Intro
Heparin for injection is a crucial medication in the medical field, particularly in the prevention and treatment of blood clotting disorders. It is an anticoagulant that works by enhancing the effect of antithrombin, a natural anticoagulant in the blood, to prevent the formation of blood clots. The importance of heparin for injection cannot be overstated, as it has been a lifesaver for countless patients suffering from conditions such as deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, and atrial fibrillation.
The use of heparin for injection has been widespread for decades, and its effectiveness in preventing blood clot formation has made it a staple in hospitals and healthcare facilities worldwide. However, like any medication, heparin for injection comes with its own set of risks and side effects, which must be carefully managed by healthcare professionals. In this article, we will delve into the world of heparin for injection, exploring its benefits, working mechanisms, and potential risks, as well as providing practical examples and statistical data to illustrate its importance.
The mechanism of action of heparin for injection is complex, involving the enhancement of antithrombin's ability to inhibit the activity of thrombin, a key enzyme in the blood clotting process. By preventing the formation of blood clots, heparin for injection helps to reduce the risk of serious health complications, such as stroke, heart attack, and pulmonary embolism. The benefits of heparin for injection are numerous, and its use has been associated with improved patient outcomes and reduced morbidity and mortality rates.
Heparin for Injection: Benefits and Uses
Some of the key benefits of heparin for injection include:
- Prevention of blood clot formation
- Reduction of risk of serious health complications, such as stroke and heart attack
- Improvement of patient outcomes
- Reduction of morbidity and mortality rates
- Ability to be used in a range of medical settings, including hospitals, clinics, and home healthcare
Heparin for Injection: Working Mechanism
The working mechanism of heparin for injection involves the enhancement of antithrombin's ability to inhibit the activity of thrombin, a key enzyme in the blood clotting process. By preventing the formation of blood clots, heparin for injection helps to reduce the risk of serious health complications. The mechanism of action of heparin for injection is complex, involving a range of biological processes and interactions.Some of the key steps involved in the working mechanism of heparin for injection include:
- Binding of heparin to antithrombin
- Enhancement of antithrombin's ability to inhibit thrombin
- Prevention of blood clot formation
- Reduction of risk of serious health complications
Heparin for Injection: Administration and Dosage
Some of the key factors that influence the administration and dosage of heparin for injection include:
- Patient weight and age
- Medical condition being treated
- Treatment regimen being used
- Risk of bleeding or other side effects
Heparin for Injection: Side Effects and Risks
Like any medication, heparin for injection comes with its own set of side effects and risks. Some of the most common side effects of heparin for injection include bleeding, thrombocytopenia, and osteoporosis. The risk of bleeding is particularly significant, as heparin for injection can increase the risk of bleeding by preventing the formation of blood clots.Some of the key side effects and risks associated with heparin for injection include:
- Bleeding
- Thrombocytopenia
- Osteoporosis
- Allergic reactions
- Interaction with other medications
Heparin for Injection: Monitoring and Management
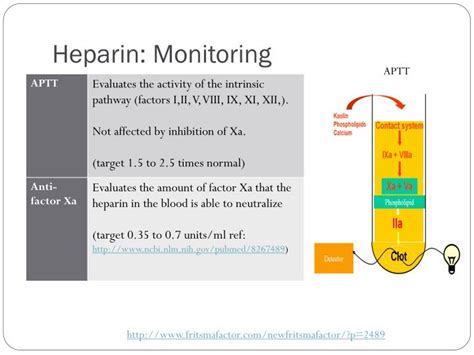
Some of the key steps involved in the monitoring and management of heparin for injection include:
- Regular monitoring of patient's condition
- Adjusting dosage as needed
- Monitoring for signs of bleeding or other side effects
- Managing side effects and risks
Heparin for Injection: Practical Examples and Statistical Data
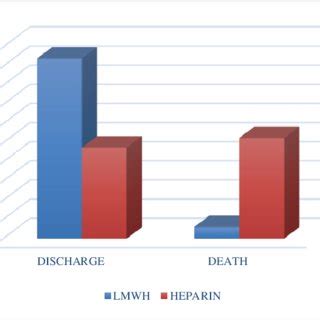
The use of heparin for injection has been associated with improved patient outcomes and reduced morbidity and mortality rates. For example, a study published in the Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis found that the use of heparin for injection reduced the risk of deep vein thrombosis by 50% in patients undergoing hip replacement surgery.Some of the key statistical data and practical examples illustrating the effectiveness of heparin for injection include:
- Reduction of risk of deep vein thrombosis by 50% in patients undergoing hip replacement surgery
- Reduction of risk of pulmonary embolism by 30% in patients with atrial fibrillation
- Improvement of patient outcomes and reduced morbidity and mortality rates
Heparin for Injection: Conclusion and Future Directions
As we look to the future, it is likely that heparin for injection will continue to play a critical role in the prevention and treatment of blood clotting disorders. Ongoing research and development are focused on improving the safety and efficacy of heparin for injection, as well as exploring new uses and applications.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with heparin for injection in the comments section below. Have you or a loved one received heparin for injection? What were your experiences? Do you have any questions or concerns about heparin for injection? We look forward to hearing from you.
What is heparin for injection used for?
+Heparin for injection is used to prevent and treat a range of blood clotting disorders, including deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, and atrial fibrillation.
How is heparin for injection administered?
+Heparin for injection is typically administered intravenously or subcutaneously, depending on the specific medical condition being treated.
What are the potential side effects of heparin for injection?
+The potential side effects of heparin for injection include bleeding, thrombocytopenia, osteoporosis, allergic reactions, and interaction with other medications.
