Intro
Discover how beta blockers work to reduce blood pressure, alleviate anxiety, and manage heart conditions, exploring their mechanisms, benefits, and side effects in cardiovascular health and stress management.
The world of medicine is filled with various treatments and medications designed to combat a wide range of health issues. Among these, beta blockers have emerged as a crucial class of drugs used to manage several cardiovascular conditions. But how do beta blockers work, and what makes them so effective in treating heart-related problems? To understand the mechanism of beta blockers, it's essential to delve into the realm of cardiovascular health and explore the intricacies of the heart's functioning.
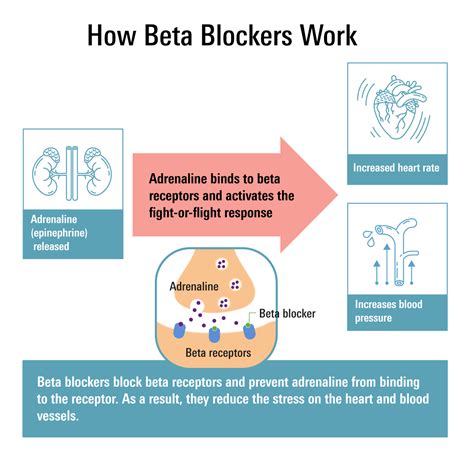
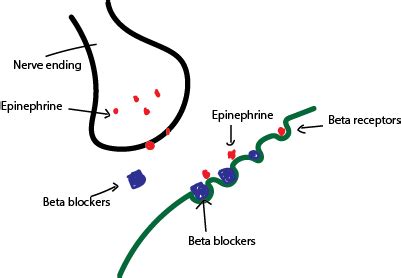
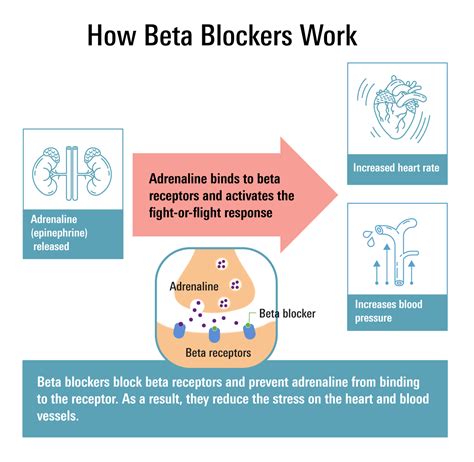
The heart is a vital organ that pumps blood throughout the body, supplying oxygen and nutrients to tissues and organs. Its functioning is influenced by the autonomic nervous system, which comprises the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. The sympathetic nervous system is responsible for the "fight or flight" response, increasing heart rate and blood pressure to prepare the body for physical activity. On the other hand, the parasympathetic nervous system promotes relaxation and reduces heart rate. Beta blockers work by targeting the sympathetic nervous system, specifically the beta receptors found in the heart and blood vessels.
The discovery of beta blockers dates back to the 1960s, and since then, they have become a cornerstone in the treatment of various cardiovascular conditions, including hypertension, angina, heart failure, and arrhythmias. But what makes beta blockers so effective? To answer this question, it's crucial to understand the working mechanism of these drugs. Beta blockers work by blocking the effects of the hormone epinephrine, also known as adrenaline, and norepinephrine on the heart and blood vessels. By doing so, they reduce the heart rate, lower blood pressure, and decrease the force of the heart's contractions.
How Beta Blockers Work
Benefits of Beta Blockers
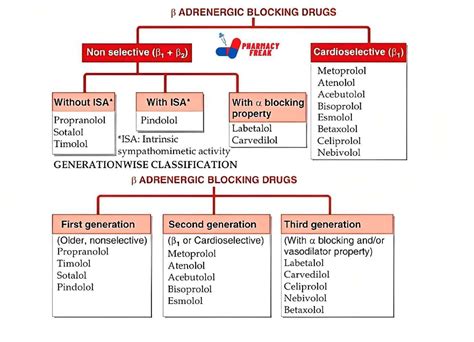
The benefits of beta blockers are numerous and well-documented. They have been shown to: * Reduce the risk of heart attack and stroke * Lower blood pressure and prevent the progression of hypertension * Improve symptoms of angina and reduce the frequency of episodes * Slow the progression of heart failure and improve survival rates * Control arrhythmias and prevent sudden cardiac death Beta blockers have also been used to treat non-cardiovascular conditions, such as performance anxiety, migraines, and glaucoma. Their ability to reduce heart rate and blood pressure makes them an effective treatment for these conditions.Types of Beta Blockers
Side Effects of Beta Blockers
While beta blockers are generally well-tolerated, they can cause several side effects, including: * Fatigue and drowsiness * Dizziness and lightheadedness * Shortness of breath and wheezing * Cold hands and feet * Digestive problems, such as constipation and diarrhea * Erectile dysfunction and decreased libido It's essential to weigh the benefits and risks of beta blockers and discuss any concerns with a healthcare provider.Working Mechanism of Beta Blockers
Steps to Take Beta Blockers
To get the most out of beta blockers, it's essential to follow these steps: * Take the medication as directed by a healthcare provider * Monitor blood pressure and heart rate regularly * Report any side effects or concerns to a healthcare provider * Do not stop taking the medication without consulting a healthcare provider * Inform a healthcare provider about any other medications or supplements being takenBenefits of Beta Blockers in Cardiovascular Health
Practical Examples of Beta Blockers
Beta blockers are used in various real-life scenarios, including: * Treating hypertension and angina in patients with cardiovascular disease * Controlling arrhythmias and preventing sudden cardiac death in patients with heart failure * Reducing the risk of heart attack and stroke in patients with high blood pressure * Improving symptoms of performance anxiety and migraines * Treating glaucoma and reducing intraocular pressureStatistical Data on Beta Blockers

FAQs on Beta Blockers
What are beta blockers?
+Beta blockers are a class of medications that block the effects of the hormone epinephrine and norepinephrine on the heart and blood vessels.
What are the benefits of beta blockers?
+The benefits of beta blockers include reducing the risk of heart attack and stroke, lowering blood pressure, improving symptoms of angina, and controlling arrhythmias.
What are the side effects of beta blockers?
+The side effects of beta blockers include fatigue, dizziness, shortness of breath, cold hands and feet, and digestive problems.
In conclusion, beta blockers are a crucial class of medications used to treat various cardiovascular conditions. Their ability to block the effects of epinephrine and norepinephrine on the heart and blood vessels makes them an effective treatment for hypertension, angina, heart failure, and arrhythmias. By understanding the working mechanism of beta blockers and their benefits, individuals can make informed decisions about their treatment options. We encourage readers to share their experiences with beta blockers and ask any questions they may have about these medications.
