Intro
Understand high CO2 blood test results, causes, and symptoms. Learn about bicarbonate levels, pH imbalance, and respiratory issues related to elevated CO2 levels, and discover treatment options for optimal health.
Elevated CO2 blood test results can be a cause for concern, and it's essential to understand what they mean and how they can impact your health. CO2, or carbon dioxide, is a naturally occurring gas in the body, and its levels can fluctuate based on various factors, including diet, lifestyle, and underlying medical conditions. In this article, we'll delve into the world of CO2 blood tests, exploring what high results signify, their potential causes, and the necessary steps to take if you receive an abnormal reading.
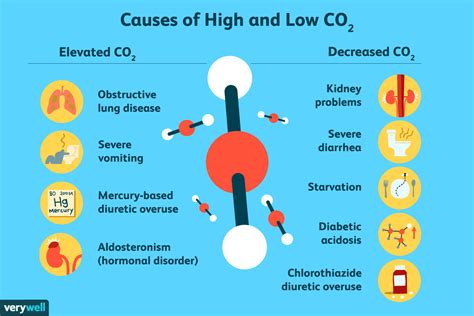
High CO2 blood test results can be an indication of an underlying issue that needs to be addressed. The body's CO2 levels are tightly regulated, and any significant deviations from the normal range can have far-reaching consequences. For instance, elevated CO2 levels can lead to respiratory problems, such as shortness of breath, and can also contribute to the development of conditions like osteoporosis and kidney stones. It's crucial to comprehend the implications of high CO2 blood test results and take proactive measures to mitigate their effects.
The human body is a complex system, and CO2 plays a vital role in maintaining its delicate balance. CO2 is produced as a byproduct of cellular metabolism, and its levels are influenced by factors like diet, physical activity, and overall health. When CO2 levels become elevated, it can be a sign of an underlying issue, such as respiratory or kidney problems. In some cases, high CO2 levels can also be a symptom of a more severe condition, like diabetes or hormonal imbalances. By understanding the causes and consequences of high CO2 blood test results, individuals can take the necessary steps to restore balance to their body and prevent long-term damage.
What is a CO2 Blood Test?

How is a CO2 Blood Test Performed?
The CO2 blood test is a relatively straightforward procedure that involves collecting a blood sample from the patient. The sample is then sent to a laboratory for analysis, where the CO2 levels are measured using specialized equipment. The test is usually performed in conjunction with other diagnostic tests, such as electrolyte panels or liver function tests, to provide a comprehensive picture of the patient's health.Causes of High CO2 Blood Test Results

It's essential to note that high CO2 levels can also be caused by certain medications, such as steroids or diuretics, and can be a side effect of various medical treatments.
Symptoms of High CO2 Levels
The symptoms of high CO2 levels can vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Common symptoms include: * Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing * Fatigue or weakness * Headaches or dizziness * Nausea or vomiting * Abdominal pain or crampingIn severe cases, high CO2 levels can lead to more serious complications, such as respiratory failure or cardiac arrest.
Interpreting CO2 Blood Test Results

Results that fall outside of the normal range can indicate an underlying issue that needs to be addressed. For instance, a CO2 level above 30 mEq/L can be a sign of respiratory acidosis, while a level below 20 mEq/L can indicate respiratory alkalosis.
What to Do if You Receive an Abnormal CO2 Blood Test Result
If you receive an abnormal CO2 blood test result, it's essential to consult with your healthcare provider to determine the underlying cause and develop a plan to address it. This may involve additional testing, such as imaging studies or electrolyte panels, to rule out underlying conditions.In some cases, treatment may be necessary to manage the underlying condition and restore balance to the body. This can include medications, lifestyle modifications, or other interventions, such as oxygen therapy or dialysis.
Treatment Options for High CO2 Levels
It's essential to work closely with your healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses your specific needs and health status.
Preventing High CO2 Levels
Preventing high CO2 levels requires a comprehensive approach that incorporates healthy lifestyle habits and regular monitoring of your health. This can include: * Eating a balanced diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains * Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water * Engaging in regular physical activity to manage stress and promote overall health * Avoiding smoking and secondhand smoke * Managing underlying medical conditions, such as diabetes or kidney diseaseBy taking proactive steps to manage your health and prevent high CO2 levels, you can reduce your risk of developing complications and promote overall well-being.
Conclusion and Next Steps
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with high CO2 blood test results in the comments section below. Additionally, if you have any questions or concerns, please don't hesitate to reach out to us. We're here to provide you with the information and support you need to manage your health and well-being.
What is a normal CO2 blood test result?
+A normal CO2 blood test result is typically between 23 and 29 mEq/L, although this can vary depending on the laboratory and the individual's age and health status.
What are the symptoms of high CO2 levels?
+The symptoms of high CO2 levels can include shortness of breath, fatigue, headaches, nausea, and abdominal pain.
How can I prevent high CO2 levels?
+Preventing high CO2 levels requires a comprehensive approach that incorporates healthy lifestyle habits, such as eating a balanced diet, staying hydrated, engaging in regular physical activity, and managing underlying medical conditions.
