Intro
Learn how hand disease spreads through 5 common ways, including poor hygiene, skin contact, and contaminated surfaces, to prevent hand infections and promote hand health.
The importance of hand health cannot be overstated, as our hands are one of the most vital parts of our body, enabling us to interact with the world around us. However, hand diseases can significantly impact our quality of life, causing pain, discomfort, and even disability. One of the primary concerns with hand diseases is their potential to spread, either to other parts of the body or to other individuals. Understanding how hand diseases spread is crucial for prevention and management. In this article, we will delve into the various ways hand diseases can spread, exploring the mechanisms, risks, and preventive measures.
Hand diseases can arise from a variety of sources, including infections, autoimmune disorders, and injuries. The spread of these diseases can occur through direct contact, contaminated objects, or even through the air in some cases. The complexity of hand anatomy, with its intricate network of bones, muscles, and nerves, makes it a challenging area to treat when diseases take hold. Moreover, the hands are constantly exposed to the environment, increasing the risk of infection and disease transmission.
The impact of hand diseases extends beyond the individual, affecting not only personal well-being but also socioeconomic aspects, as it can lead to absenteeism from work and a decrease in productivity. Therefore, it is essential to educate oneself on the ways hand diseases spread and the measures that can be taken to prevent such occurrences. By understanding these factors, individuals can better protect themselves and those around them from the potential harm caused by hand diseases.
Direct Contact Transmission

Prevention Measures for Direct Contact
To prevent the spread of hand diseases through direct contact, several measures can be taken: - Regular handwashing with soap and water, especially after using public transport, before eating, and after using the bathroom. - Using hand sanitizers when soap and water are not available. - Avoiding touching one's face, especially the mouth, nose, and eyes, as these are common entry points for pathogens. - Wearing gloves in certain situations, such as when caring for someone who is sick or when engaging in activities that involve handling potentially contaminated materials.Indirect Contact Transmission

Prevention Measures for Indirect Contact
Preventing the spread of hand diseases through indirect contact requires attention to environmental hygiene: - Regularly cleaning and disinfecting surfaces, especially in high-touch areas. - Using disposable utensils and dishes when possible. - Avoiding sharing personal items, such as towels or makeup. - Ensuring that public places have adequate cleaning schedules and hygiene facilities.Airborne Transmission
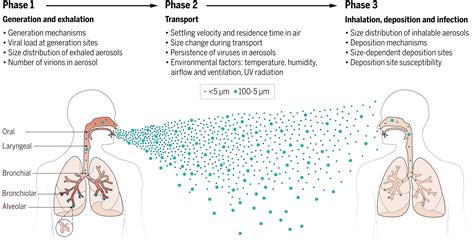
Prevention Measures for Airborne Transmission
To reduce the risk of airborne transmission: - Wearing masks in crowded areas or when around individuals who are sick. - Ensuring good ventilation in homes, workplaces, and public areas. - Avoiding close contact with individuals who are coughing or sneezing. - Staying home when feeling unwell to prevent spreading the disease to others.Vector-Borne Transmission
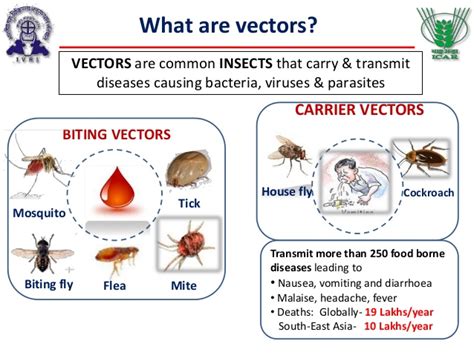
Prevention Measures for Vector-Borne Transmission
Preventing vector-borne transmission includes: - Using insect repellents when outdoors. - Wearing protective clothing, such as long sleeves and pants, in areas known to have disease-carrying insects. - Eliminating standing water around homes to reduce mosquito breeding sites. - Using screens on windows and doors to keep insects out.Fomite Transmission

Prevention Measures for Fomite Transmission
To prevent fomite transmission: - Regularly cleaning and disinfecting frequently touched surfaces and objects. - Avoiding sharing personal items that come into contact with hands. - Encouraging hand hygiene among all individuals in a household or workplace. - Implementing strict infection control practices in healthcare settings.In conclusion, the spread of hand diseases can occur through various routes, including direct contact, indirect contact, airborne transmission, vector-borne transmission, and fomite transmission. Understanding these mechanisms and implementing preventive measures are crucial for protecting oneself and others from the spread of hand diseases. By adopting good hygiene practices, being mindful of one's environment, and taking steps to minimize contact with potential sources of infection, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of contracting and spreading hand diseases.
What are the most common ways hand diseases spread?
+Hand diseases most commonly spread through direct contact with an infected person, indirect contact with contaminated objects or surfaces, and less frequently through airborne transmission or vector-borne transmission.
How can I prevent the spread of hand diseases?
+Prevention measures include regular handwashing, using hand sanitizers, avoiding touching one's face, wearing gloves when appropriate, and ensuring environmental hygiene through cleaning and disinfecting surfaces.
Are all hand diseases contagious?
+No, not all hand diseases are contagious. While some, like viral infections, can be highly contagious, others may result from non-infectious causes such as injuries or autoimmune disorders and do not spread from person to person.
We hope this comprehensive guide has provided valuable insights into the ways hand diseases spread and the critical steps that can be taken to prevent their transmission. By staying informed and adopting preventive practices, we can work together to reduce the incidence of hand diseases and promote better hand health for everyone. If you have any further questions or would like to share your experiences with hand diseases, please do not hesitate to comment below. Your feedback and stories can help others understand the importance of hand health and the measures we can all take to protect it.
