Intro
Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) is a common viral illness that affects people of all ages, but it is most prevalent among children under the age of 10. The disease is characterized by the appearance of sores or blisters on the hands, feet, and mouth, as well as fever, sore throat, and a general feeling of being unwell. HFMD is highly contagious and can spread quickly through close contact with an infected person, contaminated surfaces, or through the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes.
The importance of understanding HFMD cannot be overstated, as it can have significant implications for public health, particularly in settings such as schools, childcare centers, and hospitals. By recognizing the signs and symptoms of HFMD, individuals can take steps to prevent the spread of the disease and seek medical attention if necessary. Furthermore, knowledge of the disease can help to alleviate concerns and anxieties that may arise when a family member or loved one is diagnosed with HFMD.
In recent years, there has been an increase in the number of reported cases of HFMD worldwide, highlighting the need for greater awareness and understanding of the disease. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to HFMD, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. By exploring these topics in depth, readers will gain a better understanding of the disease and be equipped with the knowledge and skills necessary to manage and prevent its spread.
What is Hand Foot Mouth Disease?

Causes of Hand Foot Mouth Disease
The causes of HFMD can be attributed to several factors, including poor hygiene, contaminated food and water, and close contact with an infected person. In addition, certain individuals may be more susceptible to HFMD due to a weakened immune system or underlying medical conditions. For example, children under the age of 10 are more likely to contract HFMD due to their underdeveloped immune system and increased exposure to other children who may be infected.Symptoms of Hand Foot Mouth Disease
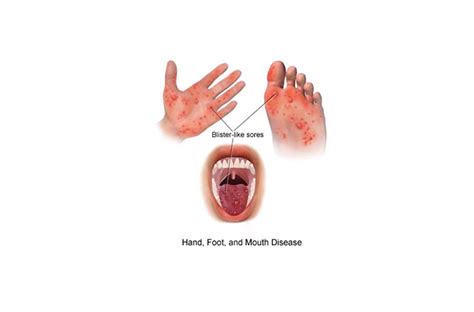
In severe cases, HFMD can lead to more serious complications, such as meningitis, encephalitis, and paralysis. It is essential to seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen over time.
Diagnosis of Hand Foot Mouth Disease
The diagnosis of HFMD is typically based on the presence of characteristic symptoms, such as sores or blisters on the hands, feet, and mouth, as well as fever and sore throat. A healthcare professional may perform a physical examination and take a medical history to rule out other possible causes of the symptoms. In some cases, a laboratory test may be ordered to confirm the diagnosis and identify the specific virus responsible for the infection.Treatment of Hand Foot Mouth Disease

Prevention of Hand Foot Mouth Disease
Prevention is key to reducing the spread of HFMD. Some effective measures include: * Practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands frequently with soap and water * Avoiding close contact with individuals who are infected * Disinfecting surfaces and objects that may be contaminated with the virus * Avoiding sharing food, drinks, or utensils with others * Staying home from work or school if symptoms are presentComplications of Hand Foot Mouth Disease

It is essential to seek medical attention immediately if symptoms worsen or if there are concerns about potential complications.
Long-term Effects of Hand Foot Mouth Disease
The long-term effects of HFMD are generally minimal, and most individuals recover fully within 7-10 days. However, in some cases, HFMD can lead to long-term complications, such as: * Neurological damage: such as cognitive impairment or motor dysfunction * Cardiac damage: such as myocardial scarring or arrhythmias * Immune system suppression: which can increase the risk of future infectionsIt is crucial to follow up with a healthcare professional after recovery to monitor for any potential long-term effects.
Hand Foot Mouth Disease in Adults
Adults who are immunocompromised or have underlying medical conditions are at higher risk of developing severe HFMD.
Hand Foot Mouth Disease in Children
Children under the age of 10 are at higher risk of contracting HFMD due to their underdeveloped immune system and increased exposure to other children who may be infected. Children with HFMD may experience: * Severe symptoms, such as high fever and irritability * Increased risk of complications, such as meningitis or encephalitis * Longer recovery time, typically 7-10 daysIt is essential for parents and caregivers to be aware of the signs and symptoms of HFMD and to seek medical attention if they suspect their child has contracted the disease.
Hand Foot Mouth Disease Outbreaks

Outbreaks can be prevented by implementing effective prevention measures, such as:
- Practicing good hygiene
- Disinfecting surfaces and objects
- Avoiding close contact with individuals who are infected
- Staying home from work or school if symptoms are present
Global Hand Foot Mouth Disease Surveillance
Global surveillance of HFMD is essential to monitor the spread of the disease and to identify potential outbreaks. The World Health Organization (WHO) and other global health authorities work together to: * Monitor HFMD cases and outbreaks * Develop and implement prevention and control measures * Provide guidance and support to countries affected by HFMDBy working together, we can reduce the spread of HFMD and prevent potential complications.
What are the symptoms of Hand Foot Mouth Disease?
+The symptoms of HFMD include fever, sore throat, fatigue, loss of appetite, sores or blisters on the hands, feet, and mouth, red rash on the hands and feet, irritability, diarrhea, and vomiting.
How is Hand Foot Mouth Disease spread?
+HFMD is spread through close contact with an infected person, contaminated surfaces, or through the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes. It can also be spread through the fecal-oral route, where the virus is shed in the stool of an infected person and can be ingested by another person through contaminated food, water, or surfaces.
Can adults get Hand Foot Mouth Disease?
+Yes, adults can get HFMD, although it is more common in children. Adults who are immunocompromised or have underlying medical conditions are at higher risk of developing severe HFMD.
How can I prevent Hand Foot Mouth Disease?
+Prevention measures include practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands frequently with soap and water, avoiding close contact with individuals who are infected, disinfecting surfaces and objects, and staying home from work or school if symptoms are present.
What are the complications of Hand Foot Mouth Disease?
+Complications of HFMD can include meningitis, encephalitis, paralysis, respiratory failure, and cardiac complications. It is essential to seek medical attention immediately if symptoms worsen or if there are concerns about potential complications.
In conclusion, Hand Foot Mouth Disease is a common viral illness that can have significant implications for public health. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of HFMD, individuals can take steps to manage and prevent the spread of the disease. We encourage readers to share this article with others to help raise awareness about HFMD and to take proactive measures to prevent its spread. If you have any questions or concerns about HFMD, please do not hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional for guidance and support.
