Intro
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is crucial for overall well-being, as high sugar glucose levels can lead to various health complications. The body's ability to regulate blood sugar levels is a delicate process, and when it is disrupted, it can have severe consequences. High sugar glucose levels, also known as hyperglycemia, can be caused by a variety of factors, including a poor diet, lack of physical activity, and certain medical conditions. Understanding the importance of managing blood sugar levels is essential for preventing and treating related health issues.
The impact of high sugar glucose levels on the body cannot be overstated. When blood sugar levels are consistently high, it can lead to damage to various organs and tissues, including the kidneys, nerves, and eyes. Furthermore, high sugar glucose levels can increase the risk of developing conditions such as heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease. It is essential to recognize the signs and symptoms of high sugar glucose levels, which can include increased thirst and urination, blurred vision, and slow healing of cuts and wounds. By being aware of these symptoms, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their blood sugar levels and prevent long-term damage.
Managing high sugar glucose levels requires a comprehensive approach that incorporates lifestyle changes, dietary modifications, and, in some cases, medication. A healthy diet that is low in added sugars, refined carbohydrates, and saturated fats can help regulate blood sugar levels. Regular physical activity, such as walking or jogging, can also improve insulin sensitivity and reduce blood sugar levels. Additionally, getting enough sleep, managing stress, and staying hydrated are all essential for maintaining healthy blood sugar levels. By adopting these habits and being mindful of their blood sugar levels, individuals can reduce their risk of developing related health complications and improve their overall quality of life.
Understanding Blood Sugar Levels
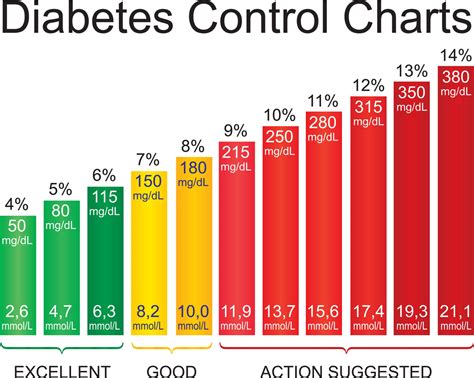
Normal Blood Sugar Levels
Normal blood sugar levels typically range from 70 to 140 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) after eating. However, these levels can vary depending on the individual and their overall health. For example, individuals with diabetes may have a higher target range for their blood sugar levels, typically between 100 and 180 mg/dL. It is essential to work with a healthcare provider to determine the optimal blood sugar range for each individual.Causes of High Sugar Glucose Levels
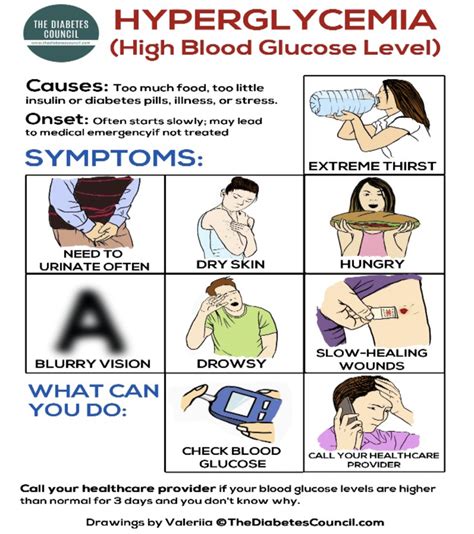
Risk Factors for High Sugar Glucose Levels
There are several risk factors that can increase the likelihood of developing high sugar glucose levels. These include: * Obesity * Physical inactivity * Family history of diabetes * Age (45 or older) * History of gestational diabetes or delivering a baby over 9 pounds * Certain ethnicities, such as African American, Hispanic/Latino, or American IndianComplications of High Sugar Glucose Levels

Managing High Sugar Glucose Levels
Managing high sugar glucose levels requires a comprehensive approach that incorporates lifestyle changes, dietary modifications, and, in some cases, medication. A healthy diet that is low in added sugars, refined carbohydrates, and saturated fats can help regulate blood sugar levels. Regular physical activity, such as walking or jogging, can also improve insulin sensitivity and reduce blood sugar levels. Additionally, getting enough sleep, managing stress, and staying hydrated are all essential for maintaining healthy blood sugar levels.Treatment Options for High Sugar Glucose Levels
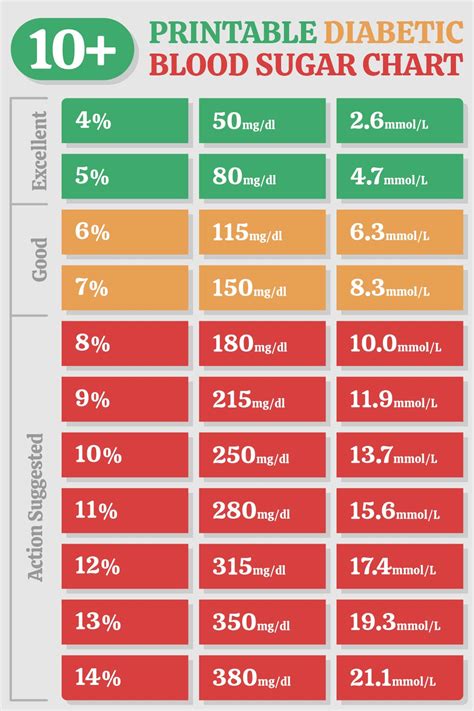
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Monitoring blood sugar levels is essential for managing high sugar glucose levels. There are several ways to monitor blood sugar levels, including: * Fasting blood sugar tests * Postprandial blood sugar tests * Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) tests * Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systemsPreventing High Sugar Glucose Levels

Healthy Eating Habits
Healthy eating habits are essential for preventing high sugar glucose levels. This includes: * Eating a balanced diet that is low in added sugars, refined carbohydrates, and saturated fats * Incorporating plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein sources into your diet * Limiting your intake of sugary drinks and fast food * Cooking at home using fresh ingredientsConclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with managing high sugar glucose levels in the comments below. If you found this article informative, please share it with others who may benefit from this information. By working together, we can promote healthy blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of related health complications.
What are the symptoms of high sugar glucose levels?
+The symptoms of high sugar glucose levels can include increased thirst and urination, blurred vision, and slow healing of cuts and wounds.
How can I prevent high sugar glucose levels?
+Preventing high sugar glucose levels requires a proactive approach that incorporates lifestyle changes and dietary modifications, such as eating a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and getting enough sleep.
What are the complications of high sugar glucose levels?
+The complications of high sugar glucose levels can include heart disease, kidney disease, nerve damage, and eye damage.
