Intro
Discover how Cefdinir works through its antibacterial properties, tackling infections with efficacy, and exploring its mechanism, dosage, and side effects, to understand this antibiotics role in treating bacterial infections.
Cefdinir is a cephalosporin antibiotic that is used to treat a variety of bacterial infections, including those of the skin, respiratory tract, and urinary tract. It is a third-generation cephalosporin, which means it has a broader spectrum of activity against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria compared to earlier generations of cephalosporins. Understanding how cefdinir works can help individuals appreciate its effectiveness and importance in treating bacterial infections.
The mechanism of action of cefdinir, like other cephalosporins, involves interfering with the synthesis of the bacterial cell wall. Bacteria have a cell wall that provides structural support and maintains the osmotic environment of the cell. Cefdinir binds to penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) located inside the bacterial cell wall, inhibiting the cross-linking of peptidoglycan chains. This inhibition weakens the cell wall, leading to osmotic instability and eventually causing the bacterial cell to lyse and die.
Cefdinir's effectiveness against a wide range of bacterial infections makes it a valuable antibiotic in clinical practice. Its ability to penetrate into tissues and fluids, such as sinus and lung tissues, enhances its therapeutic efficacy. Moreover, cefdinir has been shown to have a post-antibiotic effect, where the suppression of bacterial growth continues even after the drug has been eliminated from the system. This characteristic contributes to its effectiveness in treating infections with a relatively short treatment course.
How Cefdinir Works Against Bacterial Infections
Cefdinir's spectrum of activity includes common pathogens responsible for community-acquired pneumonia, acute bacterial sinusitis, and uncomplicated skin and skin structure infections. It is particularly effective against Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and Moraxella catarrhalis, which are common causes of respiratory infections. For urinary tract infections, cefdinir has shown efficacy against Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Proteus mirabilis.
Key Mechanisms of Cefdinir
The key to cefdinir's success lies in its pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties. It is well absorbed orally, achieving peak plasma concentrations within 2 to 4 hours. Cefdinir is distributed widely into body tissues and fluids, ensuring that therapeutic concentrations are reached at the site of infection. Its half-life of approximately 1.7 to 2.3 hours allows for twice-daily dosing, enhancing patient compliance.Cefdinir's Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics
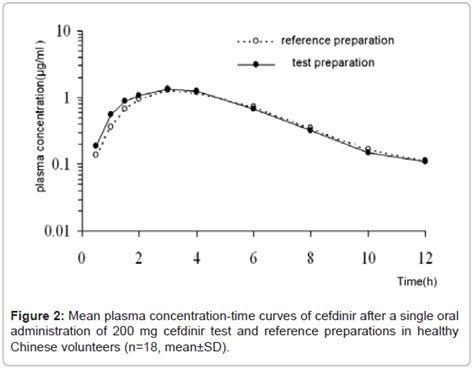
Understanding the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of cefdinir is crucial for optimizing its use. The drug's bioavailability is approximately 20-30% when taken orally, but this can be improved when taken with food. Cefdinir is primarily excreted unchanged in the urine, with a small fraction undergoing renal tubular secretion. This renal excretion suggests that dose adjustments may be necessary in patients with significant renal impairment to avoid accumulation and potential toxicity.
Benefits of Using Cefdinir
The benefits of using cefdinir include its broad spectrum of activity, convenience of twice-daily dosing, and relatively favorable side effect profile. Compared to other antibiotics, cefdinir has a lower incidence of certain adverse effects, such as diarrhea and nausea, although it can cause these in some patients. Its efficacy in treating infections caused by susceptible organisms makes it a preferred choice for many clinicians.Common Uses of Cefdinir

Cefdinir is commonly used to treat community-acquired pneumonia, acute bacterial sinusitis, uncomplicated skin and skin structure infections, and uncomplicated urinary tract infections. Its use in pediatric patients is also well established, particularly for otitis media (middle ear infections) and streptococcal pharyngitis (strep throat). The drug's safety and efficacy profile supports its use in a wide range of patients, from children to adults.
Resistance and Sensitivity
The issue of antibiotic resistance is a growing concern worldwide, and cefdinir is no exception. Resistance to cefdinir can develop through various mechanisms, including the production of beta-lactamases that inactivate the drug, alterations in PBPs that reduce drug binding, and changes in membrane permeability that decrease drug uptake. Monitoring resistance patterns is crucial for ensuring the continued effectiveness of cefdinir and other antibiotics.Managing Antibiotic Resistance
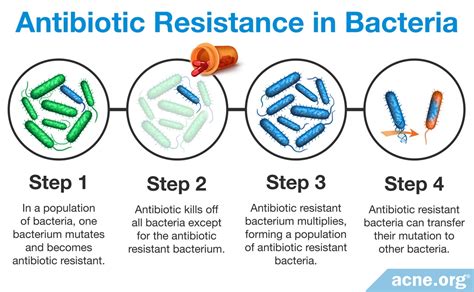
Strategies to manage antibiotic resistance include the prudent use of antibiotics, infection control practices, and the development of new antibiotics. Educating healthcare providers and the public about the appropriate use of antibiotics can help reduce the selective pressure that drives resistance. Furthermore, research into new antimicrobial agents and novel therapeutic approaches is essential for staying ahead of emerging resistance.
Future Perspectives
The future of cefdinir and other antibiotics depends on our ability to balance their use with the need to prevent resistance. As resistance continues to evolve, there will be an increasing need for new antibiotics and alternative therapies. Additionally, improving our understanding of the human microbiome and its interaction with antibiotics can provide insights into how to minimize the impact of antibiotic use on beneficial bacteria.Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, cefdinir is a valuable antibiotic for treating various bacterial infections. Its effectiveness, combined with its relatively favorable safety profile, makes it a preferred choice for many clinicians. However, the challenge of antibiotic resistance necessitates responsible use and ongoing research into new therapeutic strategies. By understanding how cefdinir works and its role in managing bacterial infections, we can better appreciate the importance of preserving its efficacy for future generations.
We invite readers to share their thoughts and experiences with cefdinir and antibiotic use in general. Your insights can contribute to a broader discussion on how to optimize antibiotic therapy while minimizing the risk of resistance. Please comment below or share this article with others who may benefit from this information.
What is cefdinir used for?
+Cefdinir is used to treat a variety of bacterial infections, including those of the skin, respiratory tract, and urinary tract.
How does cefdinir work?
+Cefdinir works by inhibiting the synthesis of the bacterial cell wall, leading to osmotic instability and cell lysis.
What are the common side effects of cefdinir?
+Common side effects of cefdinir include diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting, although it generally has a favorable side effect profile compared to other antibiotics.
