Intro
Discover Lorazepams mechanism of action, understanding its anxiolytic effects, pharmacokinetics, and benzodiazepine receptor interactions, revealing how it treats anxiety disorders, insomnia, and seizures.
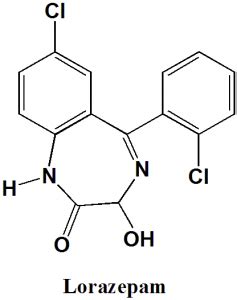
Lorazepam, commonly known by its brand name Ativan, is a medication that belongs to the benzodiazepine class. It is widely used for its anxiolytic, muscle relaxant, and sedative properties. The drug has been a staple in the treatment of anxiety disorders, insomnia, and seizures for decades. Understanding the mechanism of action of lorazepam is crucial for appreciating its therapeutic effects and potential side effects.
The importance of lorazepam lies in its ability to modulate the activity of the brain, specifically targeting the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter, meaning it reduces the activity of the neurons to which it binds. In individuals with anxiety disorders or insomnia, the brain's GABAergic system may be underactive, leading to an imbalance in neural activity. Lorazepam works by enhancing the effect of GABA, thereby restoring balance to the brain's neurotransmitter system.
Lorazepam's mechanism of action involves the potentiation of GABA's inhibitory effects on neuronal activity. This is achieved through the drug's high affinity for the benzodiazepine receptor site on the GABA_A receptor complex. When lorazepam binds to this site, it increases the frequency of chloride channel opening, allowing more chloride ions to enter the neuron. The influx of chloride ions hyperpolarizes the neuron, making it less likely to fire and thus reducing neuronal excitability. This action is the basis for lorazepam's therapeutic effects, including its ability to induce relaxation, reduce anxiety, and promote sleep.
Lorazepam Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of lorazepam play a significant role in its efficacy and safety profile. After oral administration, lorazepam is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, with peak plasma concentrations achieved within 1-4 hours. The drug undergoes extensive hepatic metabolism, primarily through glucuronidation, resulting in the formation of inactive metabolites that are excreted in the urine. Lorazepam's elimination half-life is approximately 12-18 hours, which allows for once-daily or twice-daily dosing regimens. The drug's pharmacokinetic properties contribute to its rapid onset of action and relatively long duration of effect, making it a convenient option for patients.
Therapeutic Uses of Lorazepam
Lorazepam's therapeutic applications are diverse, reflecting its broad pharmacological profile. The drug is primarily used for the short-term treatment of anxiety disorders, including generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, and social anxiety disorder. Its anxiolytic effects make it an effective adjunctive therapy for patients undergoing surgical procedures or experiencing acute stress reactions. Additionally, lorazepam is used as a hypnotic agent for the management of insomnia, particularly in cases where sleep initiation is difficult. In some cases, lorazepam may be prescribed off-label for the treatment of seizures, especially status epilepticus, due to its ability to potentiate GABAergic activity.
Benefits and Risks of Lorazepam
The benefits of lorazepam are well-documented and include its rapid onset of action, efficacy in reducing anxiety and promoting sleep, and relatively favorable side effect profile when used as directed. However, like all benzodiazepines, lorazepam carries risks, including the potential for dependence, tolerance, and withdrawal symptoms upon discontinuation. The risk of dependence is higher in individuals with a history of substance abuse or those taking the drug for extended periods. Other potential side effects include drowsiness, dizziness, and anterograde amnesia. It is essential for patients to follow their prescribed dosing regimen and consult their healthcare provider if they experience any adverse effects or concerns.Lorazepam Side Effects and Interactions
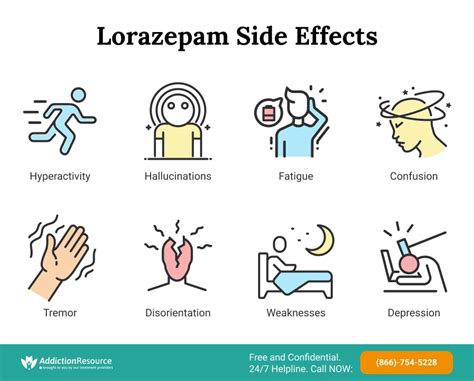
Lorazepam, like other benzodiazepines, can cause a range of side effects, from mild and transient to severe and potentially life-threatening. Common side effects include somnolence, headache, and fatigue. Less common but more serious side effects can include respiratory depression, especially when combined with other central nervous system depressants like alcohol or opioids. Lorazepam can also interact with various medications, either enhancing their effects or increasing the risk of adverse reactions. For example, concurrent use of lorazepam with antidepressants can increase the risk of sedation and respiratory depression.
Contraindications and Warnings
Lorazepam is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to benzodiazepines, acute narrow-angle glaucoma, and severe respiratory depression. It should be used with caution in patients with a history of substance abuse, respiratory disease, or hepatic impairment. Pregnant women should avoid lorazepam due to the potential risk of neonatal withdrawal syndrome and other congenital anomalies. Breastfeeding mothers should also exercise caution, as lorazepam can be excreted in breast milk.Lorazepam Dosage and Administration

