Intro
Learn optimal good blood glucose levels, normal blood sugar range, and healthy glucose monitoring techniques to manage diabetes and prediabetes, ensuring stable blood glucose control.
Maintaining a good blood glucose level is crucial for overall health and well-being. Blood glucose, also known as blood sugar, is the amount of glucose present in the blood. Glucose is a type of sugar that serves as the primary source of energy for the body's cells. When blood glucose levels are within a healthy range, the body functions properly, and the risk of developing chronic diseases is reduced. On the other hand, high or low blood glucose levels can lead to various health problems, including diabetes, heart disease, and stroke.
The importance of maintaining good blood glucose levels cannot be overstated. When blood glucose levels are elevated, the body's cells become less responsive to insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas that regulates blood sugar levels. This can lead to insulin resistance, a precursor to type 2 diabetes. Furthermore, high blood glucose levels can damage blood vessels, nerves, and organs, such as the kidneys and eyes. In contrast, low blood glucose levels can cause symptoms such as shakiness, dizziness, and confusion, and if left untreated, can lead to seizures, coma, or even death.
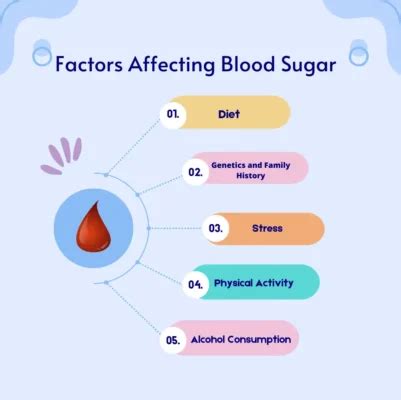
Understanding the factors that influence blood glucose levels is essential for maintaining good health. Diet, physical activity, stress, and sleep are all critical factors that can impact blood glucose levels. A healthy diet that is rich in whole foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, can help regulate blood sugar levels. Regular physical activity, such as walking, running, or swimming, can also improve insulin sensitivity and reduce blood glucose levels. Additionally, managing stress through techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing can help mitigate the negative effects of stress on blood glucose levels.
What is a Good Blood Glucose Level?

A good blood glucose level varies depending on the time of day, diet, and physical activity. For individuals without diabetes, a normal blood glucose level is typically between 70 and 99 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) when fasting, and less than 140 mg/dL two hours after eating. For individuals with diabetes, the American Diabetes Association recommends the following blood glucose targets: 80-130 mg/dL before meals, and less than 180 mg/dL one to two hours after meals.
Factors that Influence Blood Glucose Levels
Several factors can influence blood glucose levels, including:
- Diet: Consuming high amounts of sugar, refined carbohydrates, and saturated fats can raise blood glucose levels.
- Physical activity: Regular physical activity can improve insulin sensitivity and reduce blood glucose levels.
- Stress: Chronic stress can raise blood glucose levels by stimulating the release of stress hormones, such as cortisol and adrenaline.
- Sleep: Poor sleep quality and duration can disrupt blood glucose regulation and increase the risk of developing insulin resistance.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as steroids and certain psychiatric medications, can raise blood glucose levels.
Benefits of Maintaining Good Blood Glucose Levels
Maintaining good blood glucose levels offers numerous benefits, including:
- Reduced risk of chronic diseases: High blood glucose levels are a major risk factor for developing chronic diseases, such as heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease.
- Improved energy levels: When blood glucose levels are within a healthy range, the body's cells can function properly, leading to improved energy levels and reduced fatigue.
- Enhanced cognitive function: Good blood glucose levels are essential for proper brain function, and research suggests that high blood glucose levels may contribute to cognitive decline and dementia.
- Better weight management: Maintaining good blood glucose levels can help regulate appetite and metabolism, making it easier to achieve and maintain a healthy weight.
Strategies for Maintaining Good Blood Glucose Levels
Several strategies can help maintain good blood glucose levels, including:
- Eating a healthy diet: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Engaging in regular physical activity: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise, or a combination of both, per week.
- Practicing stress-reducing techniques: Try techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing to manage stress and mitigate its negative effects on blood glucose levels.
- Getting enough sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night to help regulate blood glucose levels and improve overall health.
