Intro
Learn about the normal glucose range, blood sugar levels, and healthy glucose monitoring, including fasting glucose, postprandial glucose, and target glucose levels for optimal health.
Maintaining a normal glucose range is crucial for overall health and well-being. Glucose, also known as blood sugar, is the primary source of energy for the body's cells. When glucose levels are within a normal range, the body functions properly, and the risk of developing chronic diseases like diabetes, heart disease, and stroke is reduced. In this article, we will delve into the importance of normal glucose range, its benefits, and provide guidance on how to maintain it.
The normal glucose range is typically between 70 and 110 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) for individuals who have not eaten for at least 8 hours, also known as fasting glucose levels. After eating, glucose levels may rise, but they should not exceed 140 mg/dL. Keeping glucose levels within this range is essential for preventing complications associated with diabetes, such as nerve damage, kidney disease, and vision problems. Moreover, maintaining a normal glucose range can also help prevent cognitive decline, reduce the risk of certain cancers, and promote healthy weight management.
Understanding the normal glucose range and its significance can empower individuals to take control of their health. By making informed lifestyle choices, such as following a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and monitoring glucose levels, individuals can reduce their risk of developing insulin resistance, prediabetes, and type 2 diabetes. Furthermore, maintaining a normal glucose range can also improve mental health, increase energy levels, and enhance overall quality of life. In the following sections, we will explore the benefits, working mechanisms, and steps to maintain a normal glucose range.
Benefits of Normal Glucose Range

Maintaining a normal glucose range offers numerous benefits, including:
- Reduced risk of chronic diseases like diabetes, heart disease, and stroke
- Improved cognitive function and reduced risk of cognitive decline
- Enhanced weight management and reduced risk of obesity
- Improved mental health and reduced risk of depression and anxiety
- Increased energy levels and improved physical performance
- Reduced risk of certain cancers, such as pancreatic cancer
- Improved wound healing and reduced risk of infections
Glucose Regulation Mechanisms
The body has a complex system to regulate glucose levels, involving the pancreas, liver, and other organs. When glucose levels rise after eating, the pancreas releases insulin, a hormone that helps cells absorb glucose for energy production. Conversely, when glucose levels drop, the pancreas releases glucagon, a hormone that stimulates the liver to release stored glucose into the bloodstream. This delicate balance ensures that glucose levels remain within a normal range, providing the body with a constant supply of energy.Factors Affecting Glucose Levels
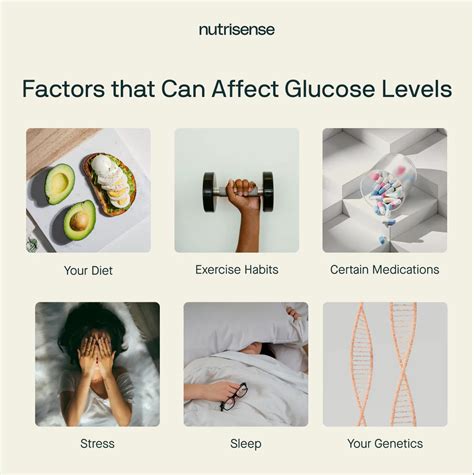
Several factors can affect glucose levels, including:
- Diet: Consuming high amounts of sugary or refined foods can cause glucose spikes
- Physical activity: Regular exercise can improve insulin sensitivity and reduce glucose levels
- Stress: Chronic stress can raise glucose levels and increase the risk of insulin resistance
- Sleep: Poor sleep quality and duration can disrupt glucose regulation
- Certain medications: Some medications, such as steroids and certain psychiatric medications, can raise glucose levels
- Hormonal changes: Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy, menopause, or puberty can affect glucose levels
Steps to Maintain Normal Glucose Range
To maintain a normal glucose range, individuals can follow these steps: 1. **Eat a balanced diet**: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods like vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. 2. **Stay hydrated**: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to help regulate glucose levels. 3. **Exercise regularly**: Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise per week. 4. **Manage stress**: Practice stress-reducing techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises. 5. **Get enough sleep**: Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night to help regulate glucose levels. 6. **Monitor glucose levels**: Regularly check glucose levels, especially if you have a family history of diabetes or are at risk of developing insulin resistance.Importance of Glucose Monitoring
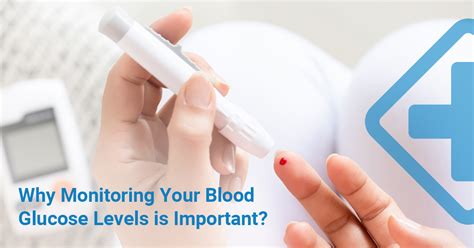
Glucose monitoring is crucial for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing insulin resistance. By regularly checking glucose levels, individuals can:
- Identify patterns and trends in glucose levels
- Adjust diet and exercise plans to maintain a normal glucose range
- Detect potential complications early, such as hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia
- Work with healthcare providers to adjust medication or treatment plans
Glucose Monitoring Methods
There are several methods to monitor glucose levels, including: * Fasting glucose tests: Measure glucose levels after an overnight fast * Oral glucose tolerance tests: Measure glucose levels after consuming a sugary drink * Continuous glucose monitoring: Use a device to track glucose levels throughout the day * Self-monitoring of blood glucose: Use a glucometer to check glucose levels at homeNormal Glucose Range in Special Populations

Normal glucose ranges may vary in special populations, such as:
- Pregnant women: Glucose levels may be lower due to increased insulin sensitivity
- Children and adolescents: Glucose levels may be higher due to increased growth and development
- Older adults: Glucose levels may be higher due to decreased insulin sensitivity and increased risk of diabetes
- Individuals with certain medical conditions: Glucose levels may be affected by conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), Cushing's syndrome, or hypothyroidism
Managing Glucose Levels in Special Populations
Individuals in special populations can manage glucose levels by: * Working with healthcare providers to develop personalized treatment plans * Following a balanced diet and exercise plan * Monitoring glucose levels regularly * Adjusting medication or treatment plans as neededConclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, maintaining a normal glucose range is essential for overall health and well-being. By understanding the benefits, working mechanisms, and steps to maintain a normal glucose range, individuals can take control of their health and reduce their risk of developing chronic diseases. We encourage readers to share their experiences and tips for managing glucose levels in the comments below. Additionally, we invite readers to explore our website for more information on glucose regulation, diabetes prevention, and healthy living.
What is the normal glucose range for adults?
+The normal glucose range for adults is typically between 70 and 110 mg/dL for fasting glucose levels and below 140 mg/dL after eating.
How can I maintain a normal glucose range?
+To maintain a normal glucose range, follow a balanced diet, stay hydrated, exercise regularly, manage stress, and get enough sleep.
What are the risks of not maintaining a normal glucose range?
+The risks of not maintaining a normal glucose range include developing insulin resistance, prediabetes, type 2 diabetes, and increasing the risk of chronic diseases like heart disease and stroke.
