Intro
The world of medicine is filled with numerous medications, each designed to tackle specific health issues. Among these, gabapentin stands out due to its versatility and effectiveness in treating a variety of conditions. Initially introduced as an antiepileptic drug, gabapentin has found its way into treating several other health issues, including nerve pain, anxiety, and even restless leg syndrome. Its multifaceted approach to healthcare makes it a subject of interest for both medical professionals and patients alike. Understanding how gabapentin works is crucial for appreciating its benefits and potential side effects.
Gabapentin's mechanism of action, although not fully understood, is believed to involve the modulation of calcium channels, which play a significant role in the transmission of nerve signals. This modulation affects the release of various neurotransmitters, which are chemicals in the brain that transmit signals from one nerve cell to another. By influencing these neurotransmitters, gabapentin can have a profound impact on how the body perceives and responds to pain, among other sensations. The drug's ability to interact with the nervous system at such a fundamental level explains its wide range of applications.
The drug's versatility and the breadth of its applications have led to extensive research into its effects and potential uses. From managing epilepsy and neuropathic pain to its off-label uses for conditions like anxiety disorders and insomnia, gabapentin's role in modern medicine continues to evolve. As with any medication, understanding its working mechanisms, benefits, and potential drawbacks is essential for patients considering its use. This knowledge not only helps in managing expectations but also in making informed decisions about one's health care.
Introduction to Gabapentin
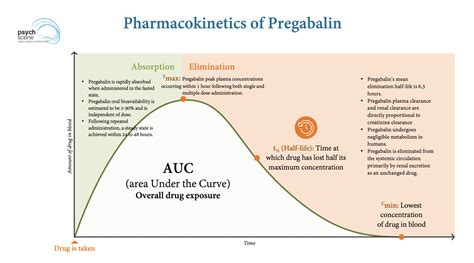
How Gabapentin Works

Modulation of Neurotransmitters
The modulation of neurotransmitters by gabapentin plays a crucial role in its therapeutic effects. Neurotransmitters are chemicals that allow different neurons to communicate with each other. They are involved in a wide range of functions, from controlling mood and appetite to regulating pain perception. By influencing the release and activity of these neurotransmitters, gabapentin can have a significant impact on both physiological and psychological processes.Benefits of Gabapentin

Working Mechanisms

Steps for Effective Use
For gabapentin to be effective, it's crucial to follow a few steps: - **Consult a Healthcare Provider:** Gabapentin should only be taken under the guidance of a healthcare provider. They will determine the appropriate dosage based on the condition being treated and the patient's medical history. - **Adhere to the Prescribed Dosage:** It's essential to take gabapentin exactly as prescribed. The dosage may need to be adjusted over time to achieve the best results. - **Monitor Side Effects:** Patients should be aware of potential side effects, such as dizziness, fatigue, and weight gain, and report them to their healthcare provider.Practical Examples and Statistical Data
Statistical Overview
- **Efficacy in Epilepsy:** Clinical trials have demonstrated that gabapentin can reduce the frequency of seizures in about 30-40% of patients with epilepsy. - **Pain Management:** In patients with diabetic neuropathy, gabapentin has been shown to reduce pain scores by an average of 40%. - **Anxiety Disorders:** While less common, gabapentin's use in anxiety disorders has shown promise, with some studies indicating a significant reduction in anxiety symptoms in patients treated with gabapentin.Conclusion and Future Directions

Final Thoughts

Call to Action

What is gabapentin primarily used for?
+Gabapentin is primarily used for its anticonvulsant and analgesic properties, managing conditions such as epilepsy and neuropathic pain.
How does gabapentin work?
+Gabapentin works by binding to voltage-gated calcium channels, reducing the release of excitatory neurotransmitters, which in turn decreases the excitability of nerve cells.
What are the common side effects of gabapentin?
+Common side effects include dizziness, fatigue, weight gain, and nausea. It's essential to discuss any side effects with a healthcare provider.
