Intro
Identify 7 key Hepatitis B signs, including liver damage, fatigue, and jaundice, to recognize symptoms of this infectious disease, and learn about vaccination, transmission, and treatment options for Hepatitis B management.
Hepatitis B is a serious liver infection caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV) that can lead to severe complications, including liver cancer and cirrhosis. It is essential to recognize the signs and symptoms of hepatitis B to seek medical attention promptly. Hepatitis B is a significant public health concern, with over 290 million people worldwide living with chronic hepatitis B infection. The virus is transmitted through bodily fluids, such as blood, semen, and vaginal fluids, and can be spread through unprotected sex, sharing needles, and from mother to child during birth.
The importance of recognizing hepatitis B signs cannot be overstated, as early detection and treatment can significantly improve outcomes. Hepatitis B can be acute or chronic, with acute infections often resolving on their own within six months. However, chronic hepatitis B can lead to severe liver damage and increase the risk of liver cancer. It is crucial to be aware of the signs and symptoms of hepatitis B to prevent transmission and ensure timely medical intervention. By understanding the risks and consequences of hepatitis B, individuals can take proactive steps to protect themselves and their loved ones.
Hepatitis B is a complex condition that requires a comprehensive approach to prevention, diagnosis, and treatment. The virus can affect anyone, regardless of age, sex, or background, and it is essential to be aware of the signs and symptoms to seek medical attention promptly. In this article, we will delve into the 7 hepatitis B signs, exploring the causes, symptoms, and consequences of this serious liver infection. We will also discuss the importance of vaccination, safe practices, and regular screening to prevent transmission and ensure timely medical intervention.
Hepatitis B Overview
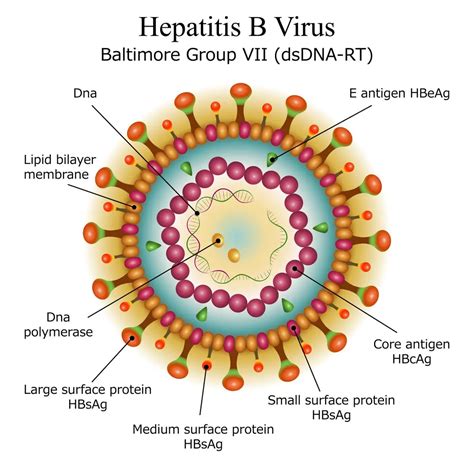
Hepatitis B Transmission
Hepatitis B is transmitted through bodily fluids, such as blood, semen, and vaginal fluids. The virus can be spread through: * Unprotected sex * Sharing needles or syringes * From mother to child during birth * Blood transfusions (although rare in countries with strict blood screening) * Sharing personal items, such as toothbrushes or razorsHepatitis B Signs and Symptoms
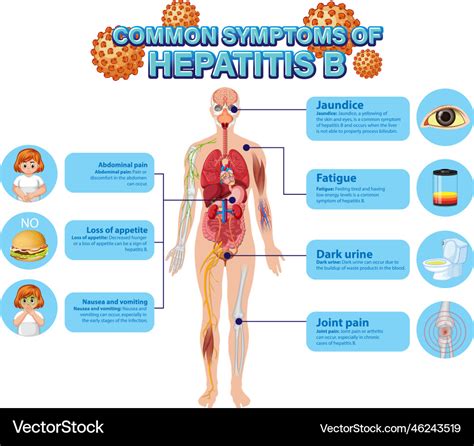
Hepatitis B Diagnosis
Hepatitis B is diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests. The diagnosis may involve: * Blood tests to detect hepatitis B antibodies and antigens * Liver function tests to assess liver damage * Imaging tests, such as ultrasound or CT scans, to evaluate liver damage * Liver biopsy to assess liver tissue damageHepatitis B Treatment

Hepatitis B Prevention
Prevention is key to reducing the risk of hepatitis B transmission. The prevention strategies include: * Vaccination: The hepatitis B vaccine is safe and effective in preventing hepatitis B infection. * Safe practices: Avoid sharing needles, syringes, and personal items, and practice safe sex. * Regular screening: Regular screening can help detect hepatitis B infection early, reducing the risk of severe liver damage.Hepatitis B Complications
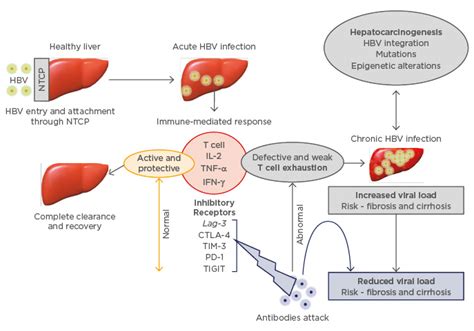
Hepatitis B Management
Managing hepatitis B involves a comprehensive approach, including: * Regular monitoring: Regular monitoring of liver function and viral load. * Lifestyle modifications: Avoiding alcohol and maintaining a healthy diet. * Medications: Antiviral medications and interferon injections to reduce viral replication. * Support: Emotional support and counseling to manage stress and anxiety.Hepatitis B and Pregnancy

Hepatitis B and Travel
Travelers to areas with high hepatitis B prevalence should take precautions to reduce the risk of transmission. The precautions include: * Vaccination: Getting vaccinated against hepatitis B before traveling. * Safe practices: Avoiding sharing needles, syringes, and personal items, and practicing safe sex. * Regular screening: Regular screening for hepatitis B infection before and after travel.Hepatitis B and Mental Health

Hepatitis B and Nutrition
A healthy diet can help manage hepatitis B, including: * Avoiding alcohol: Alcohol can exacerbate liver damage. * Eating a balanced diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. * Avoiding fatty foods: Avoiding fatty foods, which can exacerbate liver damage.Hepatitis B and Exercise

Hepatitis B and Alternative Therapies
Alternative therapies, such as acupuncture and herbal supplements, may be used to manage hepatitis B. However, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider before using any alternative therapies.What are the symptoms of hepatitis B?
+The symptoms of hepatitis B include fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea, abdominal pain, dark urine, and yellowing of the skin and eyes.
How is hepatitis B transmitted?
+Hepatitis B is transmitted through bodily fluids, such as blood, semen, and vaginal fluids, and can be spread through unprotected sex, sharing needles, and from mother to child during birth.
Can hepatitis B be cured?
+Acute hepatitis B infections often resolve on their own within six months. However, chronic hepatitis B can be managed with antiviral medications and lifestyle modifications, but it cannot be cured.
How can I prevent hepatitis B?
+Hepatitis B can be prevented through vaccination, safe practices, such as avoiding sharing needles and practicing safe sex, and regular screening.
What are the complications of hepatitis B?
+Hepatitis B can lead to severe complications, including liver cirrhosis, liver cancer, kidney disease, and blood disorders.
In summary, hepatitis B is a serious liver infection that requires prompt medical attention. Recognizing the 7 hepatitis B signs and symptoms can help individuals seek medical attention early, reducing the risk of severe liver damage and complications. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and consequences of hepatitis B, individuals can take proactive steps to protect themselves and their loved ones. We encourage readers to share this article with others, raising awareness about the importance of hepatitis B prevention and management. If you have any questions or concerns about hepatitis B, please comment below or consult with a healthcare provider.
