Intro
Nitroglycerin works quickly to relieve angina symptoms, using vasodilation to improve blood flow, reducing chest pain and discomfort with fast-acting medication.
Nitroglycerin is a medication that has been widely used for many decades to treat various heart conditions, particularly angina pectoris. It belongs to a class of medications known as nitrates, which work by relaxing and widening blood vessels to improve blood flow to the heart. This rapid improvement in blood flow helps to alleviate chest pain and discomfort associated with angina. The quick action of nitroglycerin makes it an essential medication for individuals who experience frequent angina attacks.
The importance of nitroglycerin lies in its ability to provide rapid relief from angina symptoms. Angina pectoris is a condition characterized by chest pain or discomfort due to transient myocardial ischemia, which occurs when the heart muscle does not receive enough oxygen-rich blood. This condition can be a precursor to more severe heart problems, such as heart attacks. By using nitroglycerin, individuals can quickly alleviate their symptoms and reduce the risk of further complications. Moreover, the medication's fast-acting nature allows individuals to resume their daily activities without significant interruptions.
Nitroglycerin's effectiveness in treating angina has made it a cornerstone in cardiovascular medicine. Its mechanism of action involves the release of nitric oxide, a potent vasodilator that relaxes the smooth muscles of blood vessels, leading to increased blood flow and reduced blood pressure. This vasodilatory effect reduces the workload on the heart, decreasing the oxygen demand and subsequently alleviating chest pain. The medication's rapid onset of action, typically within 1-3 minutes, makes it an ideal choice for managing acute angina attacks.
Nitroglycerin Mechanism of Action
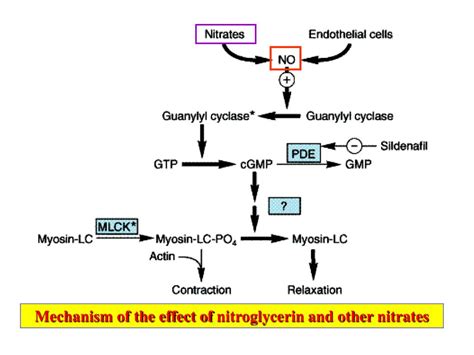
The mechanism of action of nitroglycerin is complex and involves multiple pathways. When administered, nitroglycerin is converted into nitric oxide, which then activates guanylyl cyclase, an enzyme that catalyzes the production of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP). The increased levels of cGMP lead to the relaxation of smooth muscle cells in blood vessels, resulting in vasodilation. This relaxation of blood vessels reduces peripheral resistance, decreases blood pressure, and increases blood flow to the heart, thereby alleviating angina symptoms.
Nitroglycerin Administration Routes
Nitroglycerin can be administered through various routes, including sublingual, transdermal, and intravenous. The sublingual route is the most common, where the medication is placed under the tongue, allowing for rapid absorption into the bloodstream. This route provides quick relief from angina symptoms, typically within 1-3 minutes. The transdermal route involves the use of patches or ointments, which release nitroglycerin slowly over a prolonged period, providing sustained relief from angina symptoms. Intravenous administration is typically reserved for severe cases of angina or during acute myocardial infarction.Nitroglycerin Benefits and Risks

The benefits of nitroglycerin in treating angina are well-established. The medication provides rapid relief from chest pain and discomfort, improves exercise tolerance, and reduces the risk of further cardiovascular complications. However, like all medications, nitroglycerin is associated with potential risks and side effects. Common side effects include headaches, dizziness, and lightheadedness, which are usually mild and transient. More severe side effects, such as hypotension and methemoglobinemia, can occur but are rare.
Nitroglycerin Side Effects Management
To minimize the risk of side effects, individuals taking nitroglycerin should be aware of the potential interactions with other medications and substances. For example, concurrent use of phosphodiesterase inhibitors, such as sildenafil, can increase the risk of hypotension. Additionally, individuals should avoid consuming alcohol, as it can exacerbate the vasodilatory effects of nitroglycerin. By understanding the potential side effects and taking necessary precautions, individuals can safely use nitroglycerin to manage their angina symptoms.Nitroglycerin Dosage and Administration

