Intro
Discover the Hida Scan Gallbladder, a diagnostic test using hepatobiliary iminodiacetic acid to evaluate gallbladder function, biliary ducts, and liver health, aiding in disease diagnosis and treatment of gallstones, cholecystitis, and bile duct disorders.
The Hida scan, also known as a hepatobiliary iminodiacetic acid (HIDA) scan, is a nuclear medicine test that evaluates the function and structure of the gallbladder and bile ducts. This diagnostic tool is crucial in identifying various gallbladder and biliary disorders, including gallstones, inflammation, and obstruction. In this article, we will delve into the world of Hida scans, exploring their importance, working mechanisms, benefits, and practical applications.
The Hida scan plays a vital role in diagnosing and managing gallbladder diseases, which affect millions of people worldwide. Gallbladder problems can cause severe abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting, significantly impacting an individual's quality of life. The Hida scan helps healthcare professionals to pinpoint the underlying cause of these symptoms, enabling them to develop effective treatment plans. By understanding the functioning of the gallbladder and bile ducts, medical professionals can identify potential issues before they become severe.
Gallbladder diseases can be asymptomatic, making it challenging to detect them in their early stages. However, with the help of a Hida scan, healthcare providers can identify abnormalities in the gallbladder and bile ducts, allowing for prompt intervention. This diagnostic tool is particularly useful in patients who have undergone gallbladder surgery or have a history of gallstones. The Hida scan provides valuable insights into the functioning of the gallbladder, enabling medical professionals to monitor the effectiveness of treatments and make informed decisions about patient care.
Hida Scan Procedure

Preparation and Risks
Before undergoing a Hida scan, patients are typically required to fast for several hours to ensure that the gallbladder is empty. This fasting period helps to prevent any food or bile from interfering with the scan. Patients should also inform their healthcare provider about any medications they are taking, as some medications may interact with the radiotracer. The Hida scan is generally a safe procedure, but it does involve exposure to small amounts of radiation. However, the benefits of the scan usually outweigh the risks, and healthcare professionals take necessary precautions to minimize radiation exposure.Hida Scan Benefits

Common Indications
The Hida scan is commonly used to diagnose and manage various gallbladder and biliary disorders, including: * Gallstones * Cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder) * Biliary obstruction * Bile duct stones * Post-surgical complicationsHida Scan Results
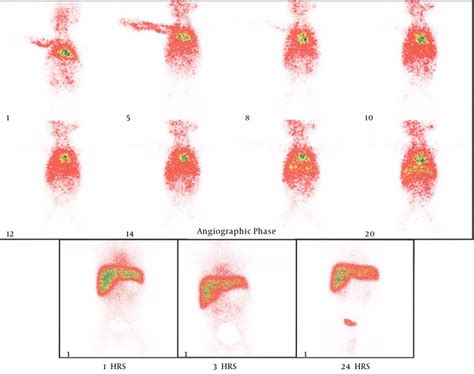
Interpretation and Follow-up
The interpretation of Hida scan results requires specialized training and expertise. Healthcare professionals use the results to develop a diagnosis and create a treatment plan. In some cases, additional testing or procedures may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis or to further evaluate the gallbladder and bile ducts. Patients should follow up with their healthcare provider to discuss the results and any necessary next steps.Gallbladder Diseases and Hida Scan

Gallbladder Disease Management
The management of gallbladder diseases depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Treatment options may include: * Surgery to remove the gallbladder (cholecystectomy) * Medications to dissolve gallstones or reduce inflammation * Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) to remove bile duct stones or treat biliary obstruction * Percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography (PTC) to drain bile from the liverHida Scan and Other Diagnostic Tools

Diagnostic Algorithm
The choice of diagnostic tool depends on the clinical presentation and suspected diagnosis. A diagnostic algorithm may be used to guide the selection of diagnostic tests, including: * Initial evaluation with ultrasound or CT scan * Follow-up with Hida scan or MRCP if initial tests are inconclusive * Use of EUS or ERCP for further evaluation or treatmentFuture Directions and Research

Current Research and Clinical Trials
Several clinical trials are currently underway to evaluate the safety and efficacy of new diagnostic and therapeutic approaches for gallbladder diseases. Patients with gallbladder diseases may be eligible to participate in these trials, which can provide access to innovative treatments and contribute to the advancement of medical knowledge.What is a Hida scan, and how does it work?
+A Hida scan is a nuclear medicine test that uses a radiotracer to evaluate the functioning of the gallbladder and bile ducts. The radiotracer is absorbed by the liver and excreted into the bile, which flows into the gallbladder and bile ducts. A special camera detects the radiation emitted by the radiotracer, producing images of the gallbladder and bile ducts.
What are the benefits of a Hida scan?
+The Hida scan offers several benefits, including high accuracy in diagnosing gallbladder diseases, non-invasive and relatively painless procedure, and ability to evaluate the functioning of the gallbladder and bile ducts.
What are the common indications for a Hida scan?
+The Hida scan is commonly used to diagnose and manage various gallbladder and biliary disorders, including gallstones, cholecystitis, biliary obstruction, and post-surgical complications.
In conclusion, the Hida scan is a valuable diagnostic tool for evaluating the functioning of the gallbladder and bile ducts. Its high accuracy, non-invasive nature, and ability to evaluate the functioning of the gallbladder and bile ducts make it an essential tool in the diagnosis and management of gallbladder diseases. We encourage readers to share their experiences with the Hida scan and to ask questions about this diagnostic tool. If you have any further questions or would like to learn more about the Hida scan, please do not hesitate to comment below or share this article with others.
