Intro
Discover causes and symptoms of high WBC count, including leukocytosis, infection, and inflammation, and learn how to manage elevated white blood cell levels with treatment options and lifestyle changes.
A high white blood cell (WBC) count, also known as leukocytosis, is a condition where the number of white blood cells in the body exceeds the normal range. White blood cells are an essential part of the immune system, helping to fight off infections and diseases. However, an elevated WBC count can be a sign of an underlying health issue that requires medical attention. In this article, we will delve into the world of high WBC counts, exploring the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options available.
The importance of understanding high WBC counts cannot be overstated. A high WBC count can be a indicator of a range of health issues, from minor infections to life-threatening diseases. By being aware of the causes and symptoms of high WBC counts, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their health and seek medical attention when necessary. Furthermore, understanding the diagnosis and treatment options available can help individuals make informed decisions about their healthcare.
A high WBC count can be caused by a variety of factors, including infections, inflammatory diseases, and even certain types of cancer. In some cases, a high WBC count may be a normal response to a minor infection, such as a cold or flu. However, in other cases, it may be a sign of a more serious underlying condition that requires medical attention. Some common causes of high WBC counts include pneumonia, tuberculosis, and appendicitis. Additionally, certain types of cancer, such as leukemia, can also cause an elevated WBC count.
Understanding White Blood Cells
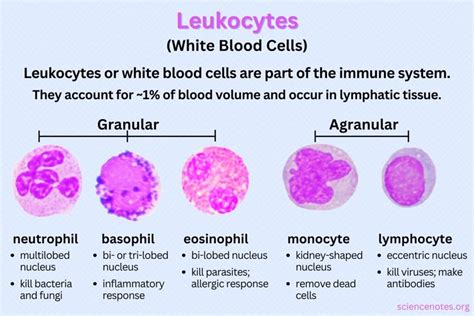
Types of White Blood Cells
There are five main types of white blood cells, each with its own unique function: * Neutrophils: These cells are the most abundant type of white blood cell and play a key role in fighting off bacterial infections. * Lymphocytes: These cells are responsible for specific immune responses, such as recognizing and attacking specific viruses and bacteria. * Monocytes: These cells mature into macrophages, which help to clean up dead cells and foreign substances. * Eosinophils: These cells play a role in fighting off parasitic infections and in allergic reactions. * Basophils: These cells are involved in inflammatory responses and play a role in allergic reactions.Causes of High WBC Count

Symptoms of High WBC Count
The symptoms of a high WBC count can vary depending on the underlying cause. Some common symptoms include: * Fever * Chills * Fatigue * Weight loss * Night sweats * Swollen lymph nodes * Joint painDiagnosis of High WBC Count

Treatment Options for High WBC Count
The treatment options for a high WBC count will depend on the underlying cause. Some common treatment options include: * Antibiotics: If the elevated WBC count is caused by a bacterial infection, antibiotics may be prescribed. * Anti-inflammatory medications: If the elevated WBC count is caused by an inflammatory disease, anti-inflammatory medications may be prescribed. * Chemotherapy: If the elevated WBC count is caused by cancer, chemotherapy may be necessary. * Supportive care: In some cases, supportive care, such as rest and hydration, may be necessary to help the body recover from an infection or illness.Complications of High WBC Count

Prevention of High WBC Count
There are several steps that can be taken to prevent a high WBC count, including: * Practicing good hygiene: Washing hands regularly and avoiding close contact with people who are sick can help to prevent the spread of infection. * Getting vaccinated: Getting vaccinated against certain diseases, such as the flu, can help to prevent infection. * Avoiding certain medications: Certain medications, such as corticosteroids, can cause an elevated WBC count. Avoiding these medications or taking them only as directed can help to prevent a high WBC count.What is a normal WBC count?
+A normal WBC count is typically between 4,000 and 11,000 cells per microliter of blood.
What are the symptoms of a high WBC count?
+The symptoms of a high WBC count can vary depending on the underlying cause, but may include fever, chills, fatigue, weight loss, and night sweats.
How is a high WBC count diagnosed?
+A high WBC count is typically diagnosed through a blood test, known as a complete blood count (CBC).
What are the treatment options for a high WBC count?
+The treatment options for a high WBC count will depend on the underlying cause, but may include antibiotics, anti-inflammatory medications, chemotherapy, and supportive care.
Can a high WBC count be prevented?
+Yes, there are several steps that can be taken to prevent a high WBC count, including practicing good hygiene, getting vaccinated, and avoiding certain medications.
