Intro
Uncover the truth about Covid contagion with 5 key facts, exploring transmission, spread, and prevention, including viral load, mask efficacy, and social distancing measures to reduce infection risk and stay safe.
The COVID-19 pandemic has been a major global health crisis, affecting millions of people worldwide. Understanding how the virus spreads and what factors contribute to its contagion is crucial in preventing further outbreaks and protecting public health. As we navigate this complex and evolving situation, it's essential to separate fact from fiction and rely on scientific evidence to inform our decisions. In this article, we'll delve into the world of COVID-19 contagion, exploring the latest research and findings to provide you with a comprehensive understanding of this critical topic.
The COVID-19 virus, also known as SARS-CoV-2, is a highly contagious pathogen that can spread through various routes, including respiratory droplets, contact with contaminated surfaces, and airborne transmission. The virus's contagiousness is influenced by several factors, including the amount of viral load, the duration of exposure, and the effectiveness of preventive measures such as masks, social distancing, and vaccination. As we strive to mitigate the spread of COVID-19, it's vital to recognize the importance of individual and collective actions in preventing the transmission of the virus.
The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the need for a multifaceted approach to public health, incorporating measures such as testing, contact tracing, and quarantine to reduce the spread of the virus. Additionally, the development and distribution of effective vaccines have been crucial in controlling the pandemic and protecting vulnerable populations. As we move forward, it's essential to continue monitoring the situation, updating our knowledge, and adapting our strategies to address the evolving challenges posed by COVID-19. By working together and relying on scientific evidence, we can overcome this global health crisis and build a safer, healthier future for all.
Understanding COVID-19 Transmission
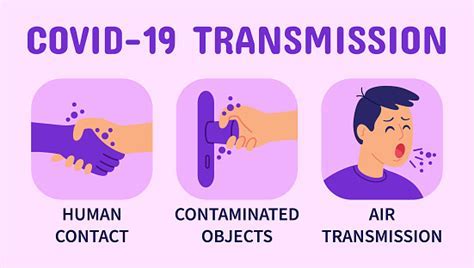
Factors Influencing COVID-19 Contagion
Several factors can influence the contagiousness of COVID-19, including the amount of viral load, the duration of exposure, and the effectiveness of preventive measures. The viral load, which refers to the amount of virus present in an infected person's respiratory secretions, can impact the likelihood of transmission. A higher viral load can increase the chances of transmission, while a lower viral load may reduce the risk. The duration of exposure is also a critical factor, as longer periods of exposure can increase the likelihood of transmission.Preventive Measures Against COVID-19

Vaccination and Herd Immunity
Vaccination plays a vital role in preventing the spread of COVID-19, as it can provide individual and herd immunity. Herd immunity occurs when a sufficient percentage of a population is immune to a virus, making it difficult for the virus to spread. Vaccination can help achieve herd immunity, reducing the risk of transmission and protecting vulnerable populations such as the elderly and those with compromised immune systems.Covid Contagion Facts and Figures

Statistical Data on COVID-19 Contagion
Statistical data on COVID-19 contagion highlights the importance of preventive measures in reducing the spread of the virus. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the COVID-19 pandemic has resulted in over 300 million reported cases and over 4.5 million reported deaths worldwide. The WHO also reports that vaccination has been instrumental in reducing the spread of the virus, with over 10 billion vaccine doses administered worldwide.Real-World Examples of COVID-19 Contagion

Lessons Learned from COVID-19 Contagion
Lessons learned from COVID-19 contagion include the importance of individual and collective actions in preventing the transmission of the virus. The pandemic has highlighted the need for a multifaceted approach to public health, incorporating measures such as testing, contact tracing, and quarantine to reduce the spread of the virus. The development and distribution of effective vaccines have also been crucial in controlling the pandemic and protecting vulnerable populations.Future Directions in COVID-19 Contagion Research

Implications for Public Health Policy
The implications of COVID-19 contagion research for public health policy are significant. The findings of these studies can inform the development of evidence-based policies and guidelines for preventing the spread of COVID-19. For instance, research on the effectiveness of masks and social distancing can inform policies on mask mandates and social distancing measures. Similarly, research on vaccination can inform policies on vaccine distribution and administration.Conclusion and Final Thoughts

We invite you to share your thoughts and questions on COVID-19 contagion in the comments section below. Your input and engagement are valuable in helping us better understand this critical topic and develop effective strategies for preventing the spread of the virus. Additionally, we encourage you to share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about COVID-19 contagion and how to protect themselves and their communities.
What is COVID-19 contagion?
+COVID-19 contagion refers to the spread of the COVID-19 virus from one person to another through various routes, including respiratory droplets, contact with contaminated surfaces, and airborne transmission.
How can I prevent COVID-19 contagion?
+You can prevent COVID-19 contagion by implementing effective preventive measures such as wearing masks, practicing social distancing, and getting vaccinated.
What are the symptoms of COVID-19?
+The symptoms of COVID-19 include fever, cough, shortness of breath, and fatigue. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it's essential to seek medical attention immediately.
