Intro
The importance of understanding how certain medications work cannot be overstated, especially when it comes to managing chronic conditions such as hypertension. One such medication is Hydralazine, which has been a cornerstone in the treatment of high blood pressure for decades. Its effectiveness and relatively simple mechanism of action make it a preferred choice for many healthcare providers. However, the intricacies of how Hydralazine works, its benefits, and its potential side effects are not as widely understood by the general public. This knowledge gap can lead to misunderstandings and misconceptions about the drug, which can impact patient compliance and overall health outcomes.
Hydralazine is a vasodilator, which means it works by relaxing the muscles in the blood vessel walls, causing the vessels to dilate. This dilation reduces blood pressure because it decreases the resistance the heart must overcome to pump blood through the body. The mechanism by which Hydralazine achieves this effect is somewhat complex and involves the release of nitric oxide, a potent vasodilator, and the subsequent relaxation of smooth muscle cells in the arterial wall. This action is crucial for managing hypertension, as high blood pressure can lead to severe complications, including heart disease, stroke, and kidney damage, if left untreated or poorly managed.
The history of Hydralazine dates back to the 1950s, and since its introduction, it has been extensively studied and used in various clinical settings. Its efficacy in lowering blood pressure has been well-documented, and it is often prescribed in combination with other antihypertensive medications to enhance its effects. Despite its widespread use, there is still much to learn about Hydralazine, particularly regarding its long-term effects, potential interactions with other drugs, and its suitability for patients with certain comorbid conditions. Understanding these aspects is vital for maximizing the benefits of Hydralazine while minimizing its risks.
Introduction to Hydralazine

Hydralazine is classified as a direct vasodilator, meaning it acts directly on the blood vessels to cause dilation, without the need for intermediate steps or mechanisms. This direct action makes it a valuable tool in the management of severe hypertension, where rapid blood pressure reduction is necessary. Its pharmacological profile includes a rapid onset of action, which can be beneficial in acute settings, and a relatively short duration of action, necessitating multiple daily doses for chronic management.
How Hydralazine Works Mechanistically
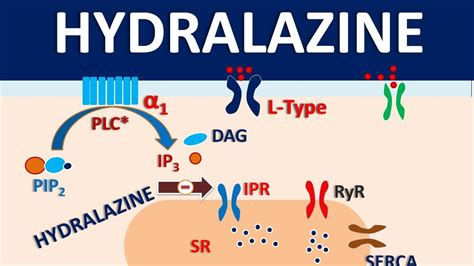
The mechanistic details of Hydralazine involve its ability to stimulate the release of nitric oxide from the endothelium, the inner lining of blood vessels. Nitric oxide then diffuses into the smooth muscle cells of the vessel wall, where it activates guanylate cyclase, leading to an increase in cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP). The increase in cGMP levels results in the relaxation of smooth muscle cells, which in turn causes the blood vessels to dilate. This vasodilation reduces peripheral resistance and lowers blood pressure. Additionally, Hydralazine may have a reflex effect on the heart, potentially increasing heart rate and contractility as the body attempts to compensate for the decreased blood pressure.
Benefits of Hydralazine
The benefits of Hydralazine are multifaceted. Its primary advantage is its effectiveness in lowering blood pressure, which can significantly reduce the risk of cardiovascular events such as heart attacks and strokes. Hydralazine is also relatively inexpensive compared to some newer antihypertensive medications, making it a more accessible option for patients. Furthermore, its use in combination with other drugs can enhance its blood pressure-lowering effects, allowing for tailored treatment regimens that meet the individual needs of patients.Side Effects and Considerations

