Intro
Discover how general anesthesia works, its effects, and risks. Learn about sedation, intubation, and anesthesia types, including local and regional anesthesia, for a safe medical procedure.
General anesthesia is a state of deep sedation, immobility, and amnesia that is induced through the administration of various medications. It is a crucial aspect of modern medicine, allowing patients to undergo surgical procedures without feeling pain, discomfort, or anxiety. The importance of general anesthesia cannot be overstated, as it has revolutionized the field of surgery and enabled medical professionals to perform complex and life-saving operations. In this article, we will delve into the world of general anesthesia, exploring its mechanisms, benefits, and applications.
General anesthesia has a rich history, dating back to the mid-19th century when the first anesthetic agents were discovered. Over the years, significant advancements have been made in the field, leading to the development of safer, more effective, and more targeted anesthetic techniques. Today, general anesthesia is used in a wide range of medical procedures, from routine surgeries to complex, high-risk operations. Despite its widespread use, many people remain unaware of the intricacies of general anesthesia, and it is essential to educate patients, medical professionals, and the general public about its workings and benefits.
The concept of general anesthesia may seem daunting, but it is a fascinating topic that warrants exploration. By understanding how general anesthesia works, individuals can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities of human physiology and the remarkable advancements that have been made in the field of medicine. Whether you are a patient, a medical professional, or simply an interested reader, this article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of general anesthesia, covering its mechanisms, applications, and benefits.
Introduction to General Anesthesia

General anesthesia is a type of anesthesia that induces a state of deep sedation, immobility, and amnesia. It is typically administered through a combination of medications, including anesthetics, sedatives, and muscle relaxants. The primary goal of general anesthesia is to render the patient unconscious and unable to feel pain, allowing medical professionals to perform surgical procedures without causing undue distress or discomfort. General anesthesia can be administered through various routes, including inhalation, injection, or a combination of both.
Types of General Anesthesia
There are several types of general anesthesia, each with its own unique characteristics and applications. The most common types of general anesthesia include: * Inhalational anesthesia: This type of anesthesia is administered through inhalation, using anesthetic agents such as sevoflurane, isoflurane, or desflurane. * Intravenous anesthesia: This type of anesthesia is administered through injection, using anesthetic agents such as propofol, midazolam, or fentanyl. * Balanced anesthesia: This type of anesthesia combines multiple anesthetic agents to achieve a balanced effect, minimizing side effects and maximizing efficacy.How General Anesthesia Works
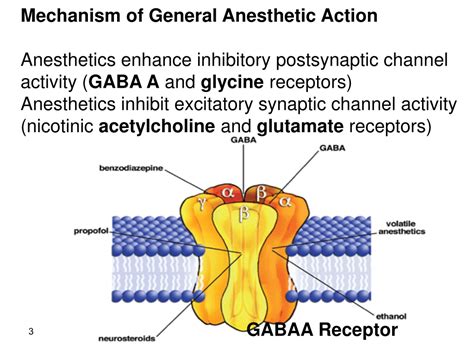
General anesthesia works by targeting specific receptors and pathways in the brain and nervous system. Anesthetic agents interact with various molecular targets, including GABA receptors, NMDA receptors, and potassium channels, to induce a state of deep sedation and immobility. The exact mechanisms of general anesthesia are complex and not fully understood, but research suggests that anesthetic agents alter the activity of neural networks, disrupting normal brain function and inducing a state of unconsciousness.
The Role of Anesthetic Agents
Anesthetic agents play a crucial role in general anesthesia, and their selection depends on various factors, including the type of surgery, patient health, and anesthetic technique. Common anesthetic agents used in general anesthesia include: * Sevoflurane: A volatile anesthetic agent used for inhalational anesthesia. * Propofol: An intravenous anesthetic agent used for induction and maintenance of anesthesia. * Fentanyl: A potent opioid analgesic used for pain management and anesthesia.Benefits of General Anesthesia

General anesthesia offers numerous benefits, making it an essential tool in modern medicine. Some of the key benefits of general anesthesia include:
- Pain relief: General anesthesia eliminates pain and discomfort, allowing patients to undergo surgical procedures without distress.
- Immobility: General anesthesia induces muscle relaxation, preventing movement and ensuring patient safety during surgery.
- Amnesia: General anesthesia causes amnesia, erasing memories of the surgical procedure and reducing anxiety and stress.
- Reduced stress: General anesthesia minimizes stress and anxiety, promoting a smooth and comfortable recovery.
Applications of General Anesthesia
General anesthesia has a wide range of applications, including: * Surgical procedures: General anesthesia is used in various surgical procedures, from routine operations to complex, high-risk surgeries. * Diagnostic procedures: General anesthesia is used in diagnostic procedures, such as endoscopy and colonoscopy, to minimize discomfort and anxiety. * Pain management: General anesthesia is used in pain management, providing relief from chronic pain and discomfort.Risks and Complications of General Anesthesia

While general anesthesia is generally safe, it carries certain risks and complications. Common risks and complications of general anesthesia include:
- Respiratory depression: General anesthesia can cause respiratory depression, leading to breathing difficulties and respiratory failure.
- Cardiac complications: General anesthesia can cause cardiac complications, including arrhythmias, hypotension, and cardiac arrest.
- Nausea and vomiting: General anesthesia can cause nausea and vomiting, leading to dehydration and electrolyte imbalances.
Minimizing Risks and Complications
To minimize risks and complications, it is essential to: * Carefully evaluate patient health and medical history. * Select appropriate anesthetic agents and techniques. * Monitor patient vital signs and anesthesia depth. * Provide adequate post-anesthesia care and support.Future Directions in General Anesthesia

The field of general anesthesia is constantly evolving, with ongoing research and developments aimed at improving safety, efficacy, and patient outcomes. Future directions in general anesthesia include:
- Development of new anesthetic agents and techniques.
- Advancements in anesthesia monitoring and technology.
- Increased focus on patient-centered care and personalized anesthesia.
Emerging Trends in General Anesthesia
Emerging trends in general anesthesia include: * Use of non-invasive anesthesia monitoring techniques. * Development of targeted anesthetic agents and therapies. * Increased emphasis on perioperative care and patient safety.What is general anesthesia?
+General anesthesia is a state of deep sedation, immobility, and amnesia induced through the administration of various medications.
How does general anesthesia work?
+General anesthesia works by targeting specific receptors and pathways in the brain and nervous system, inducing a state of deep sedation and immobility.
What are the benefits of general anesthesia?
+The benefits of general anesthesia include pain relief, immobility, amnesia, and reduced stress, making it an essential tool in modern medicine.
In conclusion, general anesthesia is a complex and fascinating topic that has revolutionized the field of medicine. By understanding its mechanisms, benefits, and applications, individuals can gain a deeper appreciation for the intricacies of human physiology and the remarkable advancements that have been made in the field of anesthesia. We invite readers to share their thoughts and experiences with general anesthesia, and to continue exploring this vital aspect of modern medicine. Whether you are a patient, a medical professional, or simply an interested reader, we hope that this article has provided a comprehensive and informative overview of general anesthesia, inspiring further discussion and discovery.
