Intro
Learn 5 ways to stop bleeding quickly, including wound care, pressure techniques, and hemostatic agents, to manage bleeding effectively and prevent complications, promoting fast recovery and healing from cuts, injuries, and trauma.
Bleeding can be a frightening and potentially life-threatening situation, whether it's due to an injury, surgery, or a medical condition. Knowing how to stop bleeding is an essential first aid skill that can help save lives. In this article, we will explore the importance of stopping bleeding, the different types of bleeding, and provide a comprehensive guide on how to stop bleeding in various situations.
The ability to stop bleeding is crucial in preventing blood loss, promoting wound healing, and reducing the risk of infection. When bleeding is not controlled, it can lead to shock, organ failure, and even death. Therefore, it is essential to know the proper techniques and methods to stop bleeding, whether it's a minor cut or a severe injury.
Bleeding can be classified into different types, including external bleeding, internal bleeding, and bleeding disorders. External bleeding occurs when blood flows out of the body through a wound or cut, while internal bleeding occurs when blood accumulates inside the body, often due to trauma or surgery. Bleeding disorders, such as hemophilia, can also cause excessive bleeding due to a deficiency in clotting factors.
Understanding the Importance of Stopping Bleeding
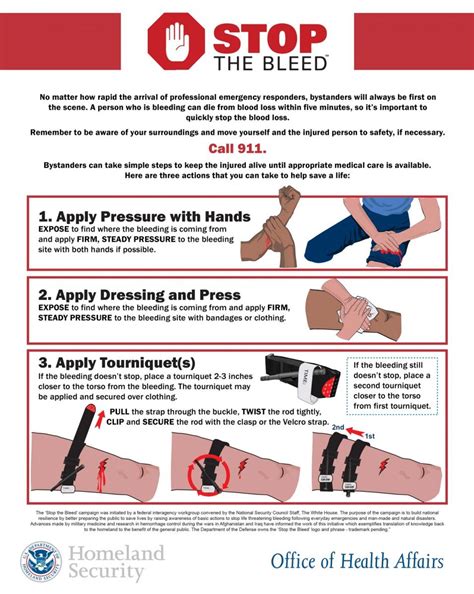
Types of Bleeding
There are several types of bleeding, including external bleeding, internal bleeding, and bleeding disorders. External bleeding occurs when blood flows out of the body through a wound or cut, while internal bleeding occurs when blood accumulates inside the body, often due to trauma or surgery. Bleeding disorders, such as hemophilia, can also cause excessive bleeding due to a deficiency in clotting factors.5 Ways to Stop Bleeding
Applying Pressure to the Wound
Applying pressure to the wound is the most effective way to stop bleeding. This can be done using a clean cloth or gauze, which should be pressed firmly onto the wound for several minutes. The pressure helps to constrict the blood vessels, reducing blood flow to the area and promoting clotting.Techniques for Applying Pressure

Elevating the Injured Area
Elevating the injured area can also help to stop bleeding by reducing blood flow to the area. This can be done by propping up the injured limb or area using pillows or other supports. Elevating the injured area can also help to reduce swelling and promote wound healing.Using Tourniquets or Hemostatic Agents
Applying Cold Compresses or Ice Packs
Applying cold compresses or ice packs can also help to stop bleeding by constricting the blood vessels and reducing blood flow to the area. Cold compresses or ice packs should be applied to the affected area for 15-20 minutes, several times a day, to promote wound healing and reduce swelling.Seeking Medical Attention

Preventing Infection
Preventing infection is critical in promoting wound healing and preventing complications. This can be done by keeping the wound clean and dry, applying antibiotic ointment, and covering the wound with a sterile dressing.Conclusion and Final Thoughts
What are the most common causes of bleeding?
+The most common causes of bleeding include injuries, surgery, and medical conditions such as hemophilia.
How do I apply pressure to a wound?
+To apply pressure to a wound, use a clean cloth or gauze and press firmly onto the wound for several minutes.
When should I seek medical attention for bleeding?
+Seek medical attention immediately if the bleeding is severe, or if you experience symptoms such as dizziness, weakness, or difficulty breathing.
We hope this article has provided you with valuable information on how to stop bleeding. If you have any further questions or concerns, please don't hesitate to comment below. Share this article with your friends and family to help spread awareness about the importance of first aid and bleeding control. Remember to always prioritize proper wound care and seek medical attention if necessary.
