Intro
Understand 5 Hgb A1c levels, a crucial diabetes metric. Learn normal, prediabetic, and diabetic ranges, including HbA1c targets, blood glucose control, and health implications.
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is crucial for overall well-being, particularly for individuals living with diabetes. One of the most important metrics for assessing blood sugar control is the Hgb A1c test. This test measures the average level of glucose in the blood over the past 2 to 3 months, providing valuable insights into how well diabetes is being managed. Understanding Hgb A1c levels is essential for making informed decisions about diet, exercise, and medication. In this article, we will delve into the world of Hgb A1c, exploring its significance, the implications of different level ranges, and practical strategies for maintaining healthy blood sugar levels.
The importance of monitoring Hgb A1c levels cannot be overstated. For individuals with diabetes, regular testing helps to identify trends in blood glucose control, allowing for timely adjustments to treatment plans. Even for those without diabetes, understanding Hgb A1c levels can provide early warnings of potential glucose metabolism issues, enabling preventive measures to be taken. The test is relatively simple, involving a blood draw that is then analyzed to determine the percentage of hemoglobin molecules that have bound to glucose. This percentage reflects average blood glucose levels over the preceding months, offering a comprehensive view of glucose control.
As we explore the intricacies of Hgb A1c levels, it becomes clear that this metric is not just a passive indicator of health but an active tool for managing diabetes and preventing its complications. By understanding what different Hgb A1c levels signify, individuals can take proactive steps to improve their glucose control, reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications, and enhance their overall quality of life. Whether you are living with diabetes, are at risk of developing the condition, or simply wish to maintain optimal health, grasping the concept of Hgb A1c levels is a vital step in your health journey.
Understanding Hgb A1c Levels
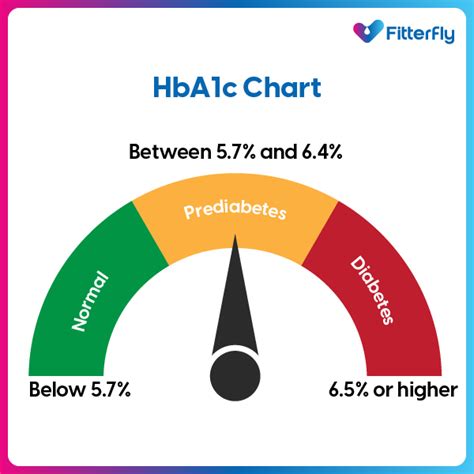
Understanding Hgb A1c levels is fundamental to managing diabetes effectively. The Hgb A1c test result is expressed as a percentage, and the American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends the following targets for different groups:
- For adults with diabetes, an Hgb A1c level less than 7% is generally recommended.
- For children with diabetes, the target is less than 7.5%.
- For pregnant women with diabetes, the goal is less than 6.5% if it can be achieved safely.
These targets are not one-size-fits-all and may be adjusted based on individual factors such as age, other health conditions, duration of diabetes, life expectancy, resources, and support system. It's also important to consider the risk of hypoglycemia, disease duration, life expectancy, and the presence of cardiovascular disease when setting personalized Hgb A1c goals.
Interpreting Hgb A1c Results
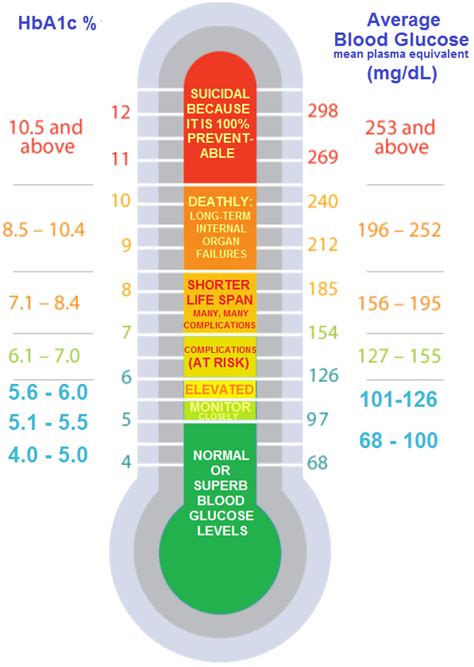
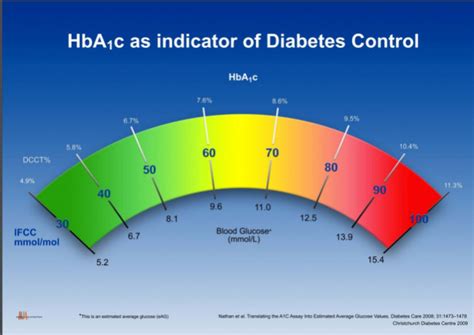
Interpreting Hgb A1c results requires understanding what the percentages mean in terms of average blood glucose levels. An Hgb A1c of 6% corresponds to an average blood glucose level of approximately 126 mg/dL, while an Hgb A1c of 7% reflects an average level of about 154 mg/dL. The higher the Hgb A1c percentage, the higher the average blood glucose levels over the past 2 to 3 months. This information can guide treatment decisions, including adjustments to medication, diet, and physical activity.Benefits of Maintaining Healthy Hgb A1c Levels
Maintaining healthy Hgb A1c levels has numerous benefits for individuals with diabetes. These benefits include:
- Reduced risk of diabetes-related complications such as heart disease, kidney disease, nerve damage, and vision problems.
