Intro
Discover the role of Glutamyl Transpeptidase Gamma Enzyme in liver health, detoxification, and antioxidant defense, exploring its connection to gamma-glutamyl transferase, enzyme activity, and oxidative stress.
The human body is comprised of numerous intricate systems, each playing a vital role in maintaining overall health and well-being. One such system is the enzymatic system, which is responsible for facilitating various chemical reactions that occur within the body. Among the numerous enzymes present in the human body, the glutamyl transpeptidase gamma enzyme, also known as gamma-glutamyltransferase (GGT) or gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (γ-GT), is a crucial enzyme that plays a significant role in the body's antioxidant defense mechanism and the metabolism of glutathione and other amino acids.
The glutamyl transpeptidase gamma enzyme is primarily found in the liver, kidneys, and pancreas, with smaller amounts present in other tissues such as the spleen, heart, and brain. This enzyme is involved in the transfer of gamma-glutamyl groups from glutathione and other gamma-glutamyl-containing compounds to amino acids and other acceptor molecules. This reaction is essential for the synthesis and degradation of glutathione, which is a vital antioxidant that protects cells from oxidative damage caused by free radicals. Elevated levels of GGT have been linked to various diseases, including liver disease, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease, making it a valuable biomarker for diagnosing and monitoring these conditions.
The importance of the glutamyl transpeptidase gamma enzyme cannot be overstated, as it plays a critical role in maintaining the body's antioxidant balance and preventing oxidative stress. Oxidative stress occurs when the body's antioxidant defenses are overwhelmed by free radicals, leading to cellular damage and potentially contributing to the development of chronic diseases. By facilitating the metabolism of glutathione and other antioxidants, the glutamyl transpeptidase gamma enzyme helps to protect cells from oxidative damage and maintain overall health and well-being. In this article, we will delve deeper into the role of the glutamyl transpeptidase gamma enzyme, its benefits, and its significance in maintaining optimal health.
What is Glutamyl Transpeptidase Gamma Enzyme?
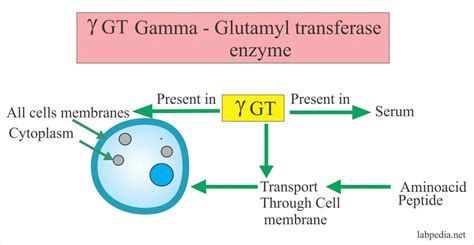
The glutamyl transpeptidase gamma enzyme is a heterodimeric enzyme composed of two subunits: a heavy chain and a light chain. The heavy chain is responsible for the enzyme's catalytic activity, while the light chain plays a role in the enzyme's stability and localization. GGT is a membrane-bound enzyme, with its active site facing the extracellular space. This allows the enzyme to interact with its substrates, including glutathione and other gamma-glutamyl-containing compounds, and facilitate the transfer of gamma-glutamyl groups to acceptor molecules.
Benefits of Glutamyl Transpeptidase Gamma Enzyme
The benefits of the glutamyl transpeptidase gamma enzyme are numerous and significant. Some of the key benefits include: * Antioxidant activity: GGT plays a critical role in the metabolism of glutathione, which is a vital antioxidant that protects cells from oxidative damage. * Detoxification: The enzyme is involved in the detoxification of various xenobiotics, including drugs and environmental pollutants. * Amino acid metabolism: GGT is involved in the metabolism of amino acids, including glutamine and glutamate, which are essential for various cellular processes. * Cellular protection: The enzyme helps to protect cells from oxidative damage and maintain cellular homeostasis.Working Mechanism of Glutamyl Transpeptidase Gamma Enzyme
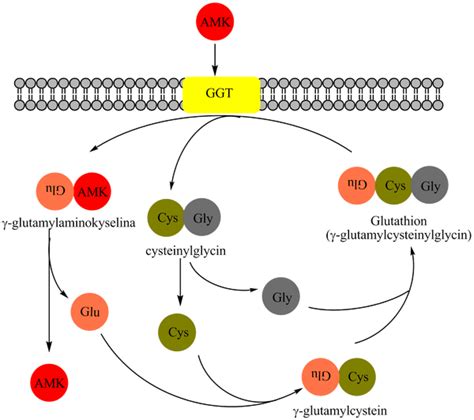
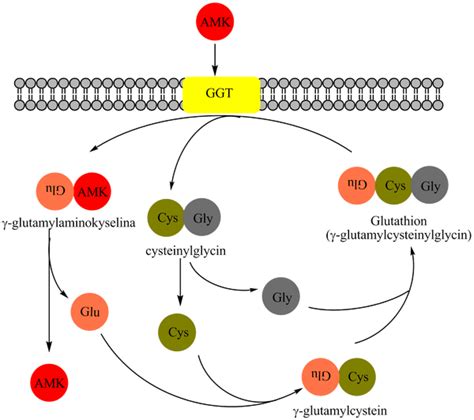
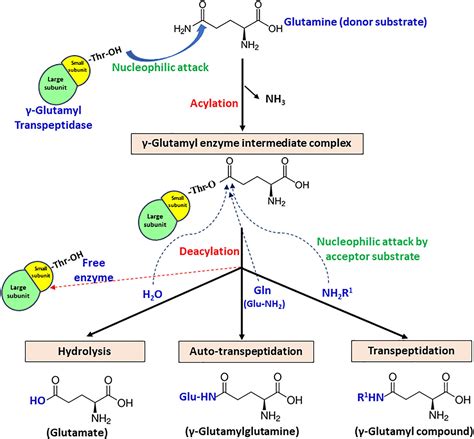
The working mechanism of the glutamyl transpeptidase gamma enzyme involves the transfer of gamma-glutamyl groups from glutathione and other gamma-glutamyl-containing compounds to acceptor molecules. This reaction is facilitated by the enzyme's active site, which is composed of a catalytic triad consisting of a cysteine residue, a glutamic acid residue, and a histidine residue. The cysteine residue plays a crucial role in the enzyme's catalytic activity, as it forms a covalent intermediate with the gamma-glutamyl group of the substrate.
