Intro
Discover symptoms and treatments for Herpes infection on hands, including Herpetic whitlow, a viral infection causing painful blisters and cold sores on fingers and hands.
Herpes infection on hands, also known as herpetic whitlow, is a viral infection caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV). This condition is characterized by the appearance of painful blisters or sores on the fingers or hands. Herpetic whitlow is highly contagious and can be spread through direct contact with an infected person or by touching contaminated surfaces. The virus can also be transmitted through breaks in the skin, such as cuts or scrapes.
The importance of understanding herpes infection on hands cannot be overstated. If left untreated, the infection can lead to serious complications, including the spread of the virus to other parts of the body, such as the eyes, brain, or spinal cord. Furthermore, herpetic whitlow can cause significant discomfort and pain, making it difficult to perform everyday activities. It is essential to recognize the symptoms of herpes infection on hands and seek medical attention promptly to prevent long-term damage and promote effective treatment.
Herpes infection on hands is a common condition that can affect anyone, regardless of age or sex. However, certain individuals are more susceptible to the infection, including healthcare workers, athletes, and people with weakened immune systems. The virus can be spread through various means, including skin-to-skin contact, contaminated equipment, or poor hygiene practices. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for herpes infection on hands, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent the spread of the virus and manage the condition effectively.
Causes and Risk Factors
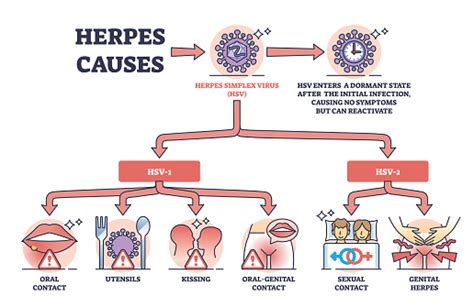
Herpes infection on hands is caused by the herpes simplex virus, which is a highly contagious virus that can be spread through direct contact with an infected person or contaminated surfaces. The virus can enter the body through breaks in the skin, such as cuts or scrapes, and cause an infection. Certain individuals are more susceptible to the infection, including healthcare workers, athletes, and people with weakened immune systems. Risk factors for herpes infection on hands include:
- Direct contact with an infected person or contaminated surfaces
- Poor hygiene practices, such as not washing hands regularly
- Weakened immune system, such as in people with HIV/AIDS or undergoing chemotherapy
- Skin breaks, such as cuts or scrapes, that provide an entry point for the virus
- Certain medical procedures, such as surgery or injections, that can increase the risk of infection
Symptoms and Diagnosis
The symptoms of herpes infection on hands can vary depending on the severity of the infection. Common symptoms include: * Painful blisters or sores on the fingers or hands * Redness and swelling around the affected area * Itching or burning sensation on the skin * Fever or chills * Swollen lymph nodes in the arm or neckDiagnosing herpes infection on hands typically involves a physical examination and laboratory tests, such as viral cultures or polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests. A healthcare professional may also perform a medical history to determine the underlying cause of the infection.
Treatment and Management
Treatment for herpes infection on hands typically involves antiviral medications, such as acyclovir or valacyclovir, which can help reduce the severity and duration of the infection. In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary to manage complications and prevent the spread of the virus. Additionally, individuals can take proactive steps to manage the condition, including:
- Keeping the affected area clean and dry
- Applying topical creams or ointments to reduce pain and discomfort
- Avoiding direct contact with others to prevent the spread of the virus
- Practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands regularly
- Getting plenty of rest and maintaining a healthy diet to support the immune system
Complications and Prevention
If left untreated, herpes infection on hands can lead to serious complications, including: * Spread of the virus to other parts of the body, such as the eyes, brain, or spinal cord * Increased risk of secondary infections, such as bacterial or fungal infections * Scarring or disfigurement of the affected area * Recurrence of the infection, which can be triggered by stress, fatigue, or other factorsPreventing herpes infection on hands involves practicing good hygiene, avoiding direct contact with infected individuals, and taking proactive steps to support the immune system. Individuals can reduce their risk of infection by:
- Washing hands regularly with soap and water
- Avoiding sharing personal items, such as towels or utensils
- Wearing gloves when coming into contact with potentially contaminated surfaces
- Getting plenty of rest and maintaining a healthy diet to support the immune system
- Avoiding stress and fatigue, which can trigger recurrence of the infection
Living with Herpes Infection on Hands
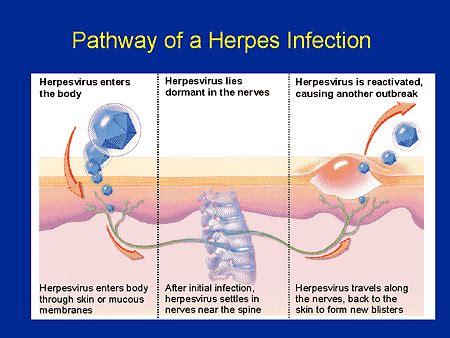
Living with herpes infection on hands can be challenging, but there are steps individuals can take to manage the condition and prevent complications. By practicing good hygiene, avoiding direct contact with others, and taking proactive steps to support the immune system, individuals can reduce their risk of infection and promote effective treatment. Additionally, seeking support from healthcare professionals, friends, and family can help individuals cope with the emotional and psychological impact of the condition.
Coping with the Emotional Impact
Herpes infection on hands can have a significant emotional and psychological impact on individuals, including feelings of anxiety, depression, and isolation. Coping with the emotional impact of the condition involves seeking support from healthcare professionals, friends, and family, as well as practicing stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation or yoga. Individuals can also join support groups or online forums to connect with others who are living with the condition.Future Directions and Research

Research on herpes infection on hands is ongoing, with a focus on developing more effective treatments and prevention strategies. Future directions for research include:
- Developing new antiviral medications that can target the herpes simplex virus more effectively
- Investigating the use of immunotherapy to boost the immune system and prevent recurrence of the infection
- Developing vaccines to prevent the spread of the virus
- Improving diagnostic techniques to detect the infection earlier and more accurately
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
Herpes infection on hands is a common condition that can have significant consequences if left untreated. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for the condition, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent the spread of the virus and manage the infection effectively. Additionally, seeking support from healthcare professionals, friends, and family can help individuals cope with the emotional and psychological impact of the condition. As research continues to advance, there is hope for more effective treatments and prevention strategies to be developed, reducing the burden of herpes infection on hands for individuals and communities worldwide.What are the symptoms of herpes infection on hands?
+The symptoms of herpes infection on hands include painful blisters or sores on the fingers or hands, redness and swelling around the affected area, itching or burning sensation on the skin, fever or chills, and swollen lymph nodes in the arm or neck.
How is herpes infection on hands treated?
+Treatment for herpes infection on hands typically involves antiviral medications, such as acyclovir or valacyclovir, which can help reduce the severity and duration of the infection. In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary to manage complications and prevent the spread of the virus.
Can herpes infection on hands be prevented?
+Yes, herpes infection on hands can be prevented by practicing good hygiene, avoiding direct contact with infected individuals, and taking proactive steps to support the immune system. Individuals can reduce their risk of infection by washing hands regularly, avoiding sharing personal items, and wearing gloves when coming into contact with potentially contaminated surfaces.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of herpes infection on hands. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to comment below or share this article with others who may benefit from this information.