The dosage and administration of nitroglycerin vary depending on the individual's response to the medication and the severity of their angina symptoms. For sublingual administration, the typical dose is 0.3-0.6 mg, which can be repeated every 5 minutes as needed, up to a maximum of 3 doses. For transdermal administration, the dose is typically 0.2-0.4 mg/hour, which can be adjusted based on the individual's response. It is essential to follow the prescribed dosage and administration instructions to minimize the risk of side effects and ensure optimal therapeutic effects.
Nitroglycerin Storage and Handling
Proper storage and handling of nitroglycerin are crucial to maintain its potency and effectiveness. The medication should be stored in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and moisture. The sublingual tablets should be kept in their original container, and the transdermal patches should be applied to a clean, dry area of skin. By following proper storage and handling procedures, individuals can ensure that their nitroglycerin remains effective and safe to use.Nitroglycerin Interactions with Other Medications

Nitroglycerin can interact with various medications, including phosphodiesterase inhibitors, beta-blockers, and calcium channel blockers. These interactions can increase the risk of side effects, such as hypotension and methemoglobinemia. Individuals taking nitroglycerin should inform their healthcare provider about all medications they are currently taking, including prescription and over-the-counter medications, to minimize the risk of interactions.
Nitroglycerin Contraindications
Nitroglycerin is contraindicated in individuals with certain medical conditions, such as severe hypotension, increased intracranial pressure, and severe anemia. Additionally, individuals with a history of methemoglobinemia or those taking medications that can increase the risk of methemoglobinemia should avoid using nitroglycerin. By understanding the contraindications and potential interactions, individuals can safely use nitroglycerin to manage their angina symptoms.Nitroglycerin and Lifestyle Modifications
In addition to taking nitroglycerin, individuals with angina can benefit from lifestyle modifications to reduce their symptoms and improve their overall cardiovascular health. These modifications include quitting smoking, exercising regularly, and maintaining a healthy diet low in saturated fats and cholesterol. By combining these lifestyle modifications with nitroglycerin therapy, individuals can effectively manage their angina symptoms and reduce the risk of further cardiovascular complications.
Nitroglycerin and Stress Reduction
Stress can exacerbate angina symptoms, and stress reduction techniques, such as meditation and deep breathing, can help alleviate symptoms. Individuals taking nitroglycerin can benefit from incorporating stress-reducing activities into their daily routine, such as yoga or tai chi. By managing stress and combining it with nitroglycerin therapy, individuals can improve their overall quality of life and reduce the frequency of angina attacks.Nitroglycerin and Future Perspectives

The future of nitroglycerin therapy looks promising, with ongoing research focused on developing new formulations and administration routes. One area of research involves the development of sustained-release formulations, which can provide prolonged relief from angina symptoms. Another area of research involves the use of nitroglycerin in combination with other medications to enhance its therapeutic effects. By continuing to advance our understanding of nitroglycerin and its therapeutic effects, we can improve the management of angina and reduce the risk of further cardiovascular complications.
Nitroglycerin and Patient Education
Patient education is essential for the effective management of angina symptoms with nitroglycerin. Individuals should be aware of the proper use and administration of the medication, as well as the potential side effects and interactions. By educating patients about nitroglycerin therapy, healthcare providers can empower them to take an active role in managing their condition and improving their overall quality of life.What is the primary use of nitroglycerin?
+Nitroglycerin is primarily used to treat angina pectoris, a condition characterized by chest pain or discomfort due to transient myocardial ischemia.
How does nitroglycerin work?
+Nitroglycerin works by relaxing and widening blood vessels, which improves blood flow to the heart and reduces the workload on the heart, thereby alleviating chest pain and discomfort.
What are the common side effects of nitroglycerin?
+Common side effects of nitroglycerin include headaches, dizziness, and lightheadedness, which are usually mild and transient.
Can nitroglycerin be used with other medications?
+Nitroglycerin can interact with various medications, including phosphodiesterase inhibitors, beta-blockers, and calcium channel blockers, which can increase the risk of side effects.
How can I store and handle nitroglycerin?
+Nitroglycerin should be stored in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and moisture, and handled according to the prescribed instructions to maintain its potency and effectiveness.
In summary, nitroglycerin is a fast-acting medication that provides rapid relief from angina symptoms. Its mechanism of action involves the relaxation and widening of blood vessels, which improves blood flow to the heart and reduces the workload on the heart. While nitroglycerin is effective in managing angina, it is essential to be aware of the potential side effects and interactions with other medications. By understanding the benefits and risks of nitroglycerin and following proper storage and handling procedures, individuals can safely use this medication to improve their quality of life. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with nitroglycerin in the comments below and to explore our website for more information on cardiovascular health and management.