While Hydralazine is generally well-tolerated, it is not without side effects. Common adverse effects include headache, nausea, and dizziness, which are often related to its vasodilatory effects and subsequent changes in blood pressure. More severe side effects, such as lupus-like syndrome, have been reported but are rare. It is essential for patients to be aware of these potential side effects and to discuss any concerns with their healthcare provider. Additionally, Hydralazine should be used with caution in patients with certain conditions, such as coronary artery disease, where its vasodilatory effects could potentially lead to decreased blood flow to the heart muscle.
Practical Considerations for Patients
For patients taking Hydralazine, several practical considerations can help maximize its benefits while minimizing its risks. Regular monitoring of blood pressure is crucial to adjust the dosage as needed and to ensure that blood pressure targets are being met. Patients should also be aware of the signs of potential side effects and know when to seek medical attention. Lifestyle modifications, such as dietary changes, increased physical activity, and smoking cessation, can also enhance the effectiveness of Hydralazine and contribute to overall cardiovascular health.Combination Therapy with Hydralazine
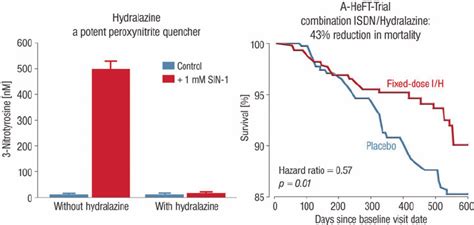
Hydralazine is often used in combination with other antihypertensive medications to achieve better blood pressure control. This approach can be particularly beneficial for patients with resistant hypertension or those who require multiple medications to manage their condition. Common combinations include Hydralazine with diuretics, beta-blockers, or ACE inhibitors, each targeting different aspects of blood pressure regulation to provide a synergistic effect. The choice of combination therapy depends on the individual patient's profile, including their comorbid conditions, potential drug interactions, and the specific characteristics of their hypertension.
Long-Term Management and Adherence
Long-term management of hypertension with Hydralazine, or any antihypertensive medication, requires a commitment to adherence. Patients must understand the importance of taking their medication as prescribed, without interruption, to maintain consistent blood pressure control. Healthcare providers play a critical role in educating patients about their medication regimen, monitoring for side effects, and adjusting the treatment plan as necessary. Additionally, simplifying the medication regimen, using once-daily formulations when possible, and leveraging reminders and support systems can improve adherence and ultimately, treatment outcomes.Future Directions and Research

Despite the extensive use of Hydralazine, there are still areas where further research is needed. Investigations into its long-term safety profile, particularly in diverse patient populations, could provide valuable insights. Moreover, exploring new formulations or delivery methods that could improve patient adherence and reduce side effects would be beneficial. The role of Hydralazine in managing hypertension in the context of emerging global health challenges, such as the increasing prevalence of obesity and diabetes, also warrants further study.
Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, Hydralazine remains a vital component of hypertension management, offering a effective and relatively straightforward approach to lowering blood pressure. Its mechanism of action, benefits, and potential side effects make it a medication that requires careful consideration and monitoring. As research continues to uncover new aspects of Hydralazine's use and effects, healthcare providers and patients must work together to optimize its benefits while minimizing its risks. By doing so, we can improve outcomes for individuals with hypertension and contribute to a broader reduction in cardiovascular disease.What is Hydralazine used for?
+Hydralazine is used to treat high blood pressure. It is a vasodilator that works by relaxing the muscles in the blood vessel walls, causing the vessels to dilate and reducing blood pressure.
How does Hydralazine work?
+Hydralazine works by stimulating the release of nitric oxide from the endothelium, leading to the relaxation of smooth muscle cells in the blood vessel walls and subsequent vasodilation.
What are the common side effects of Hydralazine?
+Common side effects of Hydralazine include headache, nausea, and dizziness. More severe side effects, such as lupus-like syndrome, are rare but can occur.
We invite readers to share their thoughts and experiences with Hydralazine, and to ask any questions they may have about its use or effects. By engaging in this conversation, we hope to foster a better understanding of this important medication and its role in managing hypertension. Whether you are a patient, a healthcare provider, or simply someone interested in learning more about health and wellness, your input is valued. Let's work together to promote awareness and improve outcomes for those affected by high blood pressure.
