, and development of new medications to control blood pressure and reduce proteinuria.
