Intro
Learn about the normal glucose range, blood sugar levels, and healthy glucose monitoring, including fasting glucose, postprandial glucose, and target glucose levels for optimal health.
Maintaining a normal glucose range is crucial for overall health and well-being. Glucose, a simple sugar, is the primary source of energy for the body's cells. The body's ability to regulate glucose levels is essential for preventing various health issues, including diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and neurological disorders. Understanding the importance of glucose regulation can help individuals take proactive steps to maintain a healthy glucose range.
The normal glucose range is typically between 70 and 99 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) when fasting, and less than 140 mg/dL two hours after eating. However, these numbers can vary depending on factors such as age, diet, and physical activity level. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the ideal glucose range for individual circumstances. By monitoring glucose levels and making informed lifestyle choices, individuals can reduce the risk of developing glucose-related health issues.
Glucose regulation is a complex process that involves the coordinated effort of multiple organs, including the pancreas, liver, and kidneys. The pancreas produces insulin and glucagon, hormones that help regulate glucose levels in the blood. Insulin facilitates the uptake of glucose by cells, while glucagon stimulates the release of glucose stored in the liver. Imbalances in glucose regulation can lead to various health problems, including hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), hyperglycemia (high blood sugar), and diabetes. Understanding how glucose regulation works can help individuals appreciate the importance of maintaining a normal glucose range.
Importance of Normal Glucose Range

Benefits of Normal Glucose Range
Some of the benefits of maintaining a normal glucose range include: * Reduced risk of diabetes and related health issues * Improved cardiovascular health * Enhanced cognitive function and reduced risk of neurological disorders * Improved kidney function and reduced risk of kidney disease * Reduced risk of certain types of cancer * Improved overall health and well-beingFactors Affecting Glucose Levels
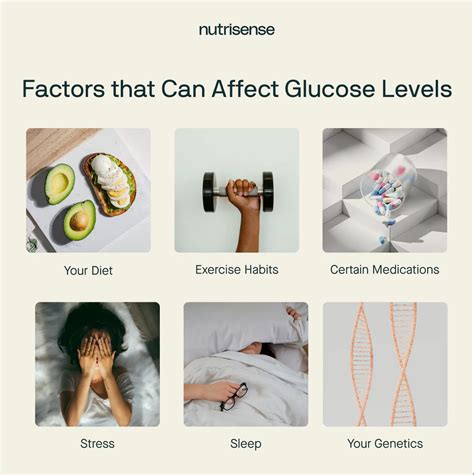
Ways to Maintain Normal Glucose Range
Some ways to maintain a normal glucose range include: * Eating a balanced diet that is low in sugar, refined carbohydrates, and saturated fats * Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking, jogging, or cycling * Practicing stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation or yoga * Getting adequate sleep and maintaining a consistent sleep schedule * Monitoring glucose levels regularly and adjusting lifestyle habits as neededGlucose Regulation and Diabetes
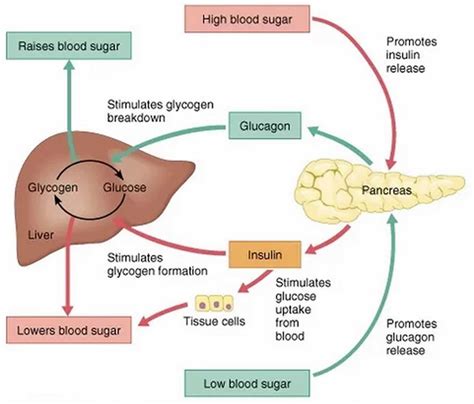
Diabetes Management
Some ways to manage diabetes include: * Monitoring glucose levels regularly * Taking medications as prescribed by a healthcare professional * Eating a balanced diet that is low in sugar, refined carbohydrates, and saturated fats * Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking, jogging, or cycling * Practicing stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation or yogaGlucose Monitoring and Testing
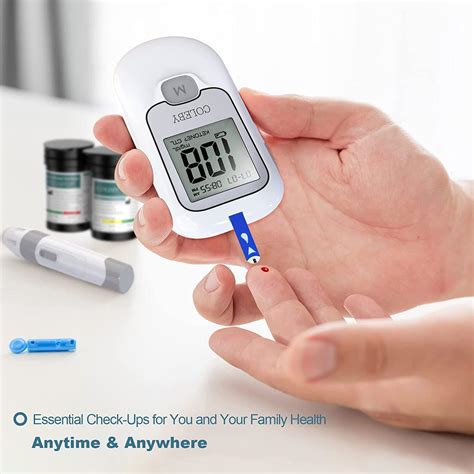
Glucose Testing Devices
Some common glucose testing devices include: * Glucose meters: These devices use a small blood sample to measure glucose levels. * Continuous glucose monitors: These devices use a small sensor to measure glucose levels continuously. * Glucose test strips: These devices use a small blood sample to measure glucose levels.Normal Glucose Range and Pregnancy
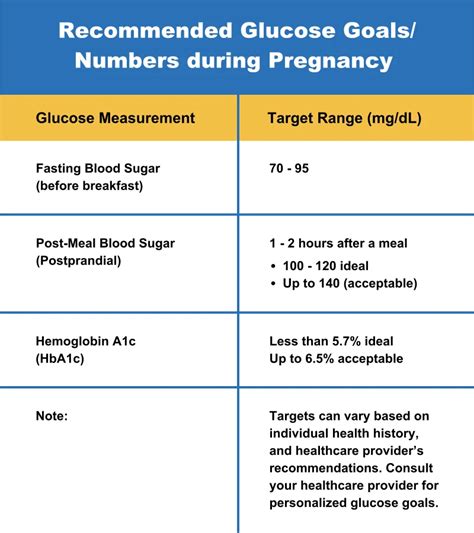
Pregnancy and Glucose Regulation
Some ways to maintain a normal glucose range during pregnancy include: * Eating a balanced diet that is low in sugar, refined carbohydrates, and saturated fats * Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking, jogging, or cycling * Practicing stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation or yoga * Getting adequate sleep and maintaining a consistent sleep schedule * Monitoring glucose levels regularly and adjusting lifestyle habits as neededNormal Glucose Range and Aging
Aging and Glucose Regulation
Some ways to maintain a normal glucose range as we age include: * Eating a balanced diet that is low in sugar, refined carbohydrates, and saturated fats * Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking, jogging, or cycling * Practicing stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation or yoga * Getting adequate sleep and maintaining a consistent sleep schedule * Monitoring glucose levels regularly and adjusting lifestyle habits as neededWhat is the normal glucose range?
+The normal glucose range is typically between 70 and 99 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) when fasting, and less than 140 mg/dL two hours after eating.
What are the benefits of maintaining a normal glucose range?
+Maintaining a normal glucose range can help to reduce the risk of developing glucose-related health issues, such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and cognitive decline.
How can I maintain a normal glucose range?
+Maintaining a normal glucose range can be achieved by eating a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, practicing stress-reducing techniques, getting adequate sleep, and monitoring glucose levels regularly.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the importance of maintaining a normal glucose range. By following the tips and guidelines outlined in this article, you can take proactive steps to reduce your risk of developing glucose-related health issues and maintain optimal overall health. If you have any questions or concerns, please don't hesitate to comment below or share this article with your friends and family. Remember, maintaining a normal glucose range is a critical aspect of overall health and well-being, and it's never too early or too late to take control of your glucose levels.
