Intro
Discover how Bupropion works through 5 mechanisms, including neurotransmitter regulation, dopamine boost, and appetite suppression, to aid smoking cessation, depression treatment, and weight loss management, with related benefits for mental health and well-being.
Bupropion, commonly known by its brand name Wellbutrin, is a medication that has been widely used for the treatment of depression and seasonal affective disorder. It is also used as a smoking cessation aid under the brand name Zyban. The mechanism of action of bupropion is complex and not fully understood, but research has shed light on several key ways it works to produce its therapeutic effects. Understanding how bupropion works can help individuals better appreciate its benefits and potential side effects.
The unique pharmacological profile of bupropion sets it apart from other antidepressants. Unlike many other medications used to treat depression, which often work by increasing the levels of serotonin in the brain, bupropion primarily affects the levels of dopamine and norepinephrine. These neurotransmitters play crucial roles in mood regulation, reward, and other functions. By influencing these neurotransmitters, bupropion can help improve mood, reduce cravings for nicotine, and increase energy levels.
Bupropion's efficacy in treating depression and aiding in smoking cessation has made it a valuable option for individuals struggling with these issues. Its ability to enhance motivation and reduce withdrawal symptoms makes it particularly useful for smokers trying to quit. Moreover, its relatively favorable side effect profile compared to some other antidepressants has contributed to its popularity. As research continues to uncover the intricacies of bupropion's mechanisms, its applications and potential benefits are likely to expand.
Introduction to Bupropion's Mechanism of Action
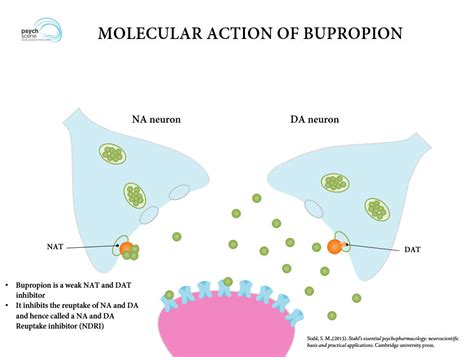
Role of Dopamine
Dopamine is often referred to as the "pleasure molecule" because of its role in reward, motivation, and pleasure. It is involved in the regulation of movement, emotion, and the ability to experience pleasure and pain. In the context of depression, dopamine levels are often found to be lower than normal. By increasing dopamine levels, bupropion can help improve mood and reduce symptoms of depression.How Bupropion Affects Norepinephrine
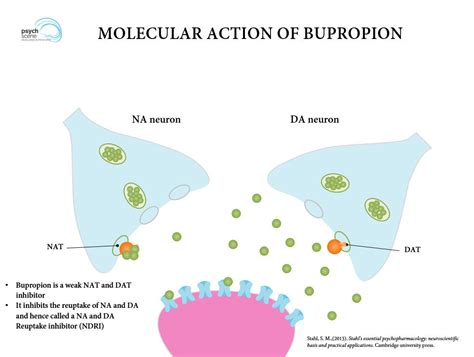
Impact on Nicotine Cravings
Bupropion's efficacy in aiding smoking cessation is believed to be partly due to its effects on dopamine and norepinephrine, which are involved in the brain's response to nicotine. Nicotine stimulates the release of these neurotransmitters, leading to feelings of pleasure and reward. By increasing the levels of dopamine and norepinephrine, bupropion can help reduce cravings for nicotine and alleviate withdrawal symptoms, making it easier for individuals to quit smoking.Bupropion's Therapeutic Benefits
Side Effects and Considerations
While bupropion is generally well-tolerated, it can cause side effects, including dry mouth, nausea, insomnia, and headaches. In rare cases, it can increase the risk of seizures, particularly in individuals with a history of seizure disorders. It is essential for individuals considering bupropion to discuss their medical history and any concerns with their healthcare provider to ensure safe and effective treatment.Conclusion and Future Directions
Final Thoughts
Bupropion's unique profile and effectiveness make it a significant component of modern psychiatric and addiction treatment. Its potential for future development and its current benefits underscore the importance of continued research into its mechanisms and applications. By understanding how bupropion works, individuals can better appreciate its value and make informed decisions about their treatment options.What is bupropion primarily used for?
+Bupropion is primarily used for the treatment of major depressive disorder and seasonal affective disorder, as well as an aid for smoking cessation.
How does bupropion work?
+Bupropion works by inhibiting the reuptake of dopamine and norepinephrine, increasing their levels in the brain, which helps improve mood and reduce nicotine cravings.
What are common side effects of bupropion?
+Common side effects of bupropion include dry mouth, nausea, insomnia, and headaches. In rare cases, it can increase the risk of seizures.
