Intro
Discover 5 crucial HbA1c facts, understanding blood sugar control, diabetes management, and glucose monitoring, to improve your health outcomes and reduce complications, with key insights into hemoglobin A1c testing and its role in assessing average blood glucose levels.
Understanding HbA1c is crucial for managing diabetes and maintaining good health. The HbA1c test, also known as the hemoglobin A1c or glycated hemoglobin test, is a blood test that measures the average level of glucose (sugar) in your blood over the past 2 to 3 months. It's a vital tool for diagnosing diabetes, prediabetes, and monitoring the effectiveness of diabetes treatment plans. The importance of HbA1c lies in its ability to provide a clear picture of how well diabetes is being managed, helping individuals and healthcare providers make informed decisions about diet, exercise, and medication.
The relevance of HbA1c in today's healthcare is underscored by the growing prevalence of diabetes worldwide. As more people are diagnosed with diabetes or prediabetes, the demand for effective management strategies increases. HbA1c testing offers a straightforward and reliable method for assessing blood glucose control, making it an indispensable component of diabetes care. Moreover, understanding HbA1c results empowers individuals to take a more active role in their health, fostering a collaborative approach between patients and healthcare providers.
The significance of HbA1c extends beyond its role in diabetes management. It also serves as an indicator of cardiovascular risk, with elevated HbA1c levels associated with an increased risk of heart disease, stroke, and other vascular complications. This broader implications highlight the need for comprehensive education on HbA1c, including how the test is performed, how to interpret results, and the importance of maintaining target HbA1c levels. By delving into these aspects, individuals can better navigate their health journey, especially those living with diabetes or at risk of developing it.
Introduction to HbA1c

How HbA1c Testing Works
The process of getting an HbA1c test is relatively straightforward. It requires a blood sample, which can be taken from a vein in the arm or, in some cases, from a fingerstick. The blood sample is then sent to a laboratory for analysis. The results are usually available within a few days and are reported as a percentage. For people without diabetes, a normal HbA1c level is typically below 5.7%. For those with diabetes, the American Diabetes Association recommends an HbA1c goal of less than 7% for most adults, though this target may vary depending on the individual's health status, duration of diabetes, life expectancy, resources, and support system.Benefits of HbA1c Testing

Interpreting HbA1c Results
Interpreting HbA1c results requires understanding the different categories defined by the HbA1c levels: - **Below 5.7%**: Normal - **5.7% to 6.4%**: Prediabetes - **6.5% or higher**: Diabetes It's also important to consider that various factors can affect HbA1c results, such as red blood cell lifespan, hemoglobin variants, and certain medical conditions. Therefore, HbA1c should be interpreted in the context of clinical presentation and other diagnostic criteria.Factors Affecting HbA1c Levels
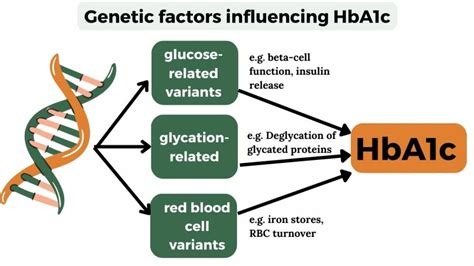
Managing HbA1c Levels
Managing HbA1c levels involves a combination of lifestyle modifications and, when necessary, medication. Key strategies include: - **Healthy Eating**: Focusing on whole, unprocessed foods like vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. - **Regular Physical Activity**: Aiming for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise, or a combination of both, per week. - **Stress Management**: Engaging in stress-reducing activities like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises. - **Adequate Sleep**: Ensuring 7-8 hours of sleep per night to help regulate blood sugar levels. - **Monitoring Blood Glucose**: Regularly checking blood glucose levels to understand how different factors affect them.HbA1c and Cardiovascular Risk
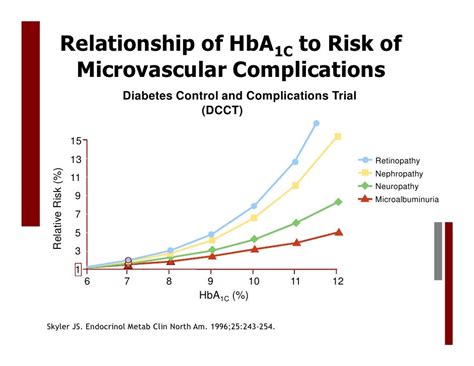
Strategies for Reducing Cardiovascular Risk
Strategies for reducing cardiovascular risk in individuals with diabetes include: - **Blood Pressure Control**: Maintaining blood pressure below 140/90 mmHg. - **Cholesterol Management**: Keeping LDL (bad) cholesterol below 100 mg/dL. - **Smoking Cessation**: Quitting smoking to reduce the risk of heart disease and stroke. - **Regular Check-ups**: Scheduling regular health check-ups to monitor cardiovascular risk factors.HbA1c in Special Populations
