Intro
Track pregnancy progress with our Hcg Levels Chart, understanding hCG ranges, normal hCG levels, and hCG doubling time to monitor fetal development and detect potential issues like miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy.
Human chorionic gonadotropin, or hCG, is a hormone produced during pregnancy that is made by the developing embryo after conception and later by the placental component syncytiotrophoblast. The level of hCG in a woman's blood and urine increases rapidly during early pregnancy, which is why it is often used as a marker for pregnancy in home pregnancy tests and in clinical settings. Understanding hCG levels can provide valuable insights into the progression and health of a pregnancy.
The importance of monitoring hCG levels lies in their ability to indicate the presence of a pregnancy and, to some extent, the health of the pregnancy. Very low levels of hCG may suggest that a pregnancy is not progressing as expected, while very high levels can be associated with certain complications, such as multiple pregnancies or molar pregnancies. However, it's crucial to interpret hCG levels within the context of individual pregnancy development, as there can be a wide range of normal levels.
Monitoring hCG levels, especially through blood tests, can offer healthcare providers insights into the viability of a pregnancy. In cases of suspected miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, or other complications, tracking the changes in hCG levels over time can be critical. For many women, understanding their hCG levels can provide reassurance about the progression of their pregnancy, though it's essential to remember that hCG levels are just one aspect of prenatal care and should be considered in conjunction with other health indicators.
Understanding hCG Levels

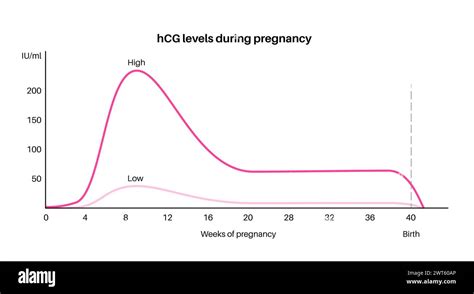
To grasp the significance of hCG levels, it's helpful to know how they typically change throughout pregnancy. Immediately after implantation, hCG levels begin to rise, becoming detectable by a blood test about 11 days after fertilization and in urine about 12-14 days after fertilization. The levels then increase rapidly, often doubling approximately every 48 hours during the first trimester. This rapid increase is a good sign that the pregnancy is progressing normally. However, the rate of increase can vary significantly among women, and what is considered a "normal" range can be quite broad.
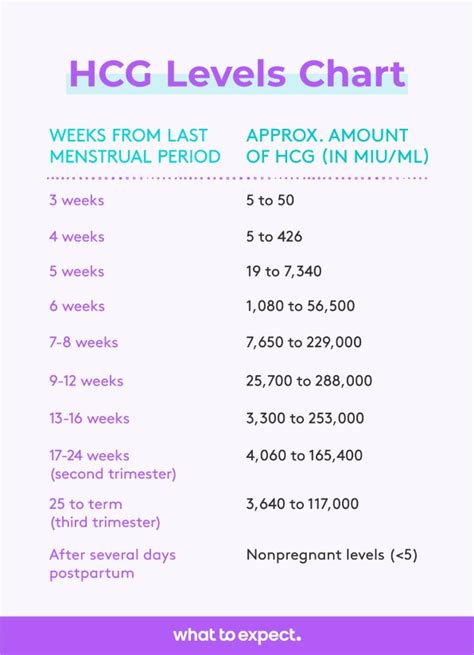
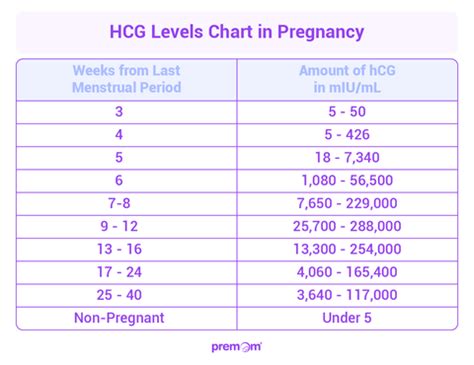
hCG Levels by Week
The following is a general guide to hCG levels during early pregnancy: - **3 weeks**: 5-50 mIU/mL - **4 weeks**: 5-426 mIU/mL - **5 weeks**: 18-7,340 mIU/mL - **6 weeks**: 1,080-56,500 mIU/mL - **7-8 weeks**: 7,650-229,000 mIU/mL - **9-12 weeks**: 25,800-288,000 mIU/mL - **13-16 weeks**: 13,300-254,000 mIU/mL - **17-24 weeks**: 4,060-165,400 mIU/mL - **25-40 weeks**: 3,640-117,000 mIU/mLInterpreting hCG Levels
Interpreting hCG levels requires considering them in the context of the overall clinical picture. For example, if a woman is experiencing symptoms of pregnancy and her hCG levels are within the expected range for her stage of pregnancy, this is generally reassuring. However, if hCG levels are not rising as expected, or if they are rising too slowly, this could indicate a potential issue, such as an ectopic pregnancy or a miscarriage.
High and Low hCG Levels
High hCG levels can be associated with multiple pregnancies (such as twins or triplets) or molar pregnancies. Low hCG levels might suggest a miscarriage or an ectopic pregnancy. However, it's critical to remember that there is a wide range of normal hCG levels, and many factors can influence these levels, including the sensitivity of the test used, the timing of the test, and individual variations in pregnancy development.hCG Levels and Pregnancy Complications
Abnormal hCG levels can sometimes indicate pregnancy complications. For instance, if hCG levels are not increasing appropriately, it may suggest a non-viable pregnancy. On the other hand, very high levels of hCG could indicate a molar pregnancy or a multiple pregnancy, both of which require special medical care.
Pregnancy Loss and hCG
In cases of pregnancy loss, hCG levels will typically decrease. Monitoring these levels can help confirm that the body is clearing the pregnancy tissue and that there are no remaining pregnancy-related complications that could pose a health risk.hCG Levels in Multiple Pregnancies
In multiple pregnancies, such as twins or triplets, hCG levels are often higher than in singleton pregnancies. This is because there are more placentas producing hCG. However, the relationship between hCG levels and the number of fetuses is not perfectly linear, and many other factors can influence hCG production.
hCG and Fetal Development
While hCG levels can provide insights into the health and progression of a pregnancy, they do not directly correlate with fetal development or the baby's size. Fetal development is monitored through ultrasound and other prenatal tests.Monitoring hCG Levels

