Intro
Discover 5 key Rhinovirus facts, exploring common cold causes, symptoms, and prevention methods, including virus transmission, infection types, and respiratory health impacts.
Rhinoviruses are a type of virus that is commonly associated with the common cold, but they can also cause more severe illnesses, such as bronchiolitis and pneumonia, especially in high-risk individuals like the elderly, young children, and people with weakened immune systems. The impact of rhinoviruses on public health is significant, with millions of cases of respiratory infections attributed to these viruses every year. Understanding rhinoviruses is crucial for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies. By delving into the details of how these viruses work, their symptoms, and the ways they spread, we can better equip ourselves to combat them.
The study of rhinoviruses has been ongoing for decades, and it has led to a wealth of information about their genetic makeup, their mechanisms of infection, and the immune system's response to them. This knowledge is essential for the development of vaccines and antiviral drugs that can specifically target rhinoviruses. Moreover, understanding the epidemiology of rhinovirus infections helps in predicting outbreaks and in planning public health interventions. Rhinoviruses are highly diverse, with over 150 serotypes identified, which complicates the development of a universal vaccine but also underscores the importance of continued research into their biology and disease-causing mechanisms.
Rhinoviruses are primarily spread through respiratory droplets that are released when an infected person coughs or sneezes, as well as through contact with contaminated surfaces. The virus can survive on surfaces for hours, making hygiene practices such as frequent handwashing and cleaning of surfaces crucial in preventing the spread of infection. Furthermore, rhinoviruses can also be spread through close contact with an infected person, highlighting the importance of social distancing measures during outbreaks. The symptoms of a rhinovirus infection can range from mild to severe and include runny nose, sneezing, coughing, and sometimes fever. In severe cases, especially in vulnerable populations, rhinovirus infections can lead to complications such as bronchitis, pneumonia, and exacerbations of asthma.
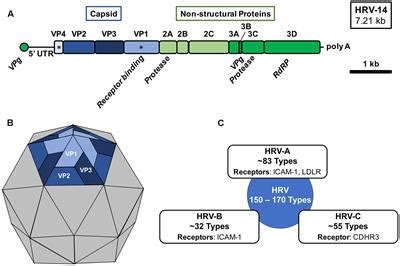
Rhinovirus Structure and Genome
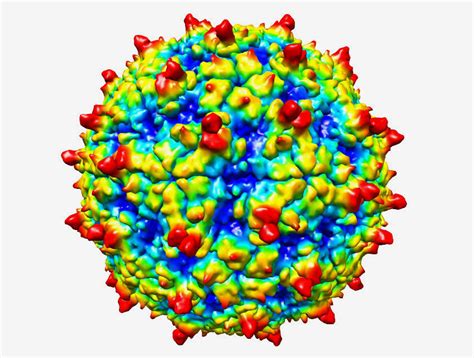
Genetic Diversity of Rhinoviruses
The genetic diversity of rhinoviruses is one of their most striking features, with three main species (A, B, and C) and over 150 serotypes identified to date. This diversity presents challenges for vaccine development, as a vaccine effective against one serotype may not protect against another. However, this diversity also means that rhinoviruses can infect cells using different receptors, such as ICAM-1 for the major group and CD155 for some members of the minor group, offering multiple potential targets for therapeutic intervention.Rhinovirus Infection Mechanism
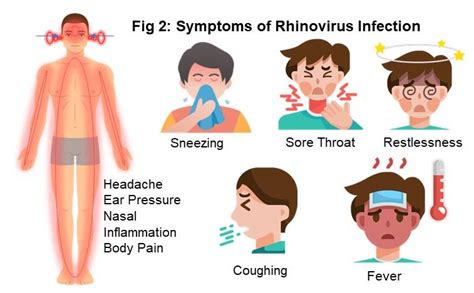
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Rhinovirus Infections
The symptoms of rhinovirus infections can vary widely, from mild upper respiratory symptoms like runny nose and sneezing to more severe lower respiratory symptoms such as wheezing and shortness of breath. Diagnosis is typically based on clinical presentation, although molecular diagnostic tests such as PCR can be used to confirm the presence of rhinovirus RNA in respiratory specimens. Accurate diagnosis is important for distinguishing rhinovirus infections from other respiratory viruses and for guiding treatment decisions.Prevention and Treatment of Rhinovirus Infections

Future Directions in Rhinovirus Research
Future research into rhinoviruses is likely to focus on the development of effective vaccines and antiviral therapies. Given the diversity of rhinoviruses, a vaccine that can protect against multiple serotypes would be highly desirable. Additionally, understanding the mechanisms by which rhinoviruses cause disease and evade the immune system can provide insights into potential therapeutic targets. Advances in molecular biology and genomics are expected to play a crucial role in these efforts, enabling a more detailed understanding of rhinovirus biology and the development of personalized treatment strategies.Rhinovirus and Asthma

