Intro
Discover 7 high A1c symptoms, including fatigue, thirst, and blurred vision, related to diabetes management, blood sugar control, and insulin resistance, to help diagnose and treat hyperglycemia effectively.
High A1c symptoms can be a significant concern for individuals living with diabetes. The A1c test, also known as the hemoglobin A1c or HbA1c test, is a blood test that measures the average level of glucose in the blood over the past 2 to 3 months. It's a crucial indicator of how well diabetes is being managed. When A1c levels are high, it can lead to a range of symptoms that affect various aspects of a person's health and wellbeing. In this article, we will delve into the importance of understanding high A1c symptoms, their implications, and what individuals can do to manage their condition effectively.
The importance of monitoring and managing A1c levels cannot be overstated. High A1c levels are associated with an increased risk of diabetes complications, including heart disease, kidney disease, nerve damage, and vision problems. By recognizing the symptoms of high A1c, individuals can take proactive steps to adjust their treatment plans, lifestyle habits, and dietary choices to bring their glucose levels under control. This not only improves their quality of life but also reduces the risk of long-term health consequences.
For individuals with diabetes, it's essential to be aware of the potential symptoms of high A1c. These symptoms can vary from person to person and may include increased thirst and urination, fatigue, blurred vision, slow healing of cuts and wounds, tingling or numbness in the hands and feet, and recurring infections. By understanding these symptoms and their underlying causes, individuals can work closely with their healthcare providers to develop personalized strategies for managing their diabetes and preventing complications.
Understanding High A1c Symptoms
Common High A1c Symptoms
Other common symptoms of high A1c include fatigue, blurred vision, and slow healing of cuts and wounds. Fatigue is a pervasive symptom that can affect every aspect of a person's life, from work and relationships to daily activities and hobbies. Blurred vision can be a particularly concerning symptom, as it may indicate damage to the blood vessels in the eyes. Slow healing of cuts and wounds is another symptom that can have significant implications, as it increases the risk of infection and further complications.Managing High A1c Symptoms
Lifestyle Changes for Managing High A1c
In addition to regular physical activity, other lifestyle changes can help manage high A1c symptoms. These include: * Eating a balanced diet that is low in added sugars, saturated fats, and refined carbohydrates * Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water * Getting enough sleep each night to help regulate glucose levels * Managing stress through techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises * Monitoring glucose levels regularly to identify patterns and trendsDietary Modifications for High A1c
Foods to Avoid with High A1c
On the other hand, there are certain foods that can exacerbate high A1c symptoms and should be avoided or consumed in moderation. These include: * Sugary drinks such as soda, sports drinks, and sweet tea * Refined carbohydrates such as white bread, sugary snacks, and processed foods * Saturated and trans fats such as those found in red meat, full-fat dairy products, and processed snacks * High-sodium foods such as canned soups, frozen meals, and processed meatsMedical Interventions for High A1c
Working with a Healthcare Provider
Working with a healthcare provider is essential for managing high A1c symptoms. By developing a personalized treatment plan, individuals can receive the support and guidance they need to manage their condition effectively. This may involve regular check-ups, glucose monitoring, and adjustments to medication or lifestyle habits.Conclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your experiences and tips for managing high A1c symptoms in the comments below. Your insights can help others who may be struggling with similar challenges. Additionally, if you found this article informative and helpful, please consider sharing it with others who may benefit from this information.
What is the normal range for A1c levels?
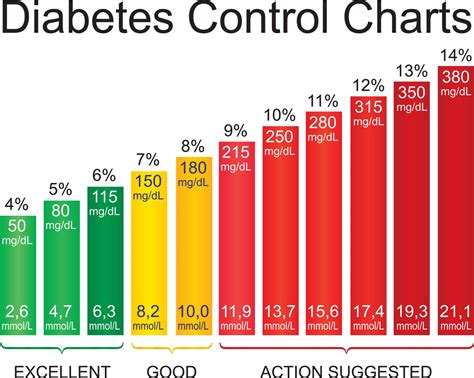
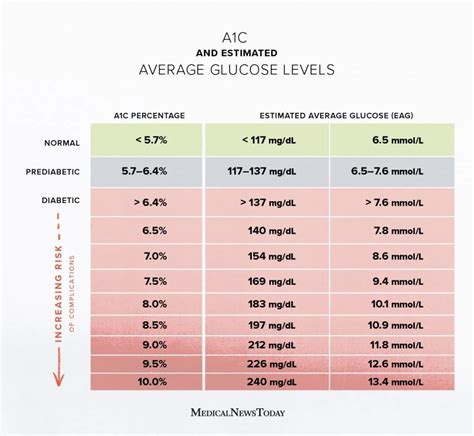
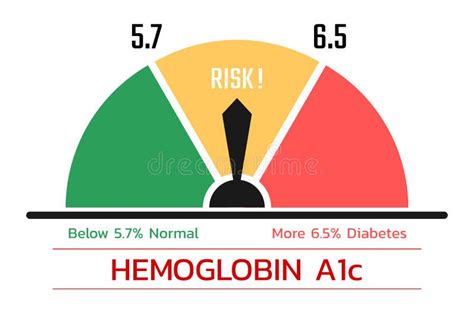
+Normal A1c levels are typically below 5.7%. Levels between 5.7% and 6.4% indicate prediabetes, while levels of 6.5% or higher indicate diabetes.
How often should I get my A1c levels checked?
+The frequency of A1c testing depends on your individual needs and health status. Typically, individuals with diabetes should have their A1c levels checked every 3 to 6 months.
What are the risks of high A1c levels?
+High A1c levels are associated with an increased risk of diabetes complications, including heart disease, kidney disease, nerve damage, and vision problems.
Can lifestyle changes alone lower A1c levels?
+Yes, lifestyle changes such as regular physical activity, a balanced diet, and weight loss can help lower A1c levels. However, in some cases, medical interventions may also be necessary.
How can I track my A1c levels at home?
+There are several ways to track your A1c levels at home, including using a glucose meter, keeping a food diary, and monitoring your physical activity levels.
