Intro
Discover how FSA works with 5 key methods, utilizing flexible spending, health savings, and dependent care benefits to maximize tax-advantaged savings and minimize healthcare costs.
The concept of FSA, or Flexible Spending Account, has been gaining popularity over the years due to its numerous benefits for employees and employers alike. An FSA is an account that allows employees to set aside a portion of their income on a pre-tax basis to pay for eligible expenses related to healthcare, childcare, or other qualified expenses. In this article, we will delve into the world of FSAs, exploring how they work, their benefits, and the various ways they can be utilized to maximize savings and reduce taxable income.
One of the primary reasons FSAs have become so popular is their ability to help individuals and families save money on healthcare expenses. With the rising costs of medical care, having a way to pay for out-of-pocket expenses with pre-tax dollars can be a significant advantage. FSAs can be used to cover a wide range of healthcare expenses, from doctor visits and prescriptions to medical equipment and procedures. By setting aside a portion of their income in an FSA, individuals can reduce their taxable income, thereby lowering their tax liability.
Another significant benefit of FSAs is their flexibility. These accounts can be used to pay for a variety of expenses, including childcare costs, elder care, and even certain types of home modifications. This flexibility makes FSAs an attractive option for individuals with diverse needs and expenses. Moreover, FSAs can be used in conjunction with other benefits, such as health savings accounts (HSAs) and health reimbursement arrangements (HRAs), to create a comprehensive benefits package.
How FSA Works
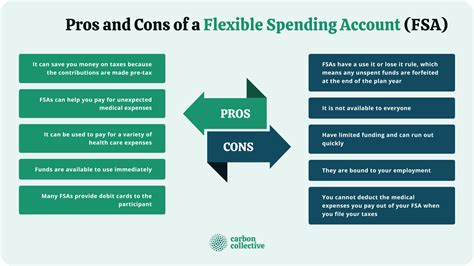
Key Components of FSA
The key components of an FSA include the contribution limit, the eligible expenses, and the claims process. The contribution limit refers to the maximum amount an employee can contribute to their FSA each year. The eligible expenses are the types of expenses that can be paid for using FSA funds, such as healthcare expenses, childcare costs, and elder care. The claims process involves submitting receipts and other documentation to the FSA administrator to reimburse expenses.Benefits of FSA

Types of FSA
There are several types of FSAs, including healthcare FSAs, childcare FSAs, and elder care FSAs. Healthcare FSAs are used to pay for medical expenses, such as doctor visits, prescriptions, and medical equipment. Childcare FSAs are used to pay for childcare costs, such as daycare or after-school programs. Elder care FSAs are used to pay for expenses related to caring for an elderly or disabled family member, such as adult day care or home care.How to Use FSA

Steps to Follow
The steps to follow when using an FSA include: * Electing to contribute to the FSA during open enrollment * Submitting claims for reimbursement for eligible expenses * Keeping receipts and other documentation for eligible expenses * Monitoring the FSA balance to ensure sufficient funds for expenses * Understanding the eligible expenses and the claims processMaximizing FSA Benefits

Strategies for Maximizing Benefits
Strategies for maximizing FSA benefits include: * Contributing the maximum amount allowed to the FSA * Keeping track of eligible expenses and submitting claims regularly * Understanding the eligible expenses and the claims process * Using the FSA to pay for expenses that may not be covered by other benefits * Monitoring the FSA balance to avoid forfeiting unused fundsFSA and Tax Savings
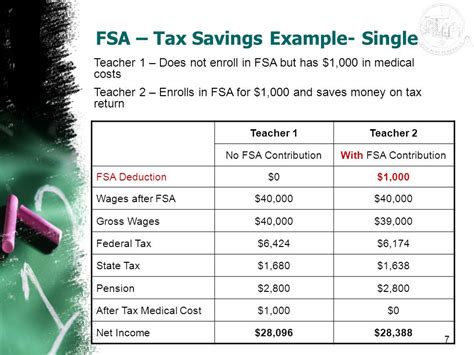
Tax Implications
The tax implications of FSAs include the reduction of taxable income, which can result in lower taxes. FSAs are also subject to certain tax rules and regulations, such as the requirement to use the funds for eligible expenses. Employees should understand the tax implications of FSAs to maximize their benefits and avoid any tax penalties.Common FSA Mistakes

Avoiding Mistakes
To avoid common FSA mistakes, employees should carefully plan their contributions and expenses. This includes understanding the eligible expenses, the contribution limit, and the claims process. Employees should also keep track of their FSA balance to ensure sufficient funds for expenses and avoid forfeiting unused funds at the end of the year.FSA and Other Benefits
Combining Benefits
Combining FSAs with other benefits can provide significant advantages, including: * Increased savings and reduced taxable income * Comprehensive coverage for healthcare expenses and other qualified expenses * Flexibility in managing benefits and expenses * Ability to pay for expenses that may not be covered by other benefitsWhat is an FSA?
+An FSA, or Flexible Spending Account, is an account that allows employees to set aside a portion of their income on a pre-tax basis to pay for eligible expenses related to healthcare, childcare, or other qualified expenses.
How do I use an FSA?
+To use an FSA, employees must first elect to contribute to their FSA during the open enrollment period. They can then submit claims for reimbursement for eligible expenses throughout the year.
What are the benefits of an FSA?
+The benefits of an FSA include the ability to reduce taxable income, budget for healthcare expenses and other qualified expenses, and pay for expenses that may not be covered by other benefits.
Can I use an FSA with other benefits?
+Yes, FSAs can be used in conjunction with other benefits, such as health savings accounts (HSAs) and health reimbursement arrangements (HRAs), to create a comprehensive benefits package.
How do I avoid common FSA mistakes?
+To avoid common FSA mistakes, employees should carefully plan their contributions and expenses, understand the eligible expenses and the claims process, and keep track of their FSA balance to ensure sufficient funds for expenses and avoid forfeiting unused funds at the end of the year.
In conclusion, FSAs can provide significant benefits for employees, including the ability to reduce taxable income, budget for healthcare expenses and other qualified expenses, and pay for expenses that may not be covered by other benefits. By understanding how FSAs work, the benefits of FSAs, and how to use FSAs effectively, employees can maximize their savings and reduce their taxable income. If you have any questions or comments about FSAs, please feel free to share them below. We would love to hear your thoughts and help you make the most of your FSA benefits.