The dosage of lorazepam varies depending on the indication, patient age, and individual response. For anxiety, the typical starting dose is 2-3 mg/day, administered two or three times daily. For insomnia, a dose of 2-4 mg at bedtime is often prescribed. In elderly patients or those with hepatic impairment, lower doses may be necessary to avoid excessive sedation. Lorazepam is available in various formulations, including oral tablets, injectable solutions, and sublingual tablets, allowing for flexibility in dosing and administration.
Special Considerations
Special considerations are necessary when prescribing lorazepam to certain patient populations. In elderly patients, the risk of falls, cognitive impairment, and excessive sedation is higher, necessitating careful dose titration and monitoring. Patients with a history of substance abuse require close supervision due to the potential for misuse and dependence. Additionally, lorazepam should be used cautiously in patients with obstructive sleep apnea, as it can worsen respiratory function during sleep.Lorazepam Withdrawal and Dependence

Lorazepam, like other benzodiazepines, carries a risk of dependence and withdrawal. Dependence can develop after as little as 4-6 weeks of regular use, especially at higher doses. Withdrawal symptoms can range from mild anxiety and insomnia to severe reactions like seizures and psychosis. The risk of dependence and withdrawal underscores the importance of using lorazepam at the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration necessary. Gradual tapering of the dose under medical supervision is recommended when discontinuing lorazepam to minimize the risk of withdrawal symptoms.
Management of Lorazepam Dependence
The management of lorazepam dependence involves a comprehensive approach, including gradual dose reduction, psychological support, and sometimes the use of alternative medications to manage withdrawal symptoms. Inpatient detoxification may be necessary for patients with severe dependence or those at risk of complicated withdrawal. Counseling and behavioral therapies are crucial components of treatment, helping patients to address underlying issues that may have contributed to their dependence on lorazepam.Lorazepam Overdose and Toxicity

Lorazepam overdose can be life-threatening, especially when combined with other central nervous system depressants. Symptoms of overdose include severe respiratory depression, somnolence, confusion, and in severe cases, coma or death. Treatment of lorazepam overdose involves supportive care, including monitoring of vital signs and respiratory function, and the administration of flumazenil, a benzodiazepine antagonist, if necessary. It is essential to seek immediate medical attention if an overdose is suspected.
Prevention of Overdose
Prevention of lorazepam overdose requires careful prescribing practices, patient education, and monitoring. Patients should be informed about the risks of overdose, especially when combining lorazepam with other substances. Prescribers should exercise caution when prescribing lorazepam to patients at risk of overdose, such as those with a history of substance abuse. Regular follow-up appointments can help identify potential issues early, allowing for timely intervention.What is lorazepam used for?
+Lorazepam is used for the treatment of anxiety disorders, insomnia, and seizures. It is also used as a sedative before surgeries or medical procedures.
How long does lorazepam stay in your system?
+The elimination half-life of lorazepam is approximately 12-18 hours, but it can stay in your system for several days after the last dose.
Can lorazepam be addictive?
+Yes, lorazepam can be addictive, especially when used for extended periods or at high doses. It is essential to follow the prescribed dosing regimen and consult your healthcare provider if you experience any signs of dependence.
In conclusion, lorazepam is a versatile benzodiazepine with a range of therapeutic applications, from anxiety disorders to insomnia and seizures. Its mechanism of action, involving the potentiation of GABAergic activity, underlies its efficacy in reducing neuronal excitability and promoting relaxation. However, lorazepam's potential for dependence, withdrawal, and overdose necessitates careful prescribing practices, patient education, and monitoring. By understanding the benefits and risks of lorazepam, healthcare providers can optimize its use, minimizing adverse effects while maximizing therapeutic outcomes. We invite readers to share their experiences or ask questions about lorazepam in the comments section below, and we encourage you to share this article with anyone who might benefit from this comprehensive overview of lorazepam.
