Intro
Glucose lab tests are a crucial diagnostic tool for assessing blood sugar levels, which is essential for maintaining overall health and preventing various diseases. The importance of glucose lab tests cannot be overstated, as they help identify individuals with diabetes, prediabetes, or other glucose-related disorders. In this article, we will delve into the world of glucose lab tests, exploring their significance, types, and interpretation.
The human body relies on glucose as its primary source of energy, and the ability to regulate blood sugar levels is vital for maintaining proper bodily functions. When glucose levels become imbalanced, it can lead to a range of health problems, including diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and neurological disorders. Glucose lab tests provide healthcare professionals with valuable insights into a patient's glucose metabolism, enabling them to make informed decisions about diagnosis, treatment, and management.
Glucose lab tests are commonly used to diagnose and monitor diabetes, a chronic condition characterized by high blood sugar levels. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), diabetes affects over 460 million people worldwide, with this number expected to rise to 578 million by 2030. The prevalence of diabetes underscores the importance of glucose lab tests in identifying individuals at risk and facilitating early intervention. By detecting abnormal glucose levels, healthcare professionals can initiate treatment, prevent complications, and improve patient outcomes.
Types of Glucose Lab Tests

There are several types of glucose lab tests, each with its unique characteristics and applications. The most common types of glucose lab tests include:
- Fasting Plasma Glucose (FPG) test: This test measures blood glucose levels after an overnight fast, typically 8-12 hours.
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT): This test assesses the body's ability to regulate blood sugar levels after consuming a sugary drink.
- Random Plasma Glucose test: This test measures blood glucose levels at any time, regardless of when the patient last ate.
- Glycated Hemoglobin (HbA1c) test: This test measures the average blood glucose levels over the past 2-3 months.
How Glucose Lab Tests Work
Glucose lab tests typically involve collecting a blood sample from the patient, which is then sent to a laboratory for analysis. The laboratory uses specialized equipment and techniques to measure the glucose levels in the blood sample. The results are then compared to established reference ranges to determine whether the patient's glucose levels are within a healthy range.Interpretation of Glucose Lab Test Results
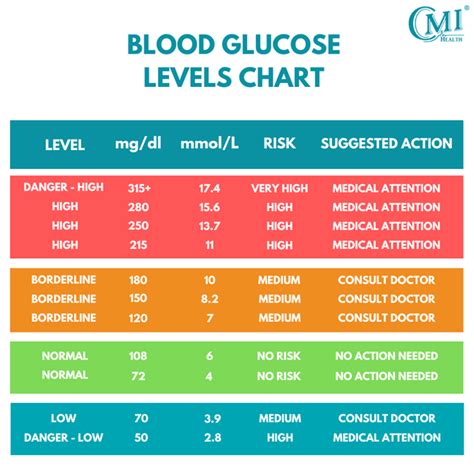
Interpreting glucose lab test results requires a thorough understanding of the reference ranges and the patient's medical history. The following are general guidelines for interpreting glucose lab test results:
- FPG test:
- Normal: < 100 mg/dL
- Impaired fasting glucose: 100-125 mg/dL
- Diabetes: ≥ 126 mg/dL
- OGTT:
- Normal: < 140 mg/dL
- Impaired glucose tolerance: 140-199 mg/dL
- Diabetes: ≥ 200 mg/dL
- Random Plasma Glucose test:
- Normal: < 140 mg/dL
- Diabetes: ≥ 200 mg/dL
- HbA1c test:
- Normal: < 5.7%
- Prediabetes: 5.7-6.4%
- Diabetes: ≥ 6.5%
Benefits of Glucose Lab Tests
Glucose lab tests offer numerous benefits, including:- Early detection and diagnosis of diabetes and prediabetes
- Monitoring of glucose levels in patients with diabetes
- Assessment of glucose metabolism in patients with other medical conditions
- Identification of individuals at risk of developing diabetes
Preparation for Glucose Lab Tests

To ensure accurate results, patients must prepare properly for glucose lab tests. The following are general guidelines for preparation:
- FPG test: Fast for 8-12 hours before the test
- OGTT: Fast for 8-12 hours before the test and avoid consuming sugary drinks or foods
- Random Plasma Glucose test: No special preparation is required
- HbA1c test: No special preparation is required
Risks and Limitations of Glucose Lab Tests
While glucose lab tests are generally safe and effective, there are some risks and limitations to consider:- False-positive or false-negative results
- Interference from certain medications or medical conditions
- Limited accuracy in patients with certain medical conditions, such as kidney or liver disease
Glucose Lab Tests in Special Populations
Glucose lab tests are essential in special populations, including:
- Pregnant women: To diagnose and manage gestational diabetes
- Children and adolescents: To diagnose and manage type 1 diabetes
- Older adults: To diagnose and manage type 2 diabetes and other glucose-related disorders
Future Directions in Glucose Lab Tests
The field of glucose lab tests is constantly evolving, with new technologies and techniques being developed to improve diagnosis and management of glucose-related disorders. Some future directions in glucose lab tests include:- Point-of-care testing: To enable rapid and convenient testing in clinical settings
- Non-invasive testing: To reduce the need for blood samples and improve patient comfort
- Artificial intelligence: To improve test accuracy and interpretation
Conclusion and Recommendations
In conclusion, glucose lab tests are a vital tool for assessing blood sugar levels and diagnosing glucose-related disorders. By understanding the different types of glucose lab tests, their interpretation, and benefits, healthcare professionals can provide optimal care for patients with diabetes and other glucose-related conditions. We recommend that patients and healthcare professionals stay informed about the latest developments in glucose lab tests and work together to improve diagnosis, treatment, and management of glucose-related disorders.
What is the normal range for fasting plasma glucose?
+The normal range for fasting plasma glucose is less than 100 mg/dL.
How often should I get a glucose lab test?
+The frequency of glucose lab tests depends on your individual needs and medical history. Consult with your healthcare provider to determine the best testing schedule for you.
Can I take a glucose lab test at home?
+Yes, there are several at-home glucose testing kits available. However, it's essential to consult with your healthcare provider before using any at-home testing kit to ensure accuracy and reliability.
What are the risks of not getting a glucose lab test?
+Not getting a glucose lab test can lead to delayed diagnosis and treatment of glucose-related disorders, increasing the risk of complications and poor health outcomes.
Can glucose lab tests be used to diagnose other medical conditions?
+Yes, glucose lab tests can be used to diagnose other medical conditions, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and pancreatic cancer.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with glucose lab tests in the comments section below. If you found this article informative, please share it with others who may benefit from this information. By working together, we can improve our understanding of glucose lab tests and promote better health outcomes for individuals with glucose-related disorders.
