Intro
Master glucose testing with 5 expert tips, including monitoring blood sugar levels, choosing the right glucose meter, and understanding test strips, to effectively manage diabetes and maintain healthy glucose control.
Glucose testing is a crucial aspect of managing diabetes and prediabetes. It helps individuals monitor their blood sugar levels, making informed decisions about their diet, exercise, and medication. With the rise of diabetes cases worldwide, understanding glucose testing is more important than ever. In this article, we will delve into the world of glucose testing, exploring its importance, benefits, and providing valuable tips for accurate and effective testing.
Glucose testing is not just for individuals with diabetes; it's also essential for those who are at risk of developing the condition. Factors such as family history, obesity, and physical inactivity can increase the likelihood of developing diabetes. By monitoring blood sugar levels, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent or delay the onset of diabetes. Furthermore, glucose testing can help identify other health issues, such as insulin resistance or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), which are often associated with blood sugar imbalances.
The importance of glucose testing cannot be overstated. It provides valuable insights into how the body regulates blood sugar levels, helping individuals make informed decisions about their lifestyle and treatment options. With the advancements in technology, glucose testing has become more accessible and convenient than ever. From traditional finger-prick tests to continuous glucose monitoring systems, there are various methods available to suit different needs and preferences. In the following sections, we will explore the benefits and working mechanisms of glucose testing, as well as provide practical tips for accurate and effective testing.
Understanding Glucose Testing
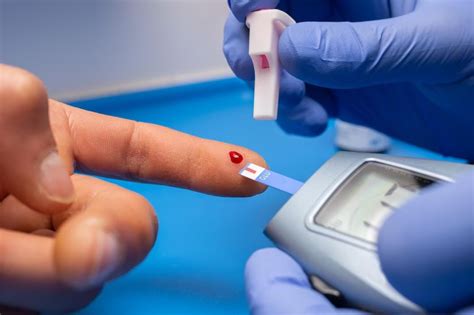
Benefits of Glucose Testing
The benefits of glucose testing are numerous. It helps individuals with diabetes monitor their blood sugar levels, making adjustments to their treatment plan as needed. Glucose testing also enables healthcare providers to diagnose and monitor diabetes, as well as other conditions associated with blood sugar imbalances. Additionally, glucose testing can help individuals identify patterns and trends in their blood sugar levels, making informed decisions about their diet, exercise, and lifestyle.Preparation and Procedure
Common Types of Glucose Tests
There are several types of glucose tests, each with its own specific requirements and purposes. These include: * Fasting plasma glucose (FPG) tests: Measure blood glucose levels after an overnight fast. * Oral glucose tolerance tests (OGTT): Measure blood glucose levels after consuming a sugary drink. * Random plasma glucose (RPG) tests: Measure blood glucose levels at any time, regardless of when the individual last ate. * Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems: Measure blood glucose levels throughout the day and night.Tips for Accurate and Effective Testing

Common Mistakes to Avoid
When it comes to glucose testing, there are several common mistakes to avoid. These include: * Not preparing properly for the test, which can lead to inaccurate results. * Using a low-quality glucose meter or test strips, which can also lead to inaccurate results. * Not keeping a record of test results, making it difficult to identify patterns and trends. * Not consulting with a healthcare provider to determine the best testing schedule for individual needs.Interpreting Test Results
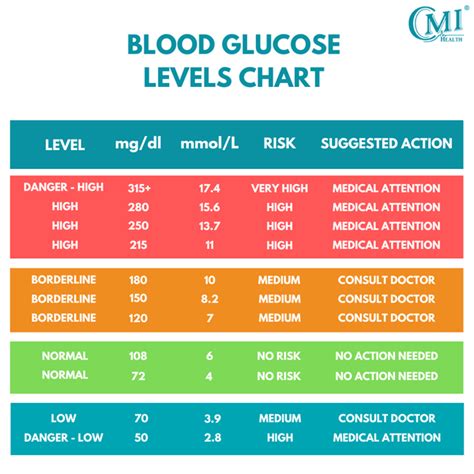
What to Do Next
If you've received abnormal glucose test results, it's essential to consult with your healthcare provider to determine the best course of action. This may include lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise modifications, or medication to help regulate blood sugar levels. In some cases, additional testing may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis or monitor the effectiveness of treatment.Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle

Additional Resources
For more information on glucose testing and diabetes management, consult the following resources: * American Diabetes Association (ADA) * Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) * National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK)Conclusion and Next Steps
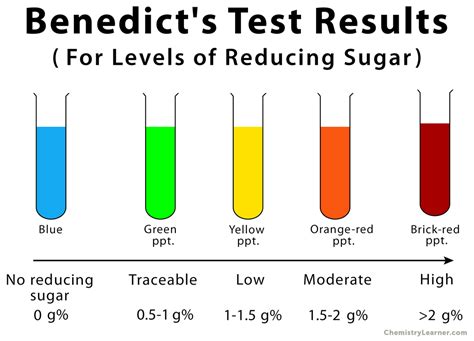
What is the normal range for glucose test results?
+Normal glucose test results are typically less than 100 mg/dL (5.6 mmol/L). However, this range may vary depending on the individual and the type of test used.
How often should I test my blood sugar levels?
+The frequency of glucose testing depends on the individual's needs and the type of diabetes they have. Consult with your healthcare provider to determine the best testing schedule for you.
What are the risks associated with glucose testing?
+The risks associated with glucose testing are generally minimal, but may include pain or bruising at the testing site, as well as inaccurate results if the test is not performed correctly.
We hope this article has provided you with valuable insights into the world of glucose testing. If you have any questions or comments, please don't hesitate to share them below. Additionally, if you found this article helpful, please consider sharing it with others who may benefit from this information. Together, we can work towards a healthier and more informed community.