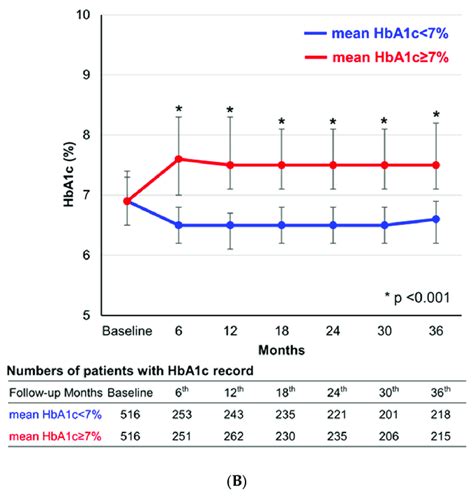
HbA1c in Pregnancy
For pregnant women with diabetes, achieving target HbA1c levels is vital to ensure the best possible outcomes for both mother and baby. This involves close monitoring of blood glucose levels and adjustments to the treatment plan as needed. The goal is to maintain blood glucose levels as close to normal as possible without causing significant hypoglycemia.Future Directions in HbA1c Testing
Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies, including wearable glucose monitors and continuous glucose monitoring systems, offer real-time glucose data, providing a more detailed picture of glucose fluctuations and trends. These technologies have the potential to revolutionize diabetes management, enabling individuals to make more informed decisions about their health and treatment.Conclusion and Recommendations
As we move forward, it's essential to continue advancing our understanding of HbA1c and its role in diabetes management. This includes exploring new technologies and strategies for improving HbA1c testing and interpretation, as well as enhancing patient education and support. By doing so, we can improve outcomes for individuals with diabetes and work towards a future where diabetes is better managed and its complications are minimized.
What is HbA1c, and why is it important for diabetes management?
+HbA1c, or glycated hemoglobin, is a blood test that measures the average level of glucose in the blood over the past 2 to 3 months. It's crucial for diagnosing diabetes, prediabetes, and monitoring the effectiveness of diabetes treatment plans, helping individuals and healthcare providers make informed decisions about diet, exercise, and medication.
How often should I get an HbA1c test if I have diabetes?
+The frequency of HbA1c testing for individuals with diabetes depends on several factors, including the type of diabetes, the effectiveness of the current treatment plan, and the presence of any complications. Generally, HbA1c tests are recommended at least twice a year for individuals with stable diabetes and more frequently for those with unstable or newly diagnosed diabetes.
What factors can affect HbA1c results, and how should I interpret my results?
+Several factors can influence HbA1c results, including diet, physical activity, certain medications, and medical conditions. Interpreting HbA1c results requires understanding these factors and considering them in the context of overall health and diabetes management. It's essential to discuss your results with your healthcare provider to understand what they mean for your specific situation and to determine the best course of action.
How can I lower my HbA1c levels if they are too high?
+Lowering HbA1c levels involves a combination of lifestyle modifications and, when necessary, adjustments to medication. Key strategies include adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, managing stress, ensuring adequate sleep, and monitoring blood glucose levels. Working closely with your healthcare provider to develop a personalized plan is crucial for achieving and maintaining target HbA1c levels.
What is the relationship between HbA1c levels and cardiovascular risk, and how can I reduce my risk?
+Elevated HbA1c levels are associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. To reduce cardiovascular risk, it's essential to manage HbA1c levels effectively, maintain healthy blood pressure and cholesterol levels, quit smoking, and engage in regular physical activity. Close collaboration with your healthcare provider is necessary to develop a comprehensive plan for reducing cardiovascular risk and managing diabetes.
In wrapping up this comprehensive overview of HbA1c, it's clear that understanding and managing HbA1c levels is pivotal for effective diabetes care and reducing the risk of long-term complications. By staying informed, adopting healthy lifestyle habits, and working closely with healthcare providers, individuals can take a proactive approach to their health, navigating the complexities of diabetes management with confidence. We invite you to share your thoughts, experiences, and questions about HbA1c and diabetes management in the comments below, contributing to a community dedicated to supporting and empowering individuals with diabetes.
