Intro
Learn about normal glucose levels, blood sugar ranges, and ideal targets for a healthy diet, understanding glucose monitoring, and managing diabetes with optimal glucose control and stable blood glucose levels.
Maintaining normal glucose levels is crucial for overall health and well-being. Glucose, a type of sugar, is the primary source of energy for the body's cells. The body regulates glucose levels through a complex process involving the pancreas, liver, and insulin. Understanding normal glucose levels is essential for preventing and managing conditions like diabetes, which affects millions of people worldwide. In this article, we will delve into the importance of normal glucose levels, how they are regulated, and what factors can affect them.
The regulation of glucose levels is a delicate balance that can be disrupted by various factors, including diet, lifestyle, and certain medical conditions. When glucose levels are not within the normal range, it can lead to serious health complications, such as nerve damage, kidney disease, and vision problems. Therefore, it is essential to understand the normal glucose levels and take steps to maintain them. Whether you are at risk of developing diabetes or simply want to maintain optimal health, understanding normal glucose levels is vital.
Normal glucose levels vary throughout the day, depending on factors such as meal times, physical activity, and sleep patterns. For example, glucose levels typically rise after eating a meal and decrease after physical activity. The body's ability to regulate glucose levels is crucial for maintaining energy homeostasis and preventing complications associated with abnormal glucose levels. In the following sections, we will explore the factors that affect glucose levels, how to maintain normal glucose levels, and the consequences of abnormal glucose levels.
What are Normal Glucose Levels?

Factors that Affect Glucose Levels
Several factors can affect glucose levels, including diet, physical activity, stress, and certain medical conditions. For example, consuming high-carbohydrate foods can cause a rapid increase in glucose levels, while regular physical activity can help lower glucose levels. Stress can also affect glucose levels by stimulating the release of stress hormones, such as cortisol and adrenaline, which can raise glucose levels. Certain medical conditions, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and Cushing's syndrome, can also affect glucose levels.How are Glucose Levels Regulated?
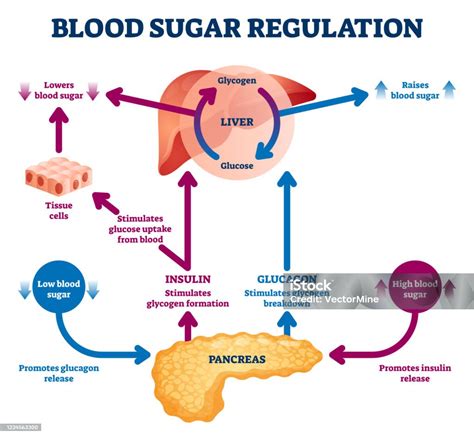
The Role of Insulin in Glucose Regulation
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that plays a crucial role in glucose regulation. Insulin facilitates the uptake of glucose by cells, thereby lowering glucose levels. Insulin also inhibits the production of glucose in the liver and stimulates the storage of glucose in the form of glycogen. In individuals with diabetes, the body either does not produce enough insulin (type 1 diabetes) or is unable to effectively use insulin (type 2 diabetes), leading to high glucose levels.Consequences of Abnormal Glucose Levels
Long-term Complications of Abnormal Glucose Levels
The long-term complications of abnormal glucose levels can be severe and debilitating. Individuals with diabetes are at increased risk of heart disease, stroke, and peripheral artery disease. They are also at increased risk of developing kidney disease, nerve damage, and vision problems. Furthermore, individuals with diabetes are at increased risk of developing infections, such as pneumonia and urinary tract infections, and are more likely to experience poor wound healing.Maintaining Normal Glucose Levels

Dietary Changes to Maintain Normal Glucose Levels
Making dietary changes can help maintain normal glucose levels. Some tips for maintaining normal glucose levels include: * Eating a balanced diet that is low in added sugars, saturated fats, and refined carbohydrates * Choosing whole, unprocessed foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins * Drinking plenty of water and limiting sugary drinks * Limiting portion sizes and eating regular meals to prevent large spikes in glucose levels * Avoiding foods that are high in sugar, salt, and unhealthy fatsMonitoring Glucose Levels
Benefits of Monitoring Glucose Levels
Monitoring glucose levels has several benefits, including: * Early detection of abnormal glucose levels * Prevention of complications associated with abnormal glucose levels * Improved glucose control * Enhanced quality of life * Reduced risk of long-term complications, such as heart disease, kidney disease, and nerve damageConclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences on maintaining normal glucose levels in the comments below. If you found this article helpful, please share it with your friends and family to help spread awareness about the importance of maintaining normal glucose levels.
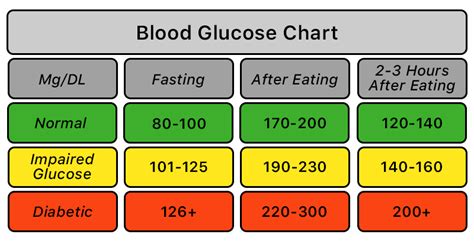
What are normal glucose levels?
+Normal glucose levels are typically between 70-100 mg/dL (3.9-5.5 mmol/L) when fasting and between 100-140 mg/dL (5.5-7.8 mmol/L) after eating a meal.
How are glucose levels regulated?
+Glucose levels are regulated by a complex process involving the pancreas, liver, and insulin. Insulin lowers glucose levels by facilitating the uptake of glucose by cells, while glucagon raises glucose levels by stimulating the release of glucose from stored energy sources.
What are the consequences of abnormal glucose levels?
+Abnormal glucose levels can have serious consequences, including nerve damage, kidney disease, and vision problems. High glucose levels can damage the blood vessels and nerves, leading to complications such as numbness, tingling, and pain in the hands and feet.