Monitoring Blood Glucose Levels
Monitoring blood glucose levels is essential for individuals with diabetes and those at risk of developing the condition. There are several ways to monitor blood glucose levels, including:
- Fasting plasma glucose test: This test measures blood glucose levels after an overnight fast.
- Oral glucose tolerance test: This test measures blood glucose levels after consuming a sugary drink.
- Continuous glucose monitoring: This involves wearing a small device that tracks blood glucose levels throughout the day.
- Self-monitoring of blood glucose: This involves using a glucose meter to track blood glucose levels at home.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When monitoring blood glucose levels, there are several common mistakes to avoid, including:
- Not testing blood glucose levels regularly: Regular testing is essential for understanding how different factors, such as diet and physical activity, affect blood glucose levels.
- Not using a glucose meter correctly: Make sure to follow the manufacturer's instructions for using a glucose meter, and calibrate the device regularly.
- Not keeping track of test results: Keep a log of test results to track progress and identify patterns.
Tips for Improving Blood Glucose Control
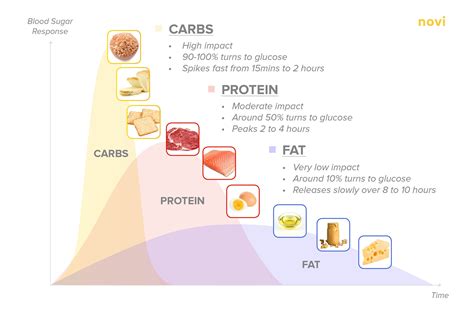
Several tips can help improve blood glucose control, including:
- Eating regular meals: Eating regular meals can help regulate blood glucose levels and prevent spikes in blood sugar.
- Choosing low-glycemic index foods: Foods with a low glycemic index, such as whole grains and non-starchy vegetables, can help regulate blood glucose levels.
- Incorporating physical activity into daily routine: Regular physical activity can improve insulin sensitivity and reduce blood glucose levels.
- Getting enough sleep: Poor sleep quality and duration can disrupt blood glucose regulation and increase the risk of developing insulin resistance.
Common Foods that Help Regulate Blood Glucose Levels
Several foods can help regulate blood glucose levels, including:
- Leafy green vegetables: Leafy green vegetables, such as spinach and kale, are rich in fiber and antioxidants, which can help regulate blood glucose levels.
- Fatty fish: Fatty fish, such as salmon and tuna, are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which can help reduce inflammation and improve insulin sensitivity.
- Sweet potatoes: Sweet potatoes are rich in fiber and antioxidants, which can help regulate blood glucose levels.
- Legumes: Legumes, such as lentils and chickpeas, are rich in fiber and protein, which can help regulate blood glucose levels.
Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, maintaining good blood glucose levels is essential for overall health and well-being. By understanding the factors that influence blood glucose levels, incorporating healthy lifestyle habits, and monitoring blood glucose levels regularly, individuals can reduce their risk of developing chronic diseases and improve their overall quality of life. If you are concerned about your blood glucose levels or would like to learn more about maintaining good blood glucose control, consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized guidance and support.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with maintaining good blood glucose levels in the comments below. What strategies have you found most effective for regulating your blood glucose levels? What challenges have you faced, and how have you overcome them? By sharing your story, you can help others who may be struggling with similar issues.
What is the normal range for blood glucose levels?
+For individuals without diabetes, a normal blood glucose level is typically between 70 and 99 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) when fasting, and less than 140 mg/dL two hours after eating.
How often should I monitor my blood glucose levels?
+The frequency of monitoring blood glucose levels depends on individual factors, such as diet, physical activity, and medication use. Consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best monitoring schedule for your needs.
What are the symptoms of high blood glucose levels?
+Symptoms of high blood glucose levels may include increased thirst and urination, blurred vision, fatigue, and slow healing of cuts and wounds.
Can I reverse insulin resistance and improve my blood glucose control?
+Yes, it is possible to reverse insulin resistance and improve blood glucose control through lifestyle changes, such as eating a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and managing stress.
What are the long-term complications of uncontrolled blood glucose levels?
+Uncontrolled blood glucose levels can lead to serious long-term complications, including heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and nerve damage.
