Intro
Discover how a high WBC count impacts health, including infection risks, inflammation, and immune system effects, and learn about leukocytosis symptoms and treatments.
A high white blood cell (WBC) count, also known as leukocytosis, can be an indication of an underlying health issue. White blood cells are a crucial part of the immune system, helping to fight off infections and diseases. However, when the WBC count becomes elevated, it can have various effects on the body. In this article, we will delve into the ways a high WBC count can impact health, exploring the potential causes, symptoms, and consequences of this condition.
Elevated WBC counts can be caused by a range of factors, including infections, inflammatory diseases, and even certain types of cancer. When the body detects a foreign invader, such as a bacterium or virus, it responds by producing more white blood cells to combat the infection. This surge in WBC production can lead to a higher-than-normal count. Additionally, conditions like leukemia, a type of blood cancer, can also cause an overproduction of white blood cells, resulting in an elevated count.
The effects of a high WBC count on health can be far-reaching and varied. Some individuals may experience mild symptoms, while others may face more severe consequences. Understanding the potential risks and complications associated with an elevated WBC count is essential for maintaining overall health and well-being. In the following sections, we will examine the different ways a high WBC count can affect health, including its impact on the immune system, cardiovascular health, and more.
Introduction to High WBC Count
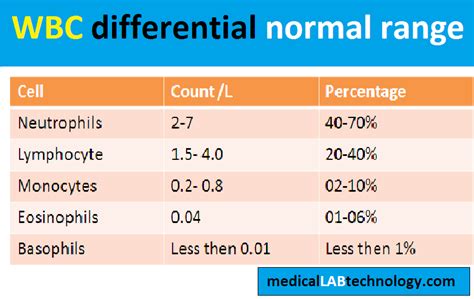
Causes of High WBC Count
The causes of a high WBC count can be divided into several categories, including infections, inflammatory diseases, and blood disorders. Infections such as pneumonia, tuberculosis, and sepsis can cause an elevated WBC count, as the body produces more white blood cells to combat the infection. Inflammatory diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and inflammatory bowel disease can also lead to an increased WBC count. Additionally, blood disorders like leukemia and lymphoma can cause an overproduction of white blood cells, resulting in an elevated count.Impact on the Immune System
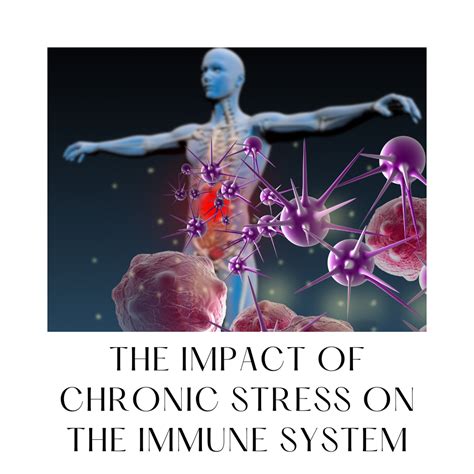
Effects on Immune Function
An elevated WBC count can affect immune function in several ways. A high WBC count can indicate that the immune system is responding to an infection or inflammation, which can lead to an overactive immune response. This can result in tissue damage and other complications, such as autoimmune diseases. Additionally, an elevated WBC count can also lead to immunosuppression, which is a state of reduced immune function. This can increase the risk of infections and other diseases.Cardiovascular Risks
Mechanisms Behind Cardiovascular Risks
The mechanisms behind the cardiovascular risks associated with a high WBC count are complex and multifaceted. One possible explanation is that an elevated WBC count may contribute to inflammation in the blood vessels, which can lead to the development of atherosclerosis. Additionally, an overactive immune response can also lead to the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, which can further contribute to cardiovascular disease.Neurological Effects
Potential Causes of Neurological Effects
The potential causes of neurological effects associated with a high WBC count are varied and complex. One possible explanation is that an elevated WBC count may indicate the presence of a neurological disorder, such as multiple sclerosis or meningitis. Additionally, an overactive immune response can also lead to the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, which can further contribute to neurological symptoms.Impact on Organ Function
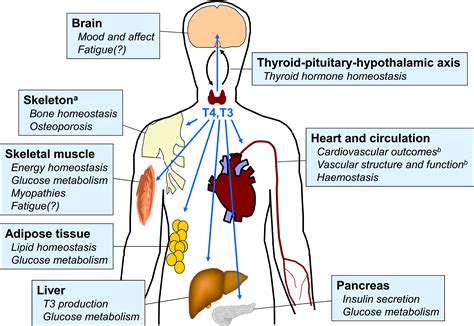
Potential Causes of Organ Damage
The potential causes of organ damage associated with a high WBC count are varied and complex. One possible explanation is that an elevated WBC count may indicate the presence of an infection or inflammation in the kidneys or liver, which can lead to organ damage and dysfunction. Additionally, an overactive immune response can also lead to the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, which can further contribute to organ damage.Conclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with high WBC counts in the comments section below. Have you or a loved one been diagnosed with an elevated WBC count? What were the symptoms, and how was the condition managed? Your insights and stories can help others better understand this complex condition and its effects on health.
What is a high WBC count?
+A high WBC count, also known as leukocytosis, is a condition where the number of white blood cells in the blood is higher than normal.
What are the causes of a high WBC count?
+The causes of a high WBC count can be divided into several categories, including infections, inflammatory diseases, and blood disorders.
What are the symptoms of a high WBC count?
+The symptoms of a high WBC count can vary depending on the underlying cause, but may include fever, fatigue, and swelling or pain in the affected area.
How is a high WBC count diagnosed?
+A high WBC count is typically diagnosed through a blood test, which measures the number of white blood cells in the blood.
What is the treatment for a high WBC count?
+The treatment for a high WBC count depends on the underlying cause, but may include antibiotics, anti-inflammatory medications, or other therapies to manage the condition.
