Intro
Discover great plant-based protein options, including legumes, nuts, and seeds, for a healthy diet with high protein content, vegan alternatives, and meat substitutes.
The importance of protein in our diets cannot be overstated. It is a crucial component for building and repairing tissues, including muscles, bones, and skin. While animal-based protein sources have traditionally been the most popular, there is a growing trend towards plant-based protein options. This shift is driven by increasing awareness of the health benefits, environmental sustainability, and animal welfare concerns associated with plant-based diets. For individuals looking to adopt a more plant-based lifestyle, it is essential to understand the various great plant-based protein options available.
Plant-based protein sources offer a wide range of benefits, from reducing the risk of heart disease and type 2 diabetes to supporting weight management and improving overall health. Moreover, plant-based diets tend to be rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals, making them a nutritious choice for those seeking a balanced diet. With the vast array of plant-based protein options now available, it has never been easier to incorporate these foods into your daily meals. From legumes and beans to nuts and seeds, the choices are diverse and delicious.
The growing demand for plant-based protein has also led to significant innovation in the food industry, with many companies developing new and exciting products. These range from plant-based meat alternatives to protein-fortified dairy substitutes, offering consumers a plethora of options to suit their tastes and dietary preferences. Whether you are a long-time vegan, a flexitarian, or simply looking to reduce your meat intake, understanding the different types of plant-based protein sources is key to making informed choices about your diet.
Introduction to Plant-Based Proteins
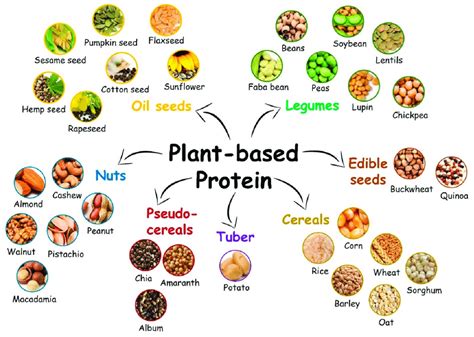
Plant-based proteins are derived from plants and offer a viable alternative to animal-based protein sources. These proteins can be found in a variety of foods, including legumes, beans, lentils, tofu, tempeh, seitan, nuts, seeds, whole grains, and soy products. Each of these sources provides a unique set of nutrients and can be incorporated into meals in various ways, from salads and stir-fries to soups and casseroles.
Types of Plant-Based Proteins
The diversity of plant-based proteins is one of their most significant advantages. Legumes, for example, are some of the richest sources of protein and include foods like chickpeas, black beans, kidney beans, and lentils. Nuts and seeds are another excellent source, with almonds, chia seeds, hemp seeds, and pumpkin seeds being particularly high in protein. Whole grains like quinoa, brown rice, and whole wheat also contain significant amounts of protein, making them a great addition to plant-based meals.Benefits of Plant-Based Proteins

The benefits of plant-based proteins are numerous and well-documented. One of the most significant advantages is their potential to reduce the risk of chronic diseases, such as heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain types of cancer. Plant-based proteins tend to be lower in saturated fats and higher in fiber, vitamins, and minerals compared to animal-based proteins, contributing to these health benefits. Additionally, plant-based diets are often associated with weight management and can help individuals maintain a healthy weight.
Nutritional Value of Plant-Based Proteins
Understanding the nutritional value of different plant-based proteins is essential for ensuring you are getting all the necessary nutrients. For instance, legumes are not only high in protein but also rich in fiber, folate, and minerals like potassium and iron. Nuts and seeds are good sources of healthy fats, antioxidants, and vitamins, particularly vitamin E and magnesium. Whole grains provide fiber, B vitamins, and minerals like selenium and manganese. By combining a variety of these foods, individuals can achieve a balanced and nutritious diet.Great Plant-Based Protein Sources

Some of the great plant-based protein sources include:
- Legumes: Chickpeas, black beans, kidney beans, lentils
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, chia seeds, hemp seeds, pumpkin seeds
- Whole Grains: Quinoa, brown rice, whole wheat
- Soy Products: Tofu, tempeh, seitan
- Meat Alternatives: Plant-based burgers, sausages, and chicken strips
- Dairy Substitutes: Soy milk, almond milk, oat milk, and vegan yogurt
Incorporating Plant-Based Proteins into Your Diet
Incorporating plant-based proteins into your diet can be simple and delicious. Start by adding legumes to your salads, using nuts and seeds as snacks, and substituting whole grains for refined grains in your meals. Explore different types of soy products and plant-based meat alternatives to find ones you enjoy. You can also experiment with various dairy substitutes in your recipes and breakfast routines.Practical Tips for a Plant-Based Diet

For those transitioning to a plant-based diet, here are some practical tips:
- Start slow: Begin by substituting one or two meals a day with plant-based options.
- Explore recipes: Look for plant-based recipes online or in cookbooks to find dishes you enjoy.
- Stock your pantry: Make sure you have a variety of plant-based protein sources and whole grains in your pantry.
- Consult a professional: If possible, consult with a dietitian or nutritionist to ensure you are getting all the necessary nutrients.
Common Challenges and Solutions
One common challenge faced by individuals adopting a plant-based diet is ensuring they get enough protein. This can be solved by consuming a variety of plant-based protein sources throughout the day. Another challenge is the potential for higher costs associated with some plant-based products. Shopping for whole foods, buying in bulk, and preparing meals at home can help mitigate these costs.Conclusion and Future Directions

As the world moves towards more sustainable and healthy eating habits, the demand for plant-based proteins is expected to grow. With ongoing innovation in the food industry, we can expect to see even more diverse and accessible plant-based protein options in the future. Whether for health, environmental, or ethical reasons, adopting a plant-based diet can be a rewarding choice, offering numerous benefits for individuals and the planet.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, great plant-based protein options are plentiful and offer a nutritious alternative to traditional animal-based proteins. By understanding the benefits, types, and ways to incorporate these proteins into your diet, you can make informed decisions about your health and well-being. As we look to the future, it's exciting to consider the potential of plant-based proteins to transform not just our diets, but our relationship with the environment and the food industry as a whole.What are some high protein plant-based foods?
+High protein plant-based foods include legumes like lentils and chickpeas, nuts and seeds such as almonds and chia seeds, whole grains like quinoa, and soy products like tofu and tempeh.
How can I ensure I get enough protein on a plant-based diet?
+To ensure you get enough protein on a plant-based diet, consume a variety of plant-based protein sources throughout the day, and consider consulting with a dietitian or nutritionist for personalized advice.
Are plant-based proteins more expensive than animal-based proteins?
+While some plant-based protein products can be more expensive, many whole plant-based foods like beans, lentils, and whole grains are affordable and can be bought in bulk, making them a cost-effective option.
We invite you to share your experiences and thoughts on plant-based proteins in the comments below. Whether you're a seasoned vegan or just starting to explore plant-based options, your insights can help others on their journey towards a healthier and more sustainable diet. Share this article with friends and family who might be interested in learning more about the benefits and diversity of plant-based proteins. Together, we can support a healthier, more environmentally conscious food culture.