Monitoring hCG levels typically involves blood tests, which can detect hCG earlier and with more sensitivity than urine tests. The frequency of monitoring depends on the individual case and the reason for testing. In many cases, once pregnancy is confirmed and deemed viable through ultrasound, hCG levels may not need to be monitored as closely unless there are concerns about the pregnancy.
hCG Levels and Ultrasound
Ultrasound is another critical tool in monitoring pregnancy, especially in conjunction with hCG levels. An ultrasound can provide direct visualization of the embryo or fetus and confirm the presence of a heartbeat, which is a strong indicator of a viable pregnancy.FAQs About hCG Levels

What do high hCG levels indicate?
+High hCG levels can indicate a multiple pregnancy or a molar pregnancy. However, high levels can also be seen in normal pregnancies, so it's essential to interpret these levels in the context of other prenatal tests and symptoms.
What are the signs of low hCG levels?
+Low hCG levels might be associated with symptoms such as light bleeding, cramping, or a lack of typical pregnancy symptoms. However, the only definitive way to determine hCG levels is through a blood test.
How often should hCG levels be monitored during pregnancy?
+The frequency of monitoring hCG levels depends on the individual case. In most pregnancies, once viability is confirmed through ultrasound, hCG levels do not need to be monitored closely unless there are concerns about the pregnancy.
In conclusion, understanding hCG levels can provide valuable insights into the health and progression of a pregnancy. While hCG levels are an important tool in prenatal care, they should be interpreted in conjunction with other health indicators and prenatal tests. For women and their healthcare providers, staying informed about hCG levels can help ensure the best possible outcomes for pregnancy. If you have concerns about your hCG levels or any aspect of your pregnancy, it's essential to discuss these with your healthcare provider, who can offer personalized guidance and care. We invite you to share your thoughts or questions about hCG levels and pregnancy in the comments below, and to share this article with others who may find it informative and helpful.
