Intro
Discover the causes and risks of high B12 levels in blood, including vitamin B12 toxicity, hyperhomocysteinemia, and methylmalonic acidemia, and learn how to manage elevated B12 levels naturally.
Elevated levels of vitamin B12 in the blood can be a cause for concern, as it may indicate an underlying health issue. Vitamin B12 is an essential nutrient that plays a crucial role in the production of red blood cells, nerve function, and DNA synthesis. While a deficiency in vitamin B12 can lead to various health problems, high levels of this vitamin can also have adverse effects. In this article, we will delve into the world of vitamin B12, exploring its importance, the causes of high levels, and the potential risks associated with elevated vitamin B12 levels in the blood.
The human body requires vitamin B12 to function properly, and a deficiency can lead to fatigue, weakness, and neurological problems. Vitamin B12 is found primarily in animal products, such as meat, fish, and dairy products, making it challenging for vegetarians and vegans to obtain sufficient amounts through their diet. However, with the help of supplements and fortified foods, it is possible to maintain adequate levels of vitamin B12. On the other hand, high levels of vitamin B12 can be a sign of an underlying health issue, such as liver or kidney disease, and it is essential to investigate the cause of elevated levels to prevent potential complications.
Vitamin B12 is a complex vitamin that plays a vital role in various bodily functions. It is involved in the production of red blood cells, which carry oxygen throughout the body. A deficiency in vitamin B12 can lead to anemia, a condition characterized by a lack of red blood cells or hemoglobin in the blood. Vitamin B12 also plays a crucial role in the maintenance of the nervous system, and a deficiency can cause neurological problems, such as numbness, tingling, and weakness in the hands and feet. Furthermore, vitamin B12 is necessary for the synthesis of DNA, the genetic material that contains the instructions for the development and function of all living organisms.
Vitamin B12 and Its Importance
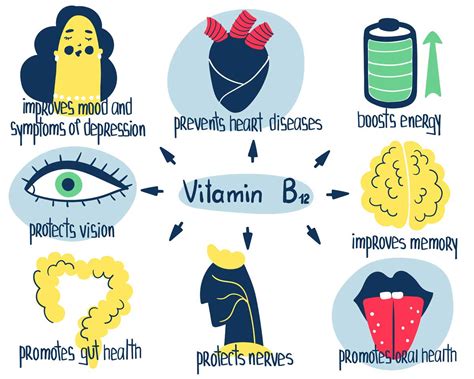
Causes of High Vitamin B12 Levels
High levels of vitamin B12 in the blood can be caused by various factors, including: * Liver disease: Liver disease, such as cirrhosis or liver cancer, can cause an increase in vitamin B12 levels. * Kidney disease: Kidney disease, such as kidney failure or kidney cancer, can also lead to elevated vitamin B12 levels. * Leukemia: Leukemia, a type of blood cancer, can cause an increase in vitamin B12 levels. * Vitamin B12 supplements: Taking high doses of vitamin B12 supplements can lead to elevated levels of this vitamin in the blood. * Fortified foods: Consuming large amounts of fortified foods, such as cereals or energy bars, can also contribute to high levels of vitamin B12.Risks Associated with High Vitamin B12 Levels
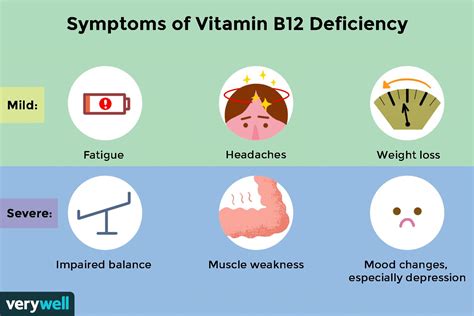
Symptoms of High Vitamin B12 Levels
The symptoms of high vitamin B12 levels can vary depending on the underlying cause. Some common symptoms include: * Diarrhea * Fatigue * Weakness * Numbness or tingling in the hands and feet * Weakness or fatigue in the arms and legs * Difficulty walking or maintaining balanceDiagnosis and Treatment of High Vitamin B12 Levels
Prevention of High Vitamin B12 Levels
Preventing high vitamin B12 levels involves maintaining a balanced diet and avoiding excessive intake of vitamin B12 supplements or fortified foods. Some tips for preventing elevated vitamin B12 levels include: * Eating a balanced diet that includes a variety of foods * Avoiding excessive intake of vitamin B12 supplements or fortified foods * Monitoring vitamin B12 levels regularly * Managing underlying medical conditions, such as liver or kidney diseaseComplications of High Vitamin B12 Levels

Long-Term Effects of High Vitamin B12 Levels
The long-term effects of high vitamin B12 levels can be severe and impact overall quality of life. Some potential long-term effects include: * Chronic diarrhea and dehydration * Persistent fatigue and weakness * Neurological problems, such as numbness or tingling in the hands and feet * Increased risk of falls and injuries * Impaired cognitive functionConclusion and Final Thoughts

What are the common causes of high vitamin B12 levels?
+High levels of vitamin B12 can be caused by various factors, including liver disease, kidney disease, leukemia, vitamin B12 supplements, and fortified foods.
What are the symptoms of high vitamin B12 levels?
+The symptoms of high vitamin B12 levels can vary depending on the underlying cause, but common symptoms include diarrhea, fatigue, weakness, numbness or tingling in the hands and feet, and difficulty walking or maintaining balance.
How can high vitamin B12 levels be prevented?
+Preventing high vitamin B12 levels involves maintaining a balanced diet, avoiding excessive intake of vitamin B12 supplements or fortified foods, monitoring vitamin B12 levels regularly, and managing underlying medical conditions.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of high vitamin B12 levels and their potential risks. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to comment below or share this article with others. By working together, we can promote awareness and education about the importance of maintaining adequate vitamin B12 levels and preventing potential health problems.
