Intro
Learn about the ideal glucose level range, normal blood sugar levels, and target glucose levels to manage diabetes and maintain healthy glucose monitoring, insulin sensitivity, and blood glucose control.
Maintaining a healthy glucose level range is crucial for overall well-being, as it directly impacts the body's ability to function properly. Glucose, a type of sugar, serves as the primary source of energy for cells throughout the body. When glucose levels are within a normal range, the body can efficiently utilize this energy source, supporting various bodily functions. However, when glucose levels become imbalanced, it can lead to a range of health issues, including diabetes, a condition characterized by the body's inability to regulate blood sugar levels effectively.
Understanding the importance of glucose level range is essential for preventing and managing diabetes, as well as other related health conditions. The human body has a complex system for regulating blood sugar levels, involving the pancreas, liver, and other organs. The pancreas produces insulin, a hormone that helps cells absorb glucose from the bloodstream, while the liver stores and releases glucose as needed. When this system is functioning properly, glucose levels remain within a healthy range, supporting optimal health and preventing potential complications.
Effective glucose level management requires a comprehensive approach, incorporating lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, and, when necessary, medication. By understanding the factors that influence glucose levels and taking proactive steps to maintain a healthy range, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing diabetes and related health issues. Furthermore, for those already diagnosed with diabetes, learning to manage glucose levels effectively is critical for preventing long-term complications, such as cardiovascular disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage.
Normal Glucose Level Range

Factors Influencing Glucose Levels
Several factors can influence glucose levels, including diet, physical activity, stress, and sleep patterns. Consuming a diet high in refined carbohydrates, sugars, and saturated fats can lead to increased glucose levels, while regular physical activity, such as walking or jogging, can help lower glucose levels by improving insulin sensitivity. Stress and lack of sleep can also disrupt glucose regulation, making it essential to manage these factors as part of a comprehensive approach to glucose level management.Diabetes and Glucose Level Range

Diabetes Management and Glucose Level Range
Effective diabetes management involves maintaining glucose levels within a target range to prevent long-term complications. This can be achieved through a combination of lifestyle modifications, including a healthy diet, regular physical activity, and stress management, as well as medication, such as metformin or insulin therapy, when prescribed by a healthcare provider. Monitoring glucose levels regularly is also crucial for understanding how different factors influence glucose levels and making informed decisions about diabetes management.Lifestyle Modifications for Glucose Level Management

Benefits of Regular Physical Activity
Regular physical activity offers numerous benefits for glucose level management, including improved insulin sensitivity, enhanced glucose uptake in the muscles, and better weight management. Physical activity can also reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease, improve mental health, and increase overall quality of life. The American Diabetes Association recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic physical activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic physical activity or a combination of both, per week, for adults with diabetes.Dietary Approaches for Glucose Level Management

Importance of Glycemic Index
The glycemic index (GI) is a measure of how quickly foods raise blood glucose levels. Foods with a high GI, such as white bread and sugary snacks, cause a rapid increase in glucose levels, while foods with a low GI, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, have a more gradual effect. Choosing foods with a low GI can help individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing diabetes manage their glucose levels more effectively.Monitoring Glucose Levels
Technological Advances in Glucose Monitoring
Recent technological advances have made glucose monitoring more convenient, accurate, and user-friendly. CGM systems, for example, use a small sensor inserted under the skin to track glucose levels continuously, providing real-time data and trends. Mobile apps and online platforms can also help individuals track their glucose levels, physical activity, and dietary habits, making it easier to manage diabetes and maintain a healthy glucose level range.Complications of Unmanaged Glucose Levels
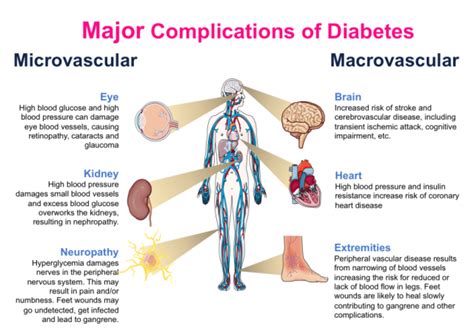
Importance of Early Detection and Treatment
Early detection and treatment of diabetes are critical for preventing long-term complications. Regular health check-ups, screenings, and monitoring can help identify individuals at risk of developing diabetes or those with undiagnosed diabetes. Prompt treatment, including lifestyle modifications and medication, can help manage glucose levels, reduce the risk of complications, and improve overall quality of life.Future Directions in Glucose Level Management

Personalized Medicine and Glucose Level Management
Personalized medicine is an emerging approach that tailors diabetes management to an individual's unique characteristics, including genetic profile, medical history, and lifestyle. This approach may involve genetic testing, biomarker analysis, and advanced imaging techniques to identify specific factors influencing glucose levels and develop targeted treatment plans. By providing more precise and effective care, personalized medicine has the potential to revolutionize glucose level management and improve outcomes for individuals with diabetes.What is the normal glucose level range?
+A fasting glucose level between 70 and 99 mg/dL is generally considered normal, while after eating, glucose levels should remain below 140 mg/dL.
How can I manage my glucose levels effectively?
+Effective glucose level management involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, including a healthy diet, regular physical activity, stress management, and adequate sleep, as well as medication, when prescribed by a healthcare provider.
What are the complications of unmanaged glucose levels?
+Unmanaged glucose levels can lead to serious complications, including cardiovascular disease, kidney damage, nerve damage, and vision problems, emphasizing the importance of early detection, treatment, and ongoing management.
In conclusion, maintaining a healthy glucose level range is essential for overall well-being, and understanding the factors that influence glucose levels is critical for effective management. By adopting a comprehensive approach that incorporates lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, and medication, when necessary, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing diabetes and related health issues. As research and development continue to advance, the future of glucose level management holds promise, with emerging technologies and therapies offering new avenues for improving diabetes care and outcomes. We invite you to share your thoughts, experiences, and questions regarding glucose level management and diabetes care, and we encourage you to explore the resources and support available for maintaining a healthy glucose level range.
