Intro
Discover how HSA works with 5 key methods, utilizing health savings accounts, flexible spending, and medical reimbursement to optimize healthcare costs, tax benefits, and financial planning strategies.
The concept of Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) has been gaining popularity over the past few years, and for good reason. These accounts offer a unique way for individuals with high-deductible health plans to save money on medical expenses while also reducing their taxable income. But how exactly do HSAs work, and what benefits can they provide to those who use them? In this article, we'll delve into the world of HSAs and explore the ins and outs of these valuable accounts.
HSAs are designed to help individuals and families with high-deductible health plans (HDHPs) cover their medical expenses. By contributing to an HSA, individuals can set aside pre-tax dollars to pay for qualified medical expenses, such as doctor visits, prescriptions, and hospital stays. This can be especially beneficial for those who have high medical expenses or who want to save for future medical needs. With the rising costs of healthcare, it's essential to have a plan in place to manage expenses, and HSAs can be a valuable tool in this regard.
One of the primary advantages of HSAs is their triple-tax advantage. Contributions to an HSA are tax-deductible, the funds grow tax-free, and withdrawals for qualified medical expenses are tax-free. This means that individuals can save money on their taxes while also building a safety net for medical expenses. Additionally, HSAs are portable, meaning that individuals can take their account with them if they change jobs or retire. This flexibility makes HSAs an attractive option for those who want to have control over their healthcare expenses.
How HSA Works
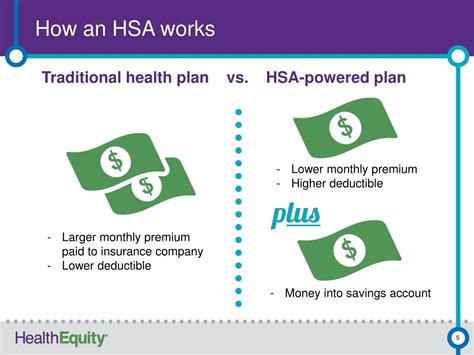
Eligibility and Contributions

Benefits of HSA

Investment Options

Using HSA Funds

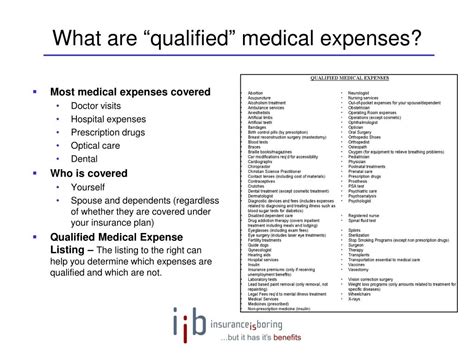
Qualified Medical Expenses
HSA and Retirement

Required Minimum Distributions

What is the annual contribution limit for HSAs?
+The annual contribution limit for HSAs is $3,600 for individual coverage and $7,200 for family coverage.
Can I use my HSA funds for non-medical expenses?
+Yes, after age 65, you can use your HSA funds for non-medical expenses without penalty, although you will be subject to income tax.
Do HSAs have required minimum distributions (RMDs)?
+No, HSAs do not have RMDs during the account holder's lifetime.
Can I invest my HSA funds?
+Yes, many HSA providers offer investment options, such as mutual funds or stocks, which allow you to grow your HSA funds over time.
What happens to my HSA funds if I die?
+If you die, your HSA funds will be distributed to your beneficiary, who can use the funds for qualified medical expenses or take a distribution subject to income tax.
In conclusion, HSAs are a valuable tool for individuals and families with high-deductible health plans. By understanding how HSAs work and the benefits they provide, individuals can make informed decisions about their healthcare expenses and retirement planning. If you have any questions or comments about HSAs, please don't hesitate to reach out. Share this article with your friends and family to help them understand the benefits of HSAs, and take the first step towards taking control of your healthcare expenses today!
