Intro
Discover the high sed rate meaning, its causes, and implications. Learn about erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) tests, inflammation indicators, and related health conditions, such as arthritis and infections, to understand elevated sed rates.
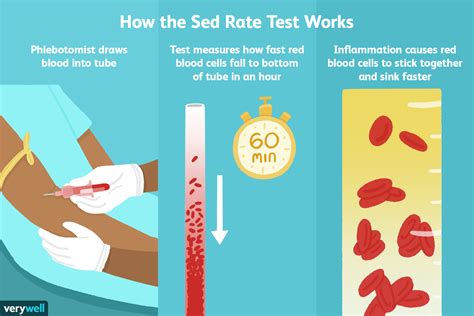
The sedimentation rate, often referred to as the sed rate or ESR, is a blood test that measures how quickly erythrocytes (red blood cells) settle at the bottom of a test tube containing a blood sample. It indirectly measures how much inflammation is in the body. A high sed rate can indicate the presence of inflammation, infection, or an autoimmune disorder. Understanding the meaning and implications of a high sed rate is crucial for both healthcare professionals and individuals concerned about their health.
The process of sedimentation is straightforward: a blood sample is placed in a tall, narrow tube, and the rate at which the red blood cells settle to the bottom is measured. The results are typically reported in millimeters per hour (mm/hr). The sed rate is considered a non-specific test because it does not diagnose a specific disease but rather indicates the presence of an inflammatory condition that may require further investigation.
Inflammation in the body can be caused by numerous factors, including infections, autoimmune diseases, and injuries. When inflammation occurs, the body produces abnormal proteins, which can cause red blood cells to clump together, leading to a faster sedimentation rate. Thus, a high sed rate can be an indicator of an underlying health issue that needs to be addressed.
Understanding Sed Rate Results

To interpret sed rate results, it's essential to consider the reference range provided by the laboratory, as these can vary. Generally, for adults, a normal sed rate is considered to be 0-22 mm/hr for women and 0-15 mm/hr for men, though these values can slightly differ based on age and the specific method used for the test. A high sed rate is typically above these ranges, indicating the presence of inflammation.
Causes of a High Sed Rate
There are numerous causes of a high sed rate, including but not limited to, infections, autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and lupus, cancers, and chronic diseases such as diabetes and kidney disease. In some cases, a high sed rate can be seen in individuals with no apparent symptoms of disease, a condition known as an elevated ESR of unknown origin. This scenario often prompts further diagnostic testing to determine the underlying cause.
Autoimmune Diseases and High Sed Rate
Autoimmune diseases are a significant group of conditions that can cause a high sed rate. These diseases occur when the body's immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues, leading to inflammation and a subsequent increase in the sed rate. Common autoimmune diseases associated with an elevated sed rate include rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), and Hashimoto's thyroiditis. Managing these conditions often involves reducing inflammation and suppressing the immune system's abnormal response.
Diagnosis and Treatment
The diagnosis of conditions associated with a high sed rate typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, laboratory tests (including the sed rate test), and sometimes imaging studies. Once the underlying cause is identified, treatment can be initiated. The goal of treatment is to reduce inflammation, manage symptoms, and address the underlying condition causing the elevated sed rate.
Treatment Approaches for High Sed Rate
Treatment for a high sed rate depends on the underlying cause. For infections, antibiotics may be prescribed. For autoimmune diseases, treatments such as corticosteroids, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), and biologic agents may be used to reduce inflammation and modulate the immune system. In cases of cancer, treatment will focus on the specific type of cancer and may include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or a combination of these.
Living with a High Sed Rate

Living with a condition that causes a high sed rate requires a comprehensive approach to health management. This includes maintaining a healthy lifestyle through a balanced diet, regular exercise, not smoking, and managing stress. It's also crucial to adhere to the prescribed treatment plan and attend follow-up appointments with healthcare providers to monitor the condition and adjust the treatment as necessary.
Lifestyle Modifications for Managing Inflammation
Certain lifestyle modifications can help manage inflammation and potentially reduce a high sed rate. These include consuming an anti-inflammatory diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, staying hydrated, and engaging in regular physical activity. Additionally, practices such as meditation and yoga can help reduce stress, which is known to exacerbate inflammatory conditions.
Monitoring and Follow-Up

Regular monitoring and follow-up with healthcare providers are essential for individuals with a high sed rate. This allows for the adjustment of treatment plans as needed, monitoring of disease progression, and early detection of potential complications. It's also an opportunity for patients to ask questions, express concerns, and learn more about their condition and how to manage it effectively.
The Role of Patient Education
Patient education plays a vital role in the management of conditions associated with a high sed rate. By understanding their condition, the implications of a high sed rate, and the importance of adherence to treatment, individuals can take a more active role in their healthcare. This includes being aware of the signs of worsening inflammation or disease progression and knowing when to seek medical help.
Future Directions and Research
Research into the causes and management of high sed rates is ongoing. Advances in medical technology and a deeper understanding of the immune system and inflammatory processes are leading to the development of new treatments and diagnostic tools. For instance, the discovery of specific biomarkers for different diseases could lead to more targeted and effective therapies.
Emerging Therapies for Inflammatory Conditions
Emerging therapies, including biologic drugs and small molecule inhibitors, offer new hope for the treatment of inflammatory conditions associated with a high sed rate. These therapies are designed to target specific components of the immune response, reducing inflammation while minimizing side effects. As research continues, it is likely that even more effective treatments will become available, improving the quality of life for individuals with these conditions.
Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, a high sed rate is an indicator of inflammation in the body and can be associated with a variety of health conditions. Understanding the causes, diagnosis, and treatment options for a high sed rate is essential for effective management. By working closely with healthcare providers, making informed lifestyle choices, and staying up-to-date with the latest research and treatments, individuals can better manage their condition and improve their overall health.
We invite you to share your thoughts and questions about high sed rates in the comments below. If you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who might benefit from this information. Your engagement and feedback are invaluable in helping us provide the most relevant and useful content.
What does a high sed rate indicate?
+A high sed rate indicates the presence of inflammation in the body, which can be caused by infections, autoimmune diseases, cancers, and other conditions.
How is a high sed rate diagnosed?
+Diagnosis of a high sed rate involves a blood test that measures the rate at which red blood cells settle to the bottom of a test tube. Further diagnostic tests may be needed to determine the underlying cause.
What are the treatment options for a high sed rate?
+Treatment options depend on the underlying cause but may include medications to reduce inflammation, such as corticosteroids and biologic agents, as well as lifestyle modifications to manage stress and promote overall health.
Can lifestyle changes help reduce a high sed rate?
+Yes, lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, managing stress, and not smoking can help reduce inflammation and potentially lower a high sed rate.
Why is regular monitoring important for individuals with a high sed rate?
+Regular monitoring allows healthcare providers to adjust treatment plans as needed, monitor disease progression, and detect potential complications early, leading to better health outcomes.
