Intro
Discover 5 health plans in California, offering medical coverage, wellness programs, and preventive care, with options for individuals, families, and groups, including HMO, PPO, and EPO plans, to suit various needs and budgets.
The world of health insurance can be overwhelming, with numerous options available to consumers. Among these options, five health plans stand out for their comprehensive coverage, flexibility, and affordability. Understanding the nuances of each plan is crucial for individuals and families seeking to make informed decisions about their healthcare. In this article, we will delve into the details of these plans, exploring their benefits, drawbacks, and what sets them apart from one another.
As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, it's essential for consumers to stay informed about the latest developments and options. The five health plans we will discuss have been designed to cater to a wide range of needs, from basic coverage to more comprehensive packages. Whether you're an individual, a family, or an employer looking to provide health benefits to your employees, there's a plan out there that can meet your requirements.
The importance of health insurance cannot be overstated. It provides financial protection against unexpected medical expenses, ensuring that individuals and families can access necessary care without breaking the bank. Moreover, health insurance promotes preventive care, encouraging policyholders to seek regular check-ups and screenings that can help detect health issues early on. With the right health plan, individuals can enjoy peace of mind, knowing that they're prepared for whatever life throws their way.
Introduction to 5 Health Plans

When it comes to choosing a health plan, there are several factors to consider. These include the plan's network of providers, coverage options, deductibles, copays, and coinsurance. It's also essential to think about the plan's premium costs, as well as any out-of-pocket expenses that may apply. In the following sections, we will explore each of these factors in more detail, providing a comprehensive overview of the five health plans.
Key Considerations for Health Plans
Some of the key considerations for health plans include the plan's provider network, which refers to the list of healthcare providers who have agreed to participate in the plan's network. This can include primary care physicians, specialists, hospitals, and other healthcare facilities. It's essential to ensure that your preferred providers are part of the plan's network, as seeing out-of-network providers can result in higher costs.
Another critical factor is the plan's coverage options, which can include medical, dental, and vision coverage. Some plans may also offer additional benefits, such as mental health services, prescription drug coverage, and wellness programs. When evaluating coverage options, it's essential to think about your individual needs and those of your family members.
Health Plan 1: HMO

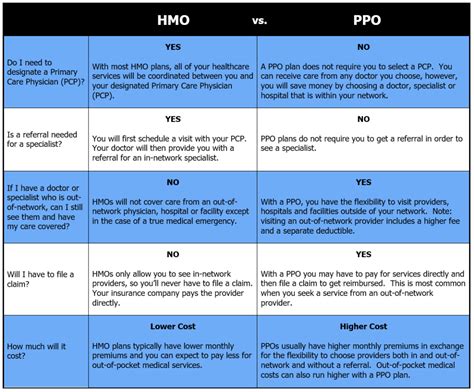
The first health plan we will discuss is the Health Maintenance Organization (HMO) plan. HMOs are a type of managed care plan that requires policyholders to receive medical care from a specific network of providers. In exchange for this restriction, HMOs often offer lower premiums and out-of-pocket costs. HMOs are a popular choice for individuals and families who value affordability and are willing to work within a specific network of providers.
One of the benefits of HMOs is their emphasis on preventive care. HMOs often provide incentives for policyholders to seek regular check-ups and screenings, which can help detect health issues early on. Additionally, HMOs typically have a lower administrative burden, as policyholders do not need to file claims or worry about out-of-network providers.
Benefits and Drawbacks of HMOs

Some of the benefits of HMOs include:
- Lower premiums and out-of-pocket costs
- Emphasis on preventive care
- Lower administrative burden
- Access to a network of providers
However, HMOs also have some drawbacks, including:
- Limited provider network
- Requirement to choose a primary care physician
- Referrals may be required to see specialists
- Out-of-network care is often not covered
Health Plan 2: PPO
The second health plan we will discuss is the Preferred Provider Organization (PPO) plan. PPOs are a type of managed care plan that offers a balance between flexibility and cost savings. With a PPO, policyholders can see any healthcare provider they choose, both in-network and out-of-network. However, seeing in-network providers typically results in lower costs and higher reimbursement rates.
One of the benefits of PPOs is their flexibility. PPOs do not require policyholders to choose a primary care physician or obtain referrals to see specialists. Additionally, PPOs often have a larger network of providers than HMOs, which can be beneficial for individuals and families who value choice.
Benefits and Drawbacks of PPOs
Some of the benefits of PPOs include:
- Flexibility to see any healthcare provider
- Larger network of providers
- No requirement to choose a primary care physician
- No referrals required to see specialists
However, PPOs also have some drawbacks, including:
- Higher premiums and out-of-pocket costs
- Higher administrative burden
- Out-of-network care may result in higher costs
- Balance billing may apply
Health Plan 3: EPO