Rhinovirus Infections in Vulnerable Populations
Rhinovirus infections can be particularly severe in vulnerable populations, including the elderly, young children, and individuals with compromised immune systems. In these groups, rhinovirus infections can lead to serious complications such as pneumonia, bronchiolitis, and respiratory failure. Preventive measures and early treatment are critical in managing rhinovirus infections in these populations, and research into effective interventions is ongoing.Public Health Impact of Rhinoviruses
Global Surveillance and Outbreak Response
Global surveillance of rhinovirus infections is essential for monitoring the spread of these viruses, identifying new serotypes, and predicting potential outbreaks. This surveillance involves the collection and analysis of data on rhinovirus infections from around the world, which can inform public health responses and guide the development of vaccines and treatments. In the event of an outbreak, rapid response strategies, including enhanced surveillance, contact tracing, and the implementation of control measures, can help to contain the spread of the virus.Rhinovirus Research and Development
Challenges and Opportunities in Rhinovirus Research
Despite the progress made in understanding rhinoviruses, there are still significant challenges to be addressed, including the development of a universal vaccine, the creation of effective antiviral treatments, and the improvement of diagnostic tests. However, these challenges also present opportunities for innovation and discovery, driving researchers to explore new ideas and approaches. The study of rhinoviruses is a dynamic field, with new findings and advancements continually shedding light on the biology of these viruses and their interactions with the human host.Conclusion and Future Perspectives
Final Thoughts
As we look to the future, it is clear that the study of rhinoviruses will remain a vibrant and important area of research. With its potential to improve human health, reduce the economic burden of respiratory illnesses, and advance our understanding of viral biology, the investigation of rhinoviruses is a pursuit that will continue to captivate scientists and public health professionals alike. By staying informed, supporting research efforts, and adopting preventive measures, we can all play a role in mitigating the impact of rhinoviruses and promoting better respiratory health for everyone.We invite you to share your thoughts and questions about rhinoviruses in the comments below. Whether you are a healthcare professional, a researcher, or simply someone interested in learning more about these fascinating viruses, your input is valued. Let's work together to advance our knowledge of rhinoviruses and to find new ways to prevent and treat the infections they cause.
What are the common symptoms of a rhinovirus infection?
+Rhinovirus infections can cause a range of symptoms, including runny nose, sneezing, coughing, and sometimes fever. In severe cases, especially in vulnerable populations, rhinovirus infections can lead to complications such as bronchitis, pneumonia, and exacerbations of asthma.
How are rhinoviruses spread?
+Rhinoviruses are primarily spread through respiratory droplets that are released when an infected person coughs or sneezes, as well as through contact with contaminated surfaces. Close contact with an infected person can also spread the virus.
Is there a vaccine available for rhinoviruses?
+Currently, there is no widely available vaccine that protects against all rhinovirus serotypes. However, research into vaccine development is ongoing, with the goal of creating a vaccine that can offer broad protection against rhinovirus infections.
What can be done to prevent the spread of rhinoviruses?
+Prevention measures include frequent handwashing, avoiding close contact with individuals who are sick, and cleaning surfaces that may be contaminated with the virus. Practicing good hygiene and staying home when sick can also help to reduce the spread of rhinoviruses.
How are rhinovirus infections treated?
+Treatment for rhinovirus infections is primarily symptomatic, with over-the-counter medications used to relieve symptoms such as cough, sore throat, and fever. In severe cases, antiviral medications or supportive care in a hospital setting may be necessary.
