Intro
Discover the common causes of groin muscle pain, including strains, pulls, and tears, and learn about related conditions like tendinitis, hernias, and sports injuries that can lead to discomfort and limited mobility.
The groin area is a sensitive and complex region of the body, and experiencing pain in this area can be uncomfortable and debilitating. Groin muscle pain can affect anyone, regardless of age or activity level, and it's essential to understand the causes and symptoms to seek proper treatment. Groin pain can be acute or chronic, and it's often a sign of an underlying condition that needs attention. In this article, we'll delve into the common causes of groin muscle pain, its symptoms, and the various treatment options available.
Groin muscle pain can be caused by a variety of factors, including injuries, overuse, or underlying medical conditions. The groin area is home to several muscles, tendons, and ligaments that work together to facilitate movement and support the body. When any of these tissues become strained, inflamed, or damaged, it can lead to pain and discomfort. Some common causes of groin muscle pain include strains or tears in the adductor muscles, which are the muscles that bring the legs together. These injuries are common in athletes who participate in sports that involve kicking, twisting, or rapid changes of direction.
The symptoms of groin muscle pain can vary depending on the underlying cause, but common symptoms include a sharp or dull ache in the groin area, swelling or bruising, limited mobility or stiffness, and pain when lifting the knee or bringing the legs together. In some cases, groin muscle pain can be accompanied by other symptoms, such as numbness or tingling in the leg, fever, or redness and warmth in the affected area. It's essential to seek medical attention if the pain is severe, persistent, or accompanied by other concerning symptoms.
Groin Muscle Pain Causes and Symptoms

Groin Muscle Pain Causes
Some common causes of groin muscle pain include: * Strains or tears in the adductor muscles * Tendonitis, which is inflammation of the tendons that connect the muscles to the bones * Bursitis, which is inflammation of the fluid-filled sacs that cushion the joints * Hernias, which occur when a weakness in the abdominal wall allows tissue to bulge through * Osteitis pubis, which is inflammation of the pubic bone and surrounding tissues * Sports-related injuries, such as soccer, football, or hockeyGroin Muscle Pain Treatment Options

Groin Muscle Pain Treatment
Some common treatment options for groin muscle pain include: * Rest, ice, and compression to alleviate symptoms * Physical therapy to improve flexibility, strength, and range of motion * Medication, such as pain relievers or anti-inflammatory medications, to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation * Surgery, in some cases, to repair damaged tissues or relieve pressure on the affected areaGroin Muscle Pain Prevention

Groin Muscle Pain Prevention Tips
Some common prevention tips for groin muscle pain include: * Warming up properly before exercise * Stretching regularly to improve flexibility * Using proper techniques when kicking or twisting * Wearing proper equipment, such as supportive clothing or protective gear * Strengthening the core and leg muscles to improve stability and supportGroin Muscle Pain Complications
Groin Muscle Pain Complications and Risks
Some common complications and risks associated with groin muscle pain include: * Chronic pain or limited mobility * Further injury or strain to the affected area * Underlying conditions, such as hernias or osteitis pubis, which require prompt medical attention * Infection or abscess formation, in rare casesGroin Muscle Pain Diagnosis
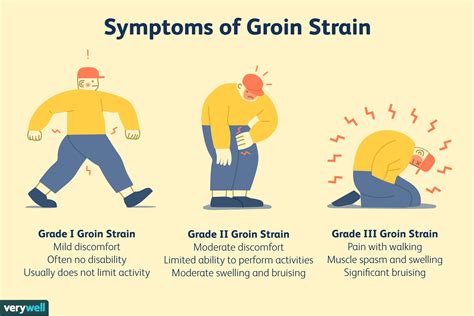
Groin Muscle Pain Diagnosis and Testing
Some common diagnostic tests and procedures for groin muscle pain include: * Physical examination to assess range of motion, strength, and tenderness * Medical history to identify underlying conditions or previous injuries * Diagnostic tests, such as X-rays or MRI, to rule out underlying conditions or further injury * Electromyography (EMG) to assess muscle function and activityGroin Muscle Pain Management

Groin Muscle Pain Management and Care
Some common management and care strategies for groin muscle pain include: * Self-care, such as rest, ice, and compression, to alleviate symptoms * Physical therapy to improve flexibility, strength, and range of motion * Medication, such as pain relievers or anti-inflammatory medications, to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation * Surgery, in some cases, to repair damaged tissues or relieve pressure on the affected areaGroin Muscle Pain Recovery

Groin Muscle Pain Recovery and Rehabilitation
Some common recovery and rehabilitation strategies for groin muscle pain include: * Rest and relaxation to allow the affected area to heal * Physical therapy to improve flexibility, strength, and range of motion * Gradual return to activity, such as exercise or sports, to avoid further injury * Ongoing medical care and monitoring to ensure proper healing and prevent complicationsWhat are the common causes of groin muscle pain?
+Groin muscle pain can be caused by a variety of factors, including injuries, overuse, or underlying medical conditions. Some common causes of groin muscle pain include strains or tears in the adductor muscles, tendonitis, bursitis, hernias, and osteitis pubis.
How is groin muscle pain diagnosed?
+Diagnosing groin muscle pain requires a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests. A healthcare professional will typically perform a physical examination to assess the affected area, including range of motion, strength, and tenderness. Additionally, diagnostic tests, such as X-rays or MRI, may be ordered to rule out underlying conditions or further injury.
What are the treatment options for groin muscle pain?
+The treatment options for groin muscle pain depend on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. In some cases, rest, ice, and compression may be sufficient to alleviate symptoms, while in other cases, physical therapy, medication, or surgery may be necessary.
In conclusion, groin muscle pain is a common condition that can affect anyone, regardless of age or activity level. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for groin muscle pain is essential to seeking proper treatment and preventing further injury. By working with a healthcare professional and following a personalized treatment plan, individuals can alleviate symptoms, improve mobility, and reduce the risk of complications. We encourage readers to share their experiences and ask questions in the comments section below, and to consult with a healthcare professional if they are experiencing persistent or severe groin muscle pain.