The steps involved in the working mechanism of GGT are as follows:
- Binding of substrate: The substrate, such as glutathione, binds to the enzyme's active site.
- Formation of covalent intermediate: The cysteine residue of the enzyme forms a covalent intermediate with the gamma-glutamyl group of the substrate.
- Transfer of gamma-glutamyl group: The gamma-glutamyl group is transferred to an acceptor molecule, such as an amino acid.
- Release of product: The product, such as glutamic acid, is released from the enzyme's active site.
Role of Glutamyl Transpeptidase Gamma Enzyme in Disease
The glutamyl transpeptidase gamma enzyme plays a significant role in various diseases, including liver disease, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. Elevated levels of GGT have been linked to these conditions, making it a valuable biomarker for diagnosing and monitoring disease progression. Some of the key diseases associated with GGT include: * Liver disease: Elevated levels of GGT are often seen in patients with liver disease, including hepatitis and cirrhosis. * Diabetes: GGT has been linked to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. * Cardiovascular disease: Elevated levels of GGT have been associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, including heart attack and stroke.Factors that Influence Glutamyl Transpeptidase Gamma Enzyme Activity
Several factors can influence the activity of the glutamyl transpeptidase gamma enzyme, including:
- Age: GGT activity tends to increase with age.
- Sex: Males tend to have higher GGT activity than females.
- Diet: A diet high in fat and sugar can increase GGT activity.
- Lifestyle: Smoking and alcohol consumption can increase GGT activity.
- Disease: Certain diseases, such as liver disease and diabetes, can increase GGT activity.
Measurement of Glutamyl Transpeptidase Gamma Enzyme Activity
GGT activity can be measured using various laboratory tests, including: * Serum GGT test: This test measures the level of GGT in the blood. * Urine GGT test: This test measures the level of GGT in the urine. * Liver function test: This test measures the level of various liver enzymes, including GGT.Practical Applications of Glutamyl Transpeptidase Gamma Enzyme
The glutamyl transpeptidase gamma enzyme has several practical applications, including:
- Diagnostic marker: GGT is used as a diagnostic marker for various diseases, including liver disease and diabetes.
- Therapeutic target: GGT is a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of various diseases, including cancer and cardiovascular disease.
- Research tool: GGT is used as a research tool to study the metabolism of glutathione and other antioxidants.
Future Directions for Glutamyl Transpeptidase Gamma Enzyme Research
Future research directions for the glutamyl transpeptidase gamma enzyme include: * Development of new diagnostic markers: Researchers are working to develop new diagnostic markers that can detect GGT activity more accurately and reliably. * Development of new therapeutic agents: Researchers are working to develop new therapeutic agents that can target GGT and treat various diseases. * Elucidation of GGT's role in disease: Researchers are working to elucidate the role of GGT in various diseases, including cancer and cardiovascular disease.Conclusion and Recommendations

In conclusion, the glutamyl transpeptidase gamma enzyme is a vital enzyme that plays a significant role in the body's antioxidant defense mechanism and the metabolism of glutathione and other amino acids. Elevated levels of GGT have been linked to various diseases, including liver disease, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease, making it a valuable biomarker for diagnosing and monitoring disease progression. Further research is needed to elucidate the role of GGT in disease and to develop new diagnostic markers and therapeutic agents.
We recommend that individuals with elevated GGT levels take steps to reduce their risk of disease, including:
- Maintaining a healthy diet and lifestyle
- Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption
- Getting regular exercise and maintaining a healthy weight
- Managing stress and getting adequate sleep
By taking these steps, individuals can help to reduce their risk of disease and maintain optimal health and well-being.
What is the normal range for GGT activity?
+The normal range for GGT activity varies depending on the laboratory and the individual, but it is typically between 0-55 U/L.
What are the symptoms of elevated GGT activity?
+The symptoms of elevated GGT activity vary depending on the underlying cause, but they may include fatigue, nausea, and abdominal pain.
How is GGT activity measured?
+GGT activity is typically measured using a serum or urine test, which detects the level of GGT in the blood or urine.