The third health plan we will discuss is the Exclusive Provider Organization (EPO) plan. EPOs are a type of managed care plan that combines elements of HMOs and PPOs. With an EPO, policyholders can see any healthcare provider within the plan's network, but out-of-network care is not covered except in emergency situations.
One of the benefits of EPOs is their balance between flexibility and cost savings. EPOs often have lower premiums than PPOs, but still offer a range of provider options. Additionally, EPOs typically have a lower administrative burden than PPOs, as policyholders do not need to worry about out-of-network providers or balance billing.
Benefits and Drawbacks of EPOs

Some of the benefits of EPOs include:
- Balance between flexibility and cost savings
- Lower premiums than PPOs
- Lower administrative burden
- Access to a network of providers
However, EPOs also have some drawbacks, including:
- Limited provider network
- Out-of-network care is not covered except in emergency situations
- Referrals may be required to see specialists
- Higher costs for out-of-network care
Health Plan 4: POS

The fourth health plan we will discuss is the Point of Service (POS) plan. POS plans are a type of managed care plan that combines elements of HMOs and PPOs. With a POS plan, policyholders can choose to see either in-network or out-of-network providers, but out-of-network care typically results in higher costs.
One of the benefits of POS plans is their flexibility. POS plans allow policyholders to see any healthcare provider they choose, both in-network and out-of-network. Additionally, POS plans often have a lower administrative burden than PPOs, as policyholders do not need to worry about balance billing or out-of-network providers.
Benefits and Drawbacks of POS Plans

Some of the benefits of POS plans include:
- Flexibility to see any healthcare provider
- Lower administrative burden
- Access to a network of providers
- Choice between in-network and out-of-network care
However, POS plans also have some drawbacks, including:
- Higher premiums and out-of-pocket costs
- Higher costs for out-of-network care
- Referrals may be required to see specialists
- Balance billing may apply
Health Plan 5: HDHP
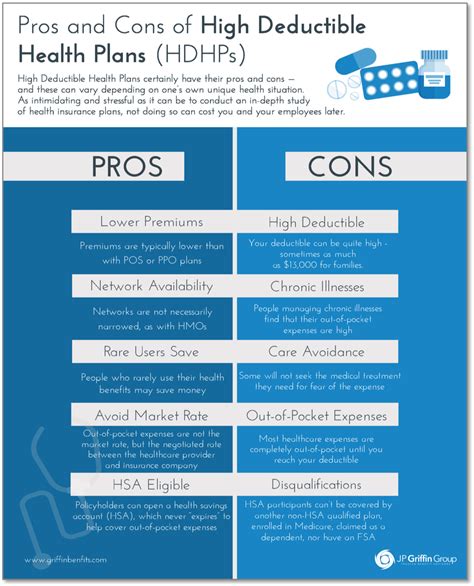
The fifth health plan we will discuss is the High-Deductible Health Plan (HDHP). HDHPs are a type of health plan that combines a high deductible with a lower premium. With an HDHP, policyholders must pay a higher deductible before the plan begins to cover medical expenses. However, HDHPs often have lower premiums and may be eligible for a Health Savings Account (HSA).
One of the benefits of HDHPs is their lower premiums. HDHPs can be a cost-effective option for individuals and families who are willing to take on more financial risk. Additionally, HDHPs may be eligible for an HSA, which can help policyholders save for medical expenses on a tax-free basis.
Benefits and Drawbacks of HDHPs

Some of the benefits of HDHPs include:
- Lower premiums
- Eligibility for a Health Savings Account (HSA)
- Tax-free savings for medical expenses
- Higher deductible may encourage policyholders to seek preventive care
However, HDHPs also have some drawbacks, including:
- Higher deductible may be a financial burden
- Out-of-pocket costs may be higher
- Limited provider network
- Referrals may be required to see specialists
What is the main difference between an HMO and a PPO?
+The main difference between an HMO and a PPO is the flexibility to see out-of-network providers. With an HMO, policyholders are typically required to see only in-network providers, while PPOs allow policyholders to see both in-network and out-of-network providers.
What is the benefit of an EPO plan?
+The benefit of an EPO plan is its balance between flexibility and cost savings. EPOs often have lower premiums than PPOs, but still offer a range of provider options.
What is the main advantage of an HDHP?
+The main advantage of an HDHP is its lower premiums. HDHPs can be a cost-effective option for individuals and families who are willing to take on more financial risk.
In conclusion, the five health plans discussed in this article offer a range of options for individuals and families seeking comprehensive coverage, flexibility, and affordability. By understanding the benefits and drawbacks of each plan, policyholders can make informed decisions about their healthcare and choose the plan that best meets their needs. Whether you're looking for a low-cost option with a high deductible or a more comprehensive plan with a lower deductible, there's a health plan out there that can provide the coverage and peace of mind you deserve. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with health plans in the comments below, and to share this article with anyone who may be seeking to navigate the complex world of health insurance.
