Intro
Discover the comprehensive GMO foods list, including genetically modified crops, ingredients, and products, to make informed choices about genetically engineered foods, genetically modified organisms, and biotech crops.
The topic of genetically modified organisms (GMOs) has been a subject of intense debate in recent years. With the increasing demand for food production to meet the needs of a growing global population, GMOs have been touted as a potential solution to improve crop yields and enhance food security. However, concerns about the safety and environmental impact of GMOs have led to a growing interest in understanding what GMOs are, how they are used in food production, and which foods are likely to contain GMOs.
The use of GMOs in food production has been a common practice in many countries, including the United States, Brazil, and Argentina. GMOs are created by introducing genes from one species into the DNA of another species, resulting in a new organism with desirable traits such as pest resistance, drought tolerance, or improved nutritional content. While some argue that GMOs are safe for human consumption and can help address global food security challenges, others raise concerns about the potential health and environmental risks associated with GMOs.
As consumers become more aware of the presence of GMOs in their food, there is a growing demand for information about which foods are likely to contain GMOs. With the lack of clear labeling requirements in many countries, it can be challenging for consumers to make informed choices about the food they eat. In this article, we will delve into the world of GMOs, explore the benefits and risks associated with GMOs, and provide a comprehensive list of common GMO foods.
What are GMOs?

How are GMOs created?
The process of creating a GMO involves several steps, including: * Identifying the desired trait: Scientists identify the trait they want to introduce into the organism, such as pest resistance or drought tolerance. * Isolating the gene: The gene responsible for the desired trait is isolated from the donor organism. * Cloning the gene: The isolated gene is cloned, or copied, using a process called polymerase chain reaction (PCR). * Transforming the host organism: The cloned gene is introduced into the host organism using a variety of techniques, such as electroporation or microinjection. * Selecting and breeding: The transformed host organism is selected and bred to produce offspring that express the desired trait.Benefits of GMOs
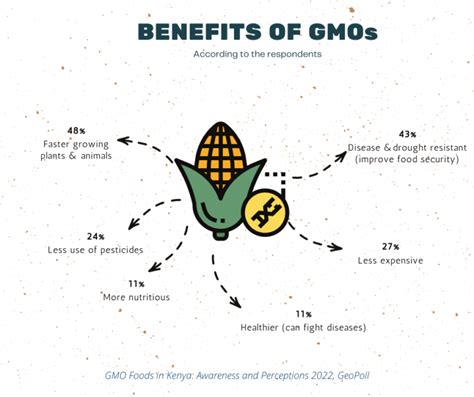
Risks associated with GMOs
While GMOs have several benefits, there are also risks associated with their use, including: * Unknown long-term health effects: The long-term health effects of consuming GMOs are not fully understood and require further research. * Environmental impact: The release of GMOs into the environment can have unintended consequences, such as the development of pesticide-resistant pests. * Contamination of non-GMO crops: GMOs can contaminate non-GMO crops through cross-pollination, potentially altering the genetic makeup of non-GMO crops.GMO Foods List

Avoiding GMOs
If you're concerned about consuming GMOs, there are several steps you can take to avoid them: * Choose organic: Organic foods are less likely to contain GMOs. * Check the label: Look for labels that indicate the product is GMO-free. * Buy from local farmers: Local farmers may be less likely to use GMOs in their crops. * Grow your own: Growing your own fruits and vegetables can ensure that they are GMO-free.GMO Labeling

International GMO Regulations
GMO regulations vary widely around the world, with some countries having strict regulations and others having more lenient regulations. In the European Union, GMOs are subject to strict regulations, including labeling requirements. In other countries, such as Brazil and Argentina, GMOs are widely used in food production and are subject to fewer regulations.Future of GMOs

Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, GMOs are a complex and multifaceted issue, with both benefits and risks associated with their use. As consumers, it's essential to stay informed about the presence of GMOs in our food and to make informed choices about the products we buy. By choosing organic, checking labels, and supporting local farmers, we can reduce our exposure to GMOs and promote more sustainable and environmentally-friendly food production practices.What are GMOs and how are they used in food production?
+GMOs, or genetically modified organisms, are living organisms whose genetic material has been altered using genetic engineering techniques. They are used in food production to improve crop yields, enhance nutritional content, and reduce pesticide use.
Are GMOs safe for human consumption?
+The safety of GMOs for human consumption is a topic of ongoing debate. While some studies suggest that GMOs are safe, others raise concerns about potential health risks. More research is needed to fully understand the long-term health effects of consuming GMOs.
How can I avoid consuming GMOs?
+To avoid consuming GMOs, choose organic products, check labels for GMO-free certifications, buy from local farmers, and grow your own fruits and vegetables. You can also support companies that use non-GMO ingredients and advocate for stricter GMO labeling regulations.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of GMOs and their use in food production. We invite you to share your thoughts and questions about GMOs in the comments below. Join the conversation and let's work together to create a more informed and sustainable food system.