- Improved quality of life through better management of diabetes symptoms.
- Enhanced physical and mental well-being, allowing for more active participation in daily activities.
- Potential reduction in medication needs or less intense treatment regimens.
- Lower risk of hypoglycemic episodes, which can be dangerous and disruptive to daily life.
Achieving and maintaining healthy Hgb A1c levels requires a multifaceted approach that includes a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and, when prescribed, adherence to medication regimens. Lifestyle modifications are often the first line of defense against rising Hgb A1c levels, offering individuals the opportunity to take control of their health through conscious choices.
Lifestyle Modifications for Healthy Hgb A1c
Lifestyle modifications play a critical role in managing Hgb A1c levels. Key strategies include: - **Dietary Changes**: Focus on consuming a balanced diet rich in whole foods, fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limit intake of sugary drinks, refined carbohydrates, and saturated fats. - **Physical Activity**: Engage in regular physical activity, aiming for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise, or a combination of both, per week. Include strength-training activities at least twice a week. - **Weight Management**: Maintain a healthy weight, as excess weight, particularly around the abdomen, can increase insulin resistance and worsen glucose control. - **Stress Management**: Practice stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises, as chronic stress can negatively impact blood glucose levels.Monitoring and Adjusting Hgb A1c Levels
Regular monitoring of Hgb A1c levels is essential for assessing the effectiveness of the current treatment plan and making necessary adjustments. This involves:
- Regular Hgb A1c Tests: Get tested as frequently as recommended by your healthcare provider, typically every 3 to 6 months, depending on your diabetes type, treatment plan, and how well your blood sugar is controlled.
- Blood Glucose Monitoring: Use a glucose meter to check blood glucose levels throughout the day, which can provide immediate feedback on how different activities, meals, and stress levels affect glucose control.
- Adjusting Treatment Plans: Work with your healthcare provider to adjust your diet, exercise, or medication based on your Hgb A1c results and blood glucose monitoring data.
By actively monitoring and managing Hgb A1c levels, individuals can better control their diabetes, reduce the risk of complications, and improve their overall health and well-being.
Technological Advances in Hgb A1c Monitoring
Technological advances have significantly improved the ease and accuracy of monitoring blood glucose and Hgb A1c levels. Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems and flash glucose monitoring systems provide real-time data on glucose levels, enabling more precise adjustments to treatment plans. Additionally, mobile apps and online platforms can help track glucose data, provide reminders for medication and testing, and offer educational resources for better diabetes management.Challenges and Considerations

Despite the importance of Hgb A1c monitoring, there are challenges and considerations that must be addressed. These include:
- Access to Healthcare: Limited access to healthcare services, particularly in underserved communities, can hinder regular monitoring and management of Hgb A1c levels.
- Cost of Testing and Treatment: The cost of Hgb A1c tests, glucose monitoring supplies, and diabetes medications can be a significant barrier for many individuals.
- Education and Awareness: Lack of awareness about the importance of Hgb A1c monitoring and how to interpret results can impede effective diabetes management.
- Psychological Factors: The psychological impact of living with diabetes, including stress, anxiety, and depression, can affect adherence to treatment plans and overall glucose control.
Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach that includes improving access to affordable healthcare, enhancing patient education, and providing psychological support.
Future Directions in Hgb A1c Management
The future of Hgb A1c management holds promise with advancements in technology, personalized medicine, and a greater emphasis on preventive care. Emerging trends include: - **Personalized Diabetes Management**: Tailoring treatment plans to individual characteristics, such as genetic profiles, lifestyle, and preferences. - **Digital Health Technologies**: Leveraging digital platforms, mobile apps, and wearable devices to enhance monitoring, education, and support for diabetes management. - **Preventive Care**: Focusing on early intervention and prevention strategies to reduce the incidence of diabetes and its complications.As research and technology continue to evolve, we can expect more effective and personalized approaches to managing Hgb A1c levels and improving outcomes for individuals with diabetes.
Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, understanding and managing Hgb A1c levels is a critical aspect of diabetes care. By grasping the significance of Hgb A1c, interpreting test results, and implementing lifestyle modifications and treatment adjustments, individuals can take proactive steps towards better health. As we look to the future, embracing technological advancements, personalized approaches, and preventive strategies will be key to improving diabetes outcomes.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with managing Hgb A1c levels. How have you incorporated lifestyle modifications and technological tools into your diabetes management plan? What challenges have you faced, and how have you overcome them? Your insights can help others in their journey towards better health. Please comment below, and let's continue the conversation on the importance of Hgb A1c management in diabetes care.
What is the normal range for Hgb A1c levels?
+For individuals without diabetes, the normal range for Hgb A1c levels is typically below 5.7%. For those with diabetes, the target is often less than 7%, though this can vary based on individual factors and guidelines from healthcare providers.
How often should I get my Hgb A1c levels checked?
+The frequency of Hgb A1c testing depends on your diabetes type, how well your diabetes is controlled, and your healthcare provider's recommendations. Generally, testing is done every 3 to 6 months.
Can lifestyle changes alone lower Hgb A1c levels?
+Yes, lifestyle changes such as a healthy diet, regular physical activity, weight loss (if needed), and stress management can significantly lower Hgb A1c levels. For some individuals, especially those with prediabetes or newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes, lifestyle changes alone may be sufficient to achieve target Hgb A1c levels.
